Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
May 2, 2025
SHARE
Currency Manipulation: How Countries Influence Exchange Rates and Global Markets
They say money makes the world go round. But what if a country could secretly tilt the playing field? Currency manipulation is one of the government’s most potent tools to gain an economic edge. Despite this, many traders and investors ignore its impact!
Understanding forex market intervention and exchange rate manipulation is vital for anyone in global finance. That’s because governments and central banks adjust interest rates and buy or sell currencies to influence their economies. These actions create massive ripple effects in forex trading, stock markets, and commodity prices.
Do you want to stay ahead of currency devaluation strategies and gain a serious advantage? In this article, we’ll explore notorious cases of currency manipulation, study the impact of manipulation on different markets, and discuss various strategies traders can use to deal with such events. Also, we will see how using our real-time market analysis tool, Bookmap, can help you track market moves and profit from them. Let’s begin.
What Is Currency Manipulation?
Currency manipulation happens when a country’s government or central bank takes action to influence exchange rates in its favor. Governments resort to such tactics to gain an economic advantage in global trade and finance.
How Does Currency Manipulation Work?
Governments and central banks use several methods to control currency value. Study the table below:
| Forex market intervention | Interest rate policies | Direct market operations |
| The central bank buys or sells large amounts of its currency to increase or decrease its value. | The central bank decreases interest rates with the intention of weakening the currency. In contrast, raising interest rates can strengthen the currency. | Governments may impose capital controls or use reserves to impact exchange rates. |
Why Do Countries Manipulate Their Currency?
A country might engage in exchange rate manipulation for a variety of reasons. The common motivations usually are to:
- Boost Exports: The weaker a currency is, the cheaper goods and services are for foreign buyers. This increases the demand for exports.
- Control Inflation: A stronger currency lowers the cost of imported goods. This helps to reduce inflation.
- Attract Foreign Investment: A stable or undervalued currency makes a country more appealing to investors.
Example: China’s Yuan Devaluation (2015)
In 2015, China deliberately weakened the yuan and allowed it to fall in value. This action was taken to support its struggling economy. A weaker Yuan resulted in cheaper and competitive Chinese exports globally.
However, this move caused instability in the forex market. It led to global concerns about central bank currency policy and trade imbalances. That’s why, even today, currency manipulation remains a controversial topic. Often, countries accuse each other of this unfair practice.
How Countries Manipulate Their Currencies?
Governments and central banks manipulate currencies. They use different strategies to influence exchange rates and gain economic advantages. Let’s check out some standard methods:
Direct Central Bank Intervention
One of the most common tactics is the central bank’s currency policy to control exchange rates. Check the graphic below to learn how this tactic is implemented:
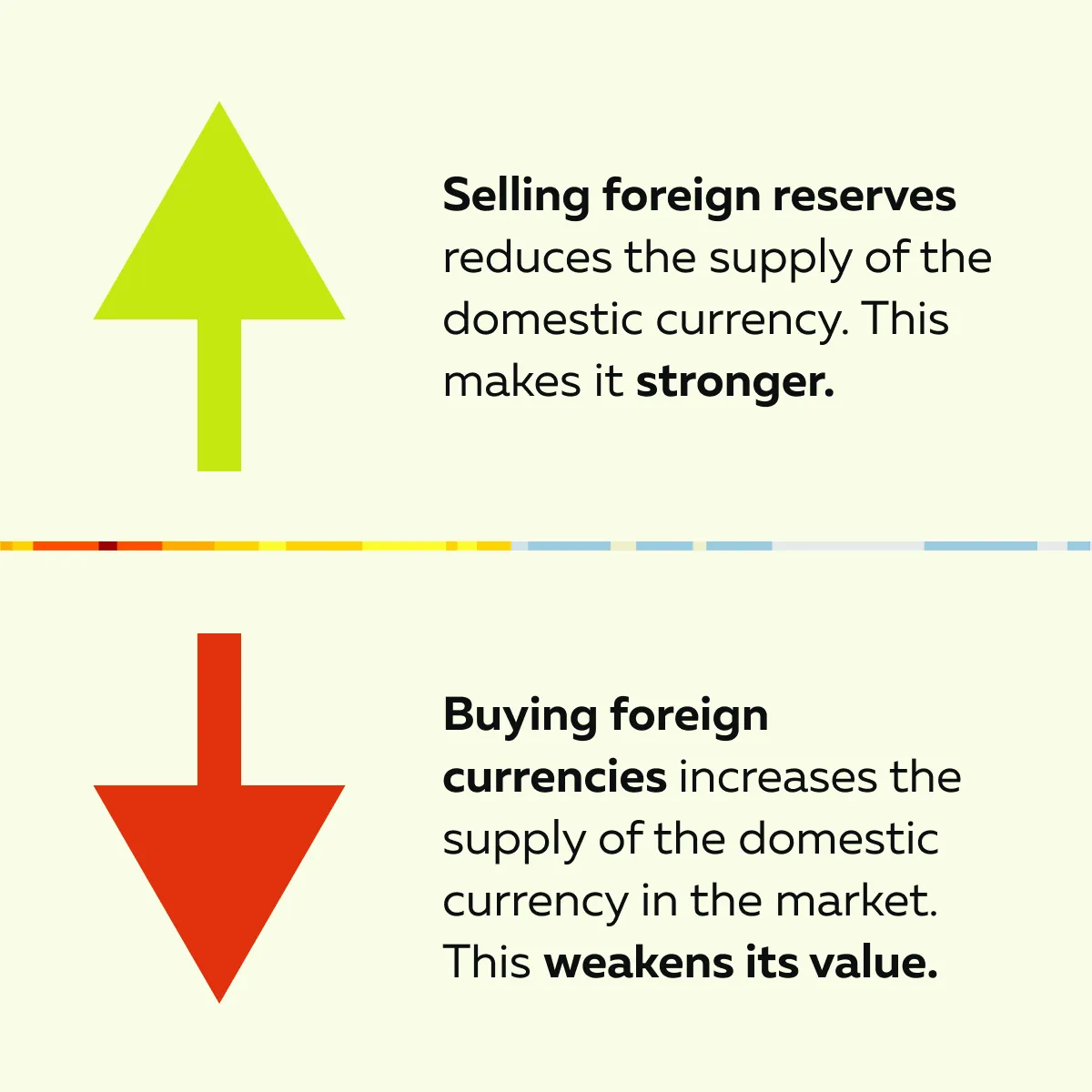
