Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
May 5, 2024
SHARE
What are ECNs?
Trading on ECNs can be done directly between traders and brokers without a middleman. As well as allowing investors around the world to trade with one another, they also allow for quick trades with lower transaction costs.
ECNs are registered and regulated by the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission).
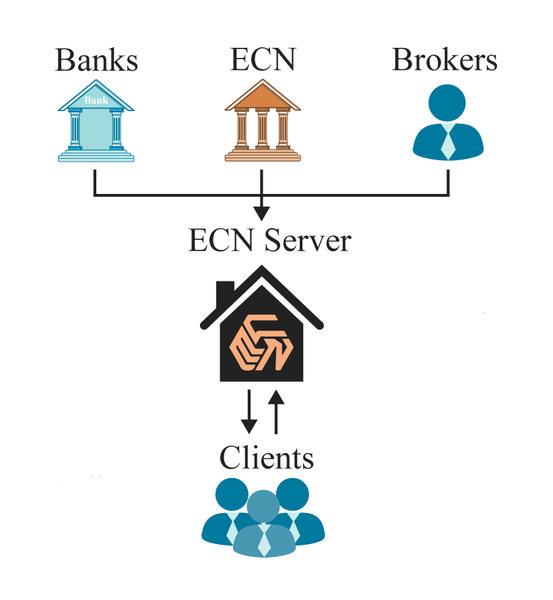
ECNs are electronic communication networks that display the best bid and offer, efficiently matching orders across participants automatically.
ECNs also offer after-hours trading, and most commonly offer stocks and foreign-exchange products. ECNs include automated trading, passive order matching, and quick execution.
What is an ECN?
Electronic communication networks are computerized systems that automatically match buy and sell orders. Investors from different geographies prefer ECN trading when they wish to make a secure transaction without using a third party, as they often offer cheaper transaction costs.
A Brief History of ECNs
The first ECN was founded in 1969. By cutting transaction costs, providing clients full access to their order books, and offering order matching outside of regular exchange hours, ECNs boosted competition among trading businesses.
The term alternative trading network or alternative trading system is sometimes used to refer to ECNs. The SEC defines ECNs as any electronic system that enables exchange market makers and OTC market makers to distribute orders to third parties for execution in whole or in part.
The Instinet, released in 1969, provided the first ever global order matching and information system. By changing regulatory law, the SEC encouraged the spread of ECNs, and by adopting the Securities Acts Amendments of 1975, the SEC encouraged the connection of information and community across all qualified securities and markets.
How do ECNs Work?
The SEC classifies ECNs as a substitute for trading systems by charging a fee for each transaction. Market makers who participate in exchanges or over-the-counter (OTC) may execute orders entirely or partially without any involvement from third parties.
Displaying and then automatically matching and executing orders across multiple market participants, they allow for trading not only during market hours, but also for after-hours trading, which is especially useful when trading in the very much international foreign exchange market across multiple time zones. You can read more about how the Forex market works here.
ECN Fees
ECNs lump all the fees charged by the networks and exchanges into a single fee, which is usually just a fraction of the price charged by broker-dealers. Since ECNs trade without a middleman, they are cheaper overall, but do charge a small fee for matching buy and sell orders.
The Main ECNs
Instinet, BATS, and NYSE Arca are three of the main ECNs.
Instinet was developed in 1969 and utilized small brokerage firms and inter-institutional trades. It is widely used by market makers for trading in the Nasdaq, although individuals and small businesses can also use it.
BATS converted its electronic communication network, or ECN, into the national securities exchange BZX, allowing BATS to participate in the United States consolidated tape plans, earn market data fees, reduce its clearing costs, and operate a primary listings business.
Archipelago, an early ECN from 1996, was merged with the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) to form NYSE Arca. NASDAQ and NYSE use this software for electronic stock trading.
Conclusion
Electronic communications networks (ECNs), which were a source of frustration for traditional stock exchanges in the late 1990s and early 2000s, have now computerized trading and link buyers and sellers of stocks and other assets via instantaneous electronic transactions.
Although electronic trading through ECNs takes several forms, they all have one thing in common: they undercut large brokerage houses and New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) firms like Merrill Lynch and Goldman Sachs.
ECNs offer lower transaction costs since they eliminate these middlemen when trading securities. Online brokerages, institutional investors, and day traders alike prefer to use ECNs because of their speed and lower costs.
Bookmap offers connections to several ECNs. Try the platform out for free today.