Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
August 19, 2024
SHARE
Market Correlations: Why They Matter and How They Impact Your Trading Journey
Navigating the stock market demands more than just luck; it requires a strategic understanding of risk management and portfolio diversification. The interplay of different assets enables traders to construct diversified portfolios, thus lessening the traders’ reliance on the performance of a single asset.
“Market correlations” emerge as a powerful tool, providing analytical insights that both individual investors and institutional players can leverage. These insights empower precise predictions about the ebb and flow of asset prices.
Let’s delve into the vital significance and practical implications of market correlations.
What Are Market Correlations?
Volatility is a common phenomenon in the stock market, and failing to account for it can lead traders to invest excessively in highly volatile assets. This oversight exposes portfolios to significant risks during market downturns.
Market correlations offer a solution by depicting the statistical relationships among different assets or securities within a financial market. By showing how asset prices move in relation to each other over a defined period, market correlations help traders strategically manage their portfolios. This understanding empowers traders to establish diversified portfolios that are better equipped to weather market fluctuations.
The Measurement Scale
Using statistics, the market correlations between two assets or securities are determined by calculating the correlation coefficient. The measurement scale ranges from -1 to 1, leading to the representation of three distinct scenarios or possibilities, as elaborated below:
| Correlation Coefficient | Type of Correlation | Impact on Assets/Securities |
| +1 | Perfect Positive Correlation | The prices of two correlated assets increase or decrease together. |
| -1 | Perfect Negative Correlation | When the price of one correlated asset increases, the price of another correlated asset decreases. |
| 0 | No Linear Correlation | The two assets are not correlated with each other.
Price movements in one asset do not affect the price of the other asset. |
Market Correlations: Types and Implications
There are three main types of market correlation: Positive, Negative, and Zero, determined by the value of the calculated correlation coefficient:

- Positive Correlation:
- The value of the correlation coefficient is closer to 1.
- This type of correlation is established between two assets that are influenced by similar market factors.
- In a positive correlation, the prices of assets move in the same direction.
- For Example:
- The stock price of Company A, which manufactures smartphones, is positively correlated to the stock price of Company B, which manufactures semiconductor chips.
- An increase in the stock price of Company A will also lead to an increase in the stock price of Company B, and vice versa.
- Negative Correlation:
- The value of the correlation coefficient is closer to -1.
- This type of correlation is established between two assets that react differently to the changing market conditions.
- In a negative correlation, the prices of assets move in opposite directions.
- For Example:
- The price of crude oil and the value of the US dollar have historically exhibited a negative correlation.
- With an increase in the price of crude oil, the value of the US dollar tends to decrease, and vice versa.
- Zero Correlation:
- The value of the correlation coefficient is closer to 0.
- This type of correlation is established between two unrelated assets.
- In zero correlation, the change in the price of one asset does not affect the price of the other asset.
- For Example:
- The stock price of a leading IT outsourcing company and the price of any agricultural commodity exhibit zero correlation.
- This is because both assets operate in different market segments or sectors.
Most Common Trading Strategies Based on Market Correlations
Most successful traders follow specific trading strategies after establishing a type of correlation. Some of the commonly used trading strategies based on market correlations are:
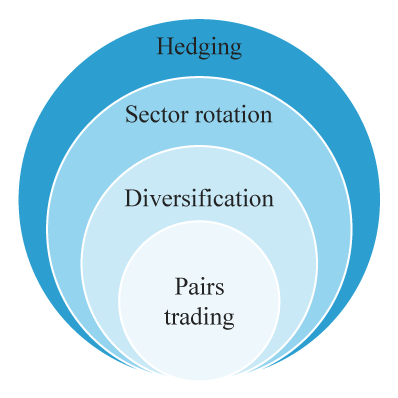
- Pairs Trading:
- Two closely related financial assets or securities are chosen, and opposing positions are concurrently taken for each of them.
- The primary aim is to benefit from the temporary deviation in their prices.
- Following this trading strategy, the traders assume that the prices of these two related assets will eventually “normalize” and revert to the relationship as established by the market correlations.
- Sector Rotation:
- It helps in maximizing the portfolio returns by increasing exposure to sectors that are anticipated to perform better considering the changing economic conditions.
- For example, a trader could decide to decrease their investment in the technology industry and instead increase their exposure to the healthcare sector, especially during periods of strong performance for the healthcare sector.
- Mostly, traders and investors assess market correlations between different sectors to create sector rotation strategies.
- Diversification:
- To mitigate the impact of market volatility, investments are made across a range of different financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, derivatives, currencies, etc.
- This boosts the stability of investments and increases long-term returns.
- A comprehensive study of market correlations helps in determining an effective diversification strategy.
- Hedging:
- This strategy aims to offset the losses sustained from the adverse price movements in an investment.
- Traders identify an asset that is negatively correlated with an existing investment and take positions in a derivative instrument (options or futures).