For more clarity, let’s read about an event related to the Swiss National Bank (SNB) in 2015:
- In 2015, the Swiss National Bank (SNB) unexpectedly voided its currency peg to the euro.
- This event led to an unexpected surge in the Swiss franc.
- This move caused massive losses for forex traders.
Interest Rate Adjustments
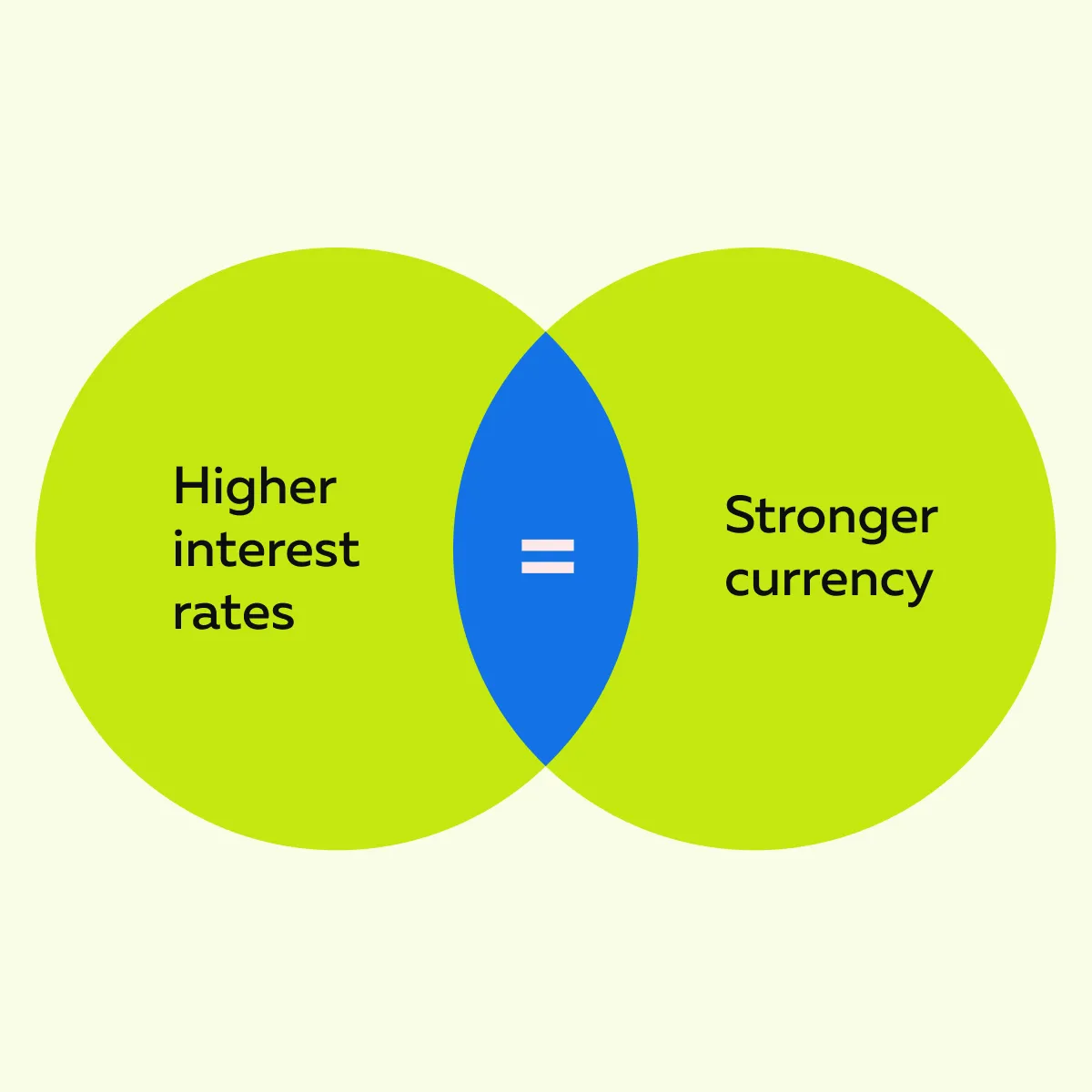
Central banks also manipulate exchange rates through interest rate policies. See the graphic below:
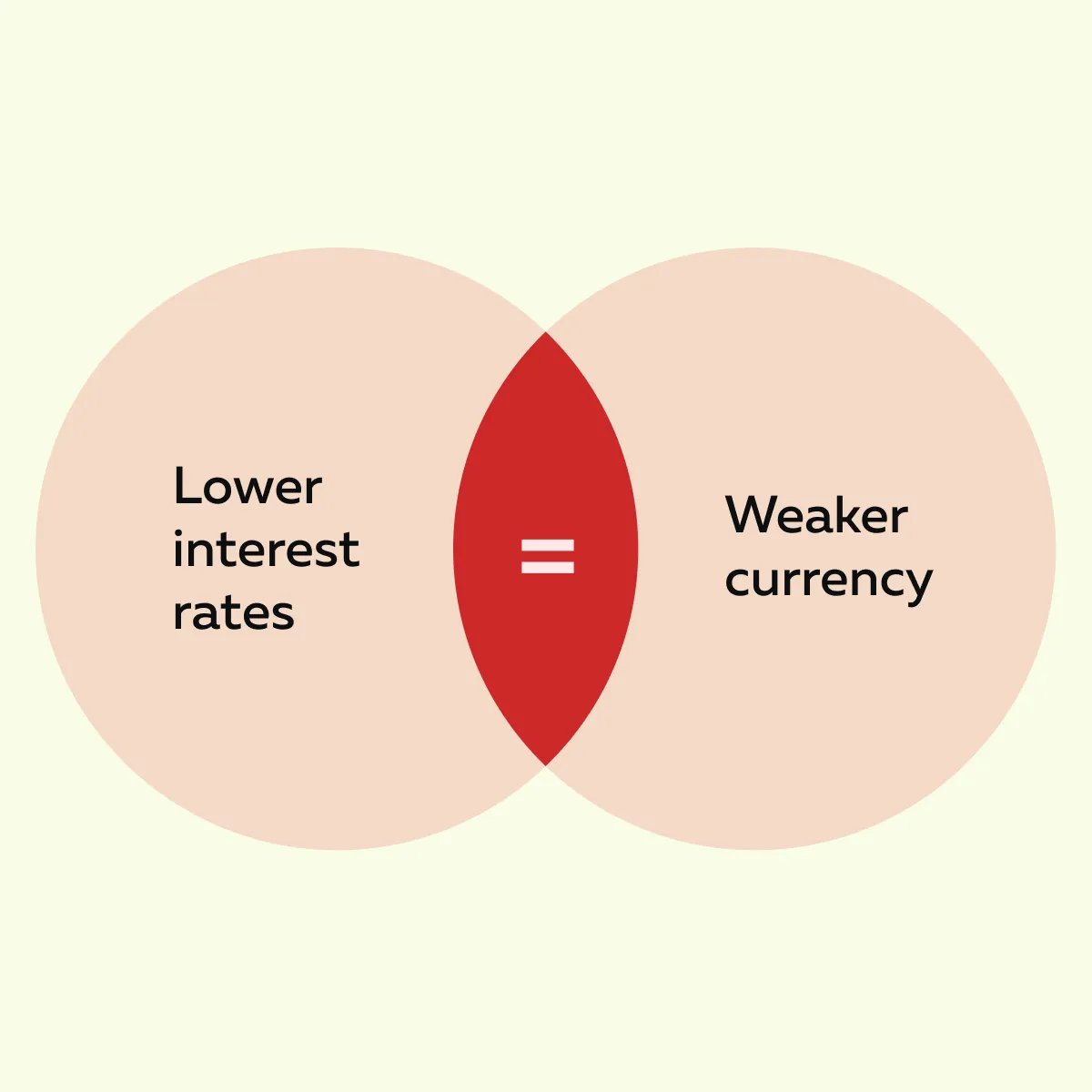
When a country decreases its interest rates, borrowing becomes much cheaper. This event, in turn, increases spending and investment. Such an environment weakens the currency and makes exports more competitive.
In contrast, raising rates attracts foreign investors looking for better returns. This increases the demand for the currency and strengthens its value.
Let’s further understand this through an example related to Japan’s Zero-Interest Rate Policy (ZIRP) :
- Japan has long maintained a zero-interest rate policy (ZIRP) to keep the yen weak.
- This policy makes Japanese exports cheaper.
- Also, this boosts its economy by increasing global demand for its products.
These strategies and other exchange rate manipulation techniques allow countries to control inflation and boost exports.
Trade Tariffs and Capital Controls
In addition to direct forex market intervention and interest rate adjustments, countries use trade tariffs and capital controls to:
- Manage their currency value,
and
- Maintain economic stability.
Let’s learn how through the table below:
| Trade Tariffs and Import Taxes | Capital Controls |
