Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
April 28, 2024
SHARE
Futures Margin: Making Leverage Work for You
Futures are financial contracts that allow you to control equivalent amounts of the underlying asset being traded for much less capital outlay. To do this, the trader that wants to buy an option needs to provide margin. In other words, futures are leveraged products.
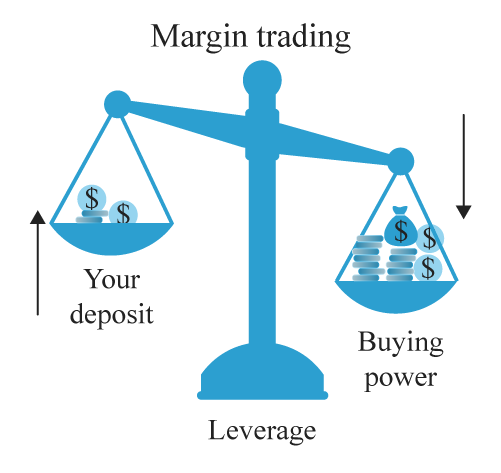
What is Margin?
Borrowing money from a brokerage firm to make a trade is known as trading on margin. Margin trading involves an investor depositing cash that serves as collateral for what is essentially a short-term loan. Often, this requires paying interest on the borrowed money. But sometimes, this can be paid out to the trader, depending on the interest in questions as well as current rates.
Definition of Margin
Margin is the amount of collateral required of an investor with their broker or exchange to cover credit risks they pose for them.
Definition of Leverage
Financial leverage is essentially borrowed money which can be used to amplify returns on investment, acquire assets, or raise funds for a business. However, it isn’t without risk, and in financial markets, leverage amplifies not just gains, but losses.
How Does Leverage Work?
The use of leverage requires a deposit, known as a margin, that allows for an increase in exposure to an underlying asset.
The provider lends you the rest of the amount you put down – a fraction of the transaction’s total value. Using a leverage ratio, you can calculate how much exposure you have compared to your margin.
Margin trading uses less capital to gain exposure to trading positions. Various financial instruments can be leveraged, such as forex, indices, stocks, commodities, Treasury bonds, and exchange-traded funds.
Leverage is especially common in the foreign exchange market, since fluctuations tend to be quite small and would require huge amounts of capital invested to have a chance of making a meaningful profit.
Why Use Leverage?
Leverage is an important feature that can be a powerful tool for a trader. This allows you to take advantage of relatively small price movements, increase your portfolio’s exposure, and just generally make your capital go further.
Pros of Leverage
Leveraged trading can be a highly effective tool if you comprehend how it works. Among its benefits are:
Increased Profits: The same amount of capital can lead to a much larger profit than if the position was executed without leverage. Another way of looking at this is as being able to control a certain position size with just a fraction of the capital.
Free Up Capital: Using leverage means you will free up capital that can be utilized in other financial opportunities, potentially even decreasing risk as you diversify your portfolio.
Shorting: Speculating on markets using leveraged products allows you to benefit from both rising and falling market movements – referred to as going short.
Cons of Leverage
Amplified Losses: While any profits are increased when using leverage, so are losses. Since you are investing less than the full required amount for that position size, a smaller price fluctuation could potentially wipe out your margin. Therefore, it is vital to make sure the risk you are taking fits into your risk management rules, and that you constantly evaluate your trade in terms of floating PnL.
No Privileges for Holders: Taking ownership of the asset is lost when you trade with leverage. When you use leveraged products, dividends may be impacted. Instead of a dividend, your account will be credited or debited according to your position’s amount.
Margin Calls: Keeping your trade open may require you to post additional funds if the trades moves against you. Receiving a margin call means you need to add capital to the position to keep it, otherwise you will be forced to close out (known as being liquidated).
Fees: The money used to open the position is effectively lent to you at the cost of your deposit when you use leverage. Often, there is a small fee charged for keeping your position open overnight.
Conclusion
Using leverage, traders can increase their exposure to the market with less capital. This comes with its benefits, such as being able to make larger profits and free up capital for other trades.
However, it’s not without its risks, and traders must understand leverage and make sure they have made the correct calculations before utilizing it in their trading.
Bookmap comes with many tools for tracking your PnL from within the platform. Click here to get started for free today.