Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
March 18, 2024
SHARE
How Exchanges Work
An exchange is a verb as well as a noun, being both the place and the act of every transaction.
When an exchange matches two opposing orders at the same price, a transaction occurs. When you turn on a financial news channel and see the scrolling price tickets, this is what you see: the last traded price.
Types of Exchanges
There are many different exchanges across the world, but they usually fit into certain asset classes. Newer traders are often attracted to global markets such as Forex or Crypto due to their lower barrier to entry and lower costs.
Stock Exchanges
A stock exchange does not own shares. Instead, it connects stock buyers with stock sellers.
Stocks can be traded on several exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. Some stocks trade on multiple exchanges, one reason why Bookmap offers the National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO) feed.
Futures Exchanges
A futures exchange is a place where people can trade standardised commodity and index futures, as well as options contracts.
Originally developed for hedgers, futures are often used by speculators in the modern day.
Crypto exchanges
Crypto are often unregulated marketplaces where users can exchange cryptocurrencies for fiat or other cryptocurrencies (and vice versa).
Unlike some traditional exchanges that are located in a physical place, crypto exchanges are simply websites on a server that function as the exchange.
Types of Orders
There are two main types of orders: aggressive and passive.
Aggressive orders are orders that consume liquidity from the market. Aggressive orders are also known as market orders, which by extension can include stop orders.
Passive orders provide liquidity. They are also known as limit orders, and by extension can also include iceberg orders.
Let’s explore these two main order types a bit further.
Market Orders
A market order says “get me in or out of the market right now, no matter the price”. Hitting the ‘market’ means the execution of the order is guaranteed. But the price is not.
In most cases, a market order will usually execute at the current bid (in the case of a sell market order) or ask price (in the case of a market buy order). But if the market order is of particularly large size relative to the available liquidity, or the market is just moving very fast, the order may execute at a vastly different (and worse) price.
Limit Orders
Orders for making a transaction at a specific price (or better) are called limit orders.
A limit order must be met with an equivalent sized market order for it to execute. Limit orders are given priority by price (the best price executes first), and then time (the first in the queue will execute first).
How Do Exchanges Execute Orders?
Different exchanges have different rules for how orders are executed, which uses something called a matching engine or order matching system. But most use the basic principles of price discovery and order queue priority.
Price Discovery
Through the dual-auction process of price discovery, a pricing mechanism finds the price at which buyers and sellers will match. Price discovery targets the equilibrium price based on the available liquidity in the order book.
Multiple buyers and sellers bid and offer in a real-time auction until a price is reached—the market price.
Order queue priority
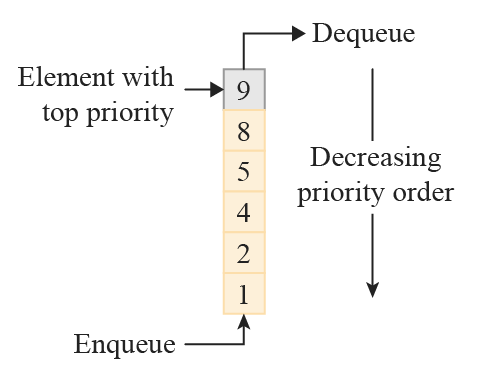
The price and time at which an order was placed determine the order’s priority in the queue.
After price priority (the highest bids and the lowest offers) are executed first, orders are then handled based on the first-come, first-served basis (the queue system).
Orders that have been sitting in the book for longer get priority. If an order is modified by price or size, it will be reset to the back of the time-priority queue.
Conclusion
Exchanges are (often) virtual marketplaces where market participants can transact assets listed on that exchange.
All exchanges have specific rules, but not all are regulated (such as many exchanges in crypto) that protect users.
Exchanges allow various methods of executing trades, some more advanced than others, and these trades aid the price discovery mechanism that values a security.
Bookmap is a high-performance trading platform that lets you see “inside” the exchange, showing you the market and its mechanics.
You can try it out today for free. Click here to get started.