| By applying tariffs on foreign goods, a country can significantly lessen imports. This measure helps to strengthen its currency. | Some governments may resort to restricting the flow of money in and out of the country. Such a restriction prevents currency fluctuations and financial instability. |
For example:
- China has implemented strict capital controls to prevent massive outflows of money .
- This policy stabilized the yuan.
- It limits how much currency investors and businesses can move abroad.
- By doing so, China maintains control over exchange rates and reduces the risk of rapid devaluation.
Stay ahead of market volatility by tracking liquidity shifts with Bookmap .
4 Notorious Cases of Currency Manipulation
Throughout history, several countries have manipulated currency to gain economic advantages. From China’s yuan devaluation to Japan’s weak yen policy, these interventions have influenced global trade and financial markets.
Here are four major cases where the forex market intervention and exchange rate manipulation made headlines:
Case I: China and the Yuan (CNY)
- For years, China has been accused of currency manipulation.
- By doing so, it maintains an economic advantage in global trade.
- The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) periodically interferes with the forex market.
- It manipulates the value of the yuan (CNY).
- By controlling the exchange rate, China ensures that its exports remain competitive.
The U.S. and other nations have often pointed fingers at China’s exchange rate manipulation. Their stance is that an artificially weakened yuan offers Chinese exporters an unfair edge. This ongoing dispute has even led to friction between China and the U.S., with tariffs and economic policies often used as countermeasures.
Case II: Japan and the Yen (JPY)
- Japan has a long history of forex market intervention.