Trading Actions Vary Based on Different Types of Correlations
Once a type of correlation is established, the next step is to take appropriate actions under each scenario. Now, let’s gain insights into the recommended trading actions for each trading strategy in the following table.
| Trading Strategies | Positive Correlation (+1) | Negative Correlation (-1) | Zero Correlation (0) |
| Pairs Trading | Traders short-sell the overperforming asset and simultaneously buy the underperforming asset. | Traders mostly buy the underperforming asset and short-sell the overperforming asset. | Trading strategies are adapted flexibly since historical prices and patterns may be less influential due to the lack of consistent correlation. |
| Sectors Rotation | Sectors that show “growth potential” are favored. | Sectors that are predicted to perform well when others decline are favored. | Market analysis is performed independent of correlation trends. |
| Diversification | Traders invest in assets that are likely to benefit from different economic conditions. | A balanced portfolio is constructed by including assets with negative correlation. | To improve portfolio performance, zero correlated assets are included as their performance does not significantly impact the portfolio. |
| Hedging | Traders take a position in a positively correlated asset to hedge the primary investment. The idea is that if the primary investment decreases in value, the positively correlated asset may increase, offsetting potential losses. | Traders take a position in a negatively correlated asset to hedge the primary investment. The goal is to mitigate losses in the primary investment by benefiting from the potential increase in value of the negatively correlated asset when the primary investment declines. | A zero-correlated asset is used to hedge against potential market downturns. |
Factors Influencing Market Correlations
Market correlations depend on a variety of factors. The degree to which correlated assets move together or in opposite directions depends on a variety of factors, which are discussed below:
a) Macroeconomic Conditions
Various economic indicators, including the GDP growth rate, fluctuations in the inflation rate, and unemployment rates, have an impact on market correlations:
- Economic Cycles:
- The market correlations change during the different phases of the economic cycle, primarily, Expansion and Contraction.
- For example,
- During the expansion phase, growth sectors like technology exhibit a higher degree of correlation.
- During the contraction phase, sectors known for stability and resilience, such as staples and utilities, exhibit a higher correlation.
- Interest Rates:
- Changes in interest rates can impact the various asset classes and alter their correlation.
- For example, when interest rates rise, it can lead to a decrease in bond prices due to the inverse relationship between interest rates and bond yields. On the other hand, rising interest rates might impact equity prices in various ways, potentially causing shifts in investor preferences for different types of assets.
b) Geopolitical Events
The stock market is heavily influenced by investor sentiments. In addition to economic conditions, various geopolitical events like trade tensions, political instability, and conflicts can spark market reactions, leading to changes in correlations between different assets.
In light of these influences, it’s important to delve deeper into how these events manifest in market behavior. This leads us to explore how investors react to uncertainty, often seeking safe-haven assets during times of political instability. Additionally, these events can have ripple effects, altering the prospects of specific sectors. Let’s delve into these aspects in more detail.
- Search For Safe Haven Assets:
- During times of political instability, most investors seek safe-haven assets.
- This boosts the demand for gold and U.S. Treasuries, thereby changing the correlation between these assets and other assets.
- Impact on Specific Sectors:
- Several geopolitical events can instantly make a particular sector favorable or unfavorable.
- For example,
- Stocks of energy companies might get influenced by changes in oil prices due to geopolitical tensions in oil-producing regions.
c) Market Sentiment
The overall mood and perception of the market participants majorly impact the correlation between different assets. Such market scenarios are:
- Risk-On vs. Risk-Off
- There are periods of market optimism (risk-on) when investors chase market returns. It increases the correlations between riskier assets like stocks and commodities.
- Whereas, during periods of risk aversion or market pessimism (“risk-off”), correlations of safe-haven assets increase.
- Herding Behavior
- Situations of market panics or bubbles stimulate market sentiments and drive investors to make similar decisions.
- This increases the positive correlation among assets as investors buy or sell collectively.
Utilizing Bookmap for Analyzing Correlations
Bookmap, a tool trusted by traders, offers valuable resources for dissecting market correlations. It serves as a reliable platform for insightful market analysis, providing essential insights into market correlations.
Key Advantages
Experience innovative approaches to unlocking market dynamics and correlations through the following features:
- Order Flow Setups: Visualize the buy and sell orders within the order book, pinpointing significant price levels along with potential support/resistance zones.
- Market Pulse Add-on: Gain real-time forward-looking insights through a suite of per-instrument widgets that measure and display events generated by different sources, including order flow, order book, options, liquidations, and more. Market Pulse enables comprehensive monitoring of multiple instruments, enhancing your understanding of market behavior all in one place.
- Multi-Asset Analysis: Employ correlation analysis to multiple assets like futures, stocks, and cryptocurrencies.
- Visual Representation: Spot correlation between assets and understand price patterns through Bookmap’s visual representation of market data, including heatmaps and charts.
Conclusion
In the dynamic world of trading, the significance of maintaining a diversified portfolio cannot be underestimated. Market correlations provide insights into the statistical relationships among different asset classes, offering valuable information about market trends and patterns that can guide traders in forming effective trading strategies.
Gain an Edge in Trading: Start analyzing the market with Bookmap and uncover hidden opportunities that can enhance your trading performance.