- It often develops monetary policies that keep weakening the yen (JPY).
- By doing so, Japan supports its export-driven economy.
- Over the years, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) has consistently maintained low interest rates.
- It green-lighted a zero-interest rate policy (ZIRP) to catalyze borrowing and spending.
- These moves made the yen weaker, enhancing the competitiveness of Japanese exports.
In addition to interest rate policies, Japan has directly intervened in currency markets by buying or selling yen to influence its value. This central bank currency policy benefits major Japanese exporters like:
- Toyota,
- Sony,
and
- Honda.
Such policies allow them to sell goods more competitively in global markets. However, Japan’s exchange rate manipulation has often been criticized by other countries that see it as an unfair trade advantage.
Case III: Switzerland and the Swiss Franc (CHF)
- Switzerland has actively engaged in the forex market intervention.
- It usually tries to control the value of the Swiss franc (CHF) and protect its economy.
- The Swiss National Bank (SNB) has repeatedly manipulated the franc to weaken it.
- It develops policies that are meant to keep the Swiss franc from appreciating too much.
- That’s because a strong CHF makes Swiss exports more expensive.
- A currency appreciation hurts industries like luxury goods and pharmaceuticals.
In 2015, the SNB suddenly removed its currency peg to the euro (which had kept the franc artificially weak). This decision caused the Swiss franc to surge overnight. Consequently, there were massive losses for forex traders. It also caused global market instability.
Case IV: U.S. and the Dollar (USD)
Unlike some countries that engage in direct forex market intervention, the U.S. does not openly manipulate the dollar (USD). However, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy influences its value. Let’s see how:
- Interest rate hikes and cuts by the Federal Reserve impact the strength of the USD.
- Raising interest rates attracts foreign investment.
- This event increases the demand for dollars and strengthens the currency.
- Lowering rates has the opposite effect, which makes the dollar weaker.
Let’s gain more clarity through an example related to the 2022-2023 rate hikes:
- To fight inflation, the Federal Reserve increased interest rates aggressively.
- This event caused the dollar to surge.
- This move benefited U.S. consumers by reducing import costs.
- However, at the same time, it harmed the interests of emerging markets with USD-denominated debt.
- That’s because it made loan repayments more expensive.
This case demonstrates how a central bank’s currency policy can have global effects without direct exchange rate manipulation.
The Impact of Currency Manipulation on Traders
Currency manipulation creates both risks and opportunities for traders. Check the graphic below to learn how currency manipulation impacts the market:
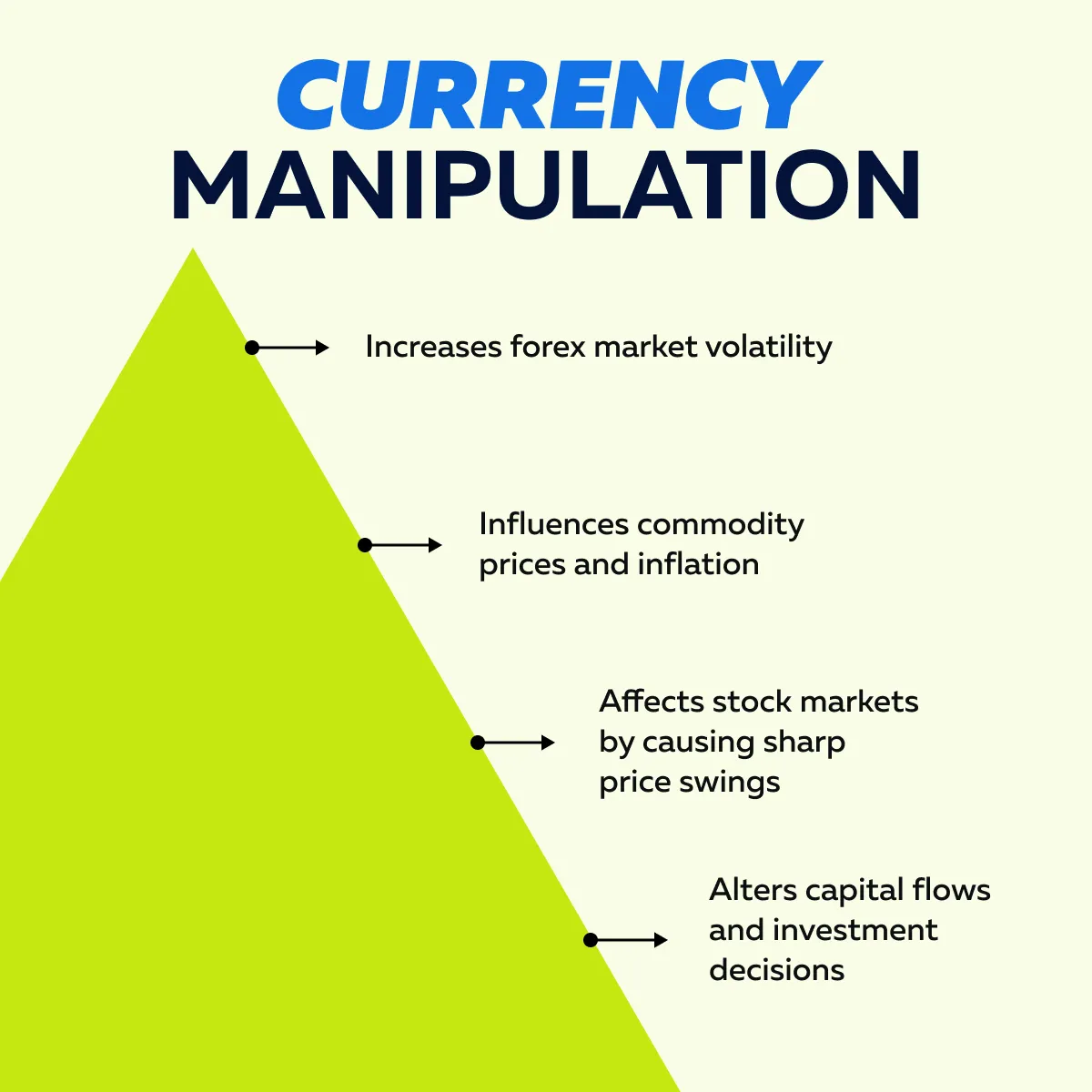
Let’s understand in detail:
Forex Market Volatility
When a central bank meddles with the forex market, it can create significant volatility. Usually, this causes rapid price movements in currency pairs. These fluctuations offer both risks and opportunities for traders. Let’s see how:
| Sudden price swings | Increases uncertainty |
| Unexpected interventions (such as interest rate changes or direct currency purchases) can lead to sharp movements in exchange rates. | Traders must constantly monitor central bank currency policy to anticipate the likely shifts in the market. |
For example:
- Assume that the Bank of Japan (BOJ) unexpectedly lowers interest rates.
- Now, it could weaken the yen (JPY).
- This event might also cause the USD/JPY currency pair to surge.
- This can happen as it will be more lucrative for investors to move capital into the stronger U.S. dollar.
- Such moves create profitable trading opportunities.
- However, it also poses risks for those caught on the wrong side of the trade.
Effects on Commodities and Inflation
Currency manipulation doesn’t just impact forex traders. It also affects commodity prices and inflation. Check the graphic below:
When a country’s currency weakens, imported goods become more expensive. Generally, the weakening of a currency leads to inflation. Moreover, a declining currency often leads to higher gold and oil prices. That’s because investors look for assets that hold value.
Let’s understand better through an example:
- When China weakens the yuan (CNY), Chinese investors often resort to using gold to hedge against inflation and currency instability.
- This event increases gold demand and pushes prices higher in global markets.
Stock Market Reactions
Currency manipulation and exchange rate fluctuations significantly impact stock markets, particularly for companies with global operations. Check the graphic below:
Be aware that when a country’s currency strengthens, it deters foreign buyers due to an increase in the price of exports. This hurts multinational companies that rely on international sales. In contrast, companies that sell products abroad benefit when the currency is weak. That’s because their goods become cheaper and more competitive in global markets.
For example:
- Say the euro (EUR) weakens.
- Now, it can lead to capital outflows.
- This happens as investors move money into stronger currencies like the U.S. dollar (USD).
- This move negatively impacted European stock indices.
- Also, it reduces investor confidence and leads to lower stock prices.
Similarly, companies like Toyota thrive when the yen (JPY) weakens. This happens as their exports become more affordable overseas. As a trader or investor, you must closely monitor the central bank’s currency policy to assess likely stock market movements.
How Traders Can Profit from Currency Manipulation?
You can capitalize on currency manipulation by using strategies like the following:
- Forex trading,
- Hedging with futures and options ,
- Tracking liquidity shifts.
Also, by understanding central bank interventions and exchange rate manipulation, traders can anticipate market moves and seize profit opportunities in the ever-changing forex market. Let’s see how:
Forex Trading Strategies
Traders who understand central bank currency policy and exchange rate manipulation can use specific strategies to capitalize on market movements :
- Watch Central Bank Announcements:
- As a forex trader, you can closely monitor:
- Central bank meetings,
- Interest rate decisions,
- As a forex trader, you can closely monitor:
and
- Intervention signals.
- A sudden rate cut or direct forex market intervention can cause sharp price movements.
- It can create short-term trading opportunities.
- For example,
- Say the Federal Reserve unexpectedly raises interest rates.
- Now, the USD may strengthen.
- This event provides a chance to trade USD pairs.
- Carry Trade Strategy
- This strategy takes advantage of interest rate differences between currencies.
- Traders borrow in low-interest currencies (e.g., yen [JPY]).
- Simultaneously, they invest in higher-yield currencies (e.g., U.S. dollar/USD) to profit from interest rate spreads.
- For example,
- Say a country with low rates, like Japan, is following ZIRP.
- Now, traders can borrow cheap JPY and invest in assets with higher returns elsewhere.
Monitor currency manipulation in real time with Bookmap’s liquidity tools .
Hedging with Futures & Options
Forex traders and businesses also use futures and options to protect themselves from sudden currency fluctuations caused by central bank interventions or exchange rate manipulation. Let’s see how:
- Forex Futures
- These contracts allow traders to lock in an exchange rate for a future date.
- This strategy reduces the risk of unexpected currency moves.
- Options Contracts
- These contracts give traders the option (but not the obligation) to purchase or sell a currency at a set price.
- This strategy provides flexibility in uncertain markets.
For Example:
- Say a U.S. company relies on Chinese suppliers.
- The company’s management is concerned that the yuan (CNY) will weaken due to the intervention of the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) in the forex markets.
- To protect themselves against this risk, the company could:
- Buy forex options that allow you to purchase yuan at a fixed rate.
- Use futures contracts to secure a stable exchange rate for future transactions.
Using Bookmap to Track Liquidity Shifts
Our platform, Bookmap, is a powerful tool for forex traders worldwide. It allows you to analyze liquidity shifts. Also, you can detect institutional reactions to currency manipulation and central bank interventions. Let’s see how it benefits you:
- Monitor Order Flow on Bookmap:
- You can track large buy and sell orders on Bookmap.
- This data lets you see how major players react to exchange rate manipulation in real time.
- Track Liquidity Levels on Bookmap :
- Please note that sharp changes in liquidity can signal upcoming forex market interventions.
- This observation allows you to position yourself before a major move.
For more clarity, let’s study an example related to detecting hidden liquidity before a currency intervention:
- Say the trader is using Bookmap’s heatmap.
- They notice unusually high liquidity levels in the USD/JPY pair right before the Bank of Japan (BOJ) announces a rate cut.
- This early insight lets the trader anticipate a yen (JPY) depreciation.
- Based on this belief, they position themselves accordingly for a profitable trade.
Conclusion
Currency manipulation plays a significant role in the forex market, stock market, and commodities trading. When central banks intervene (whether by adjusting interest rates, buying or selling currencies, or imposing capital controls), these actions create market volatility that traders must deal with carefully.
Generally, exchange rate manipulation leads to sharp price swings for forex traders. At the same time, export-driven companies benefit from a weaker currency, while multinational firms struggle with a stronger one. In the commodities market, a weaker currency often drives up prices for gold and oil (as investors seek safer assets).
To stay ahead, traders like you should closely monitor central bank currency policies and interest rate decisions. Also, you can start using our powerful market analysis tool, Bookmap. It allows you to visualize order flow, track liquidity shifts, and detect institutional reactions to central bank moves.
By using our platform, Bookmap’s heatmap, and liquidity tracking features, you can better understand market movements. See how central bank interventions impact currency trends using Bookmap’s advanced order flow insights .
