Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Stocks
March 28, 2025
SHARE
How to Boost Returns with Options Strategies on High Dividend Stocks

Ask any investor; they say dividends are the gift that keeps on giving! But what if you could make them even better? That’s where options strategies for dividend stocks come in. By using smart options trades, you can boost your income, smartly manage trading risk, and maximize stock ownership benefits.
Are you wondering how to do this? In this article, you will understand that dividend investing alone may not always generate the highest returns. While holding dividend stocks can provide steady income, options strategies like covered calls and vertical spreads on dividend stocks can enhance returns with options beyond the regular dividend yield. You’ll learn how to earn premium income, hedge against market downturns, and even buy stocks at a discount using cash-secured puts.
We will start with why options are helpful for dividend stocks and then move on to detailed explanations of covered calls, vertical spreads, and cash-secured puts. Finally, we will discuss risks, tax implications, and how market trends impact these strategies. Want to have a solid understanding of how to enhance your dividend stock portfolio using options? Read till the end!
Why Use Options on High Dividend Stocks?
As an investor looking to maximize your earnings from high-yield stocks, you can use options strategies for dividend stocks. This will help you generate additional returns beyond just “dividends.”
One approach to doing this is selling covered calls. Here, you hold the stock and sell call options to collect premium income. This strategy works well with stable dividend stocks since the premium adds an extra layer of profit.
For example:
- Suppose an investor owns shares of a reliable and high-yield company.
- They write a covered call at a slightly higher strike price.
- If the stock remains below this price, they keep both the shares and the premium.
- If exercised, they still benefit from capital appreciation and dividend payments.
This method boosts returns but also provides some downside protection. Therefore, it is ideal for income-focused investors.
How to Maximize Returns in Low-Volatility Markets?
Please note that many high-dividend stocks belong to sectors like:
- Utilities,
- Consumer staples, and
- Healthcare.
They experience lower price fluctuations. In such conditions, traders can enhance returns with options and create active income. Here, selling a vertical spread on dividend stocks is one way to profit from limited price movements.
For example,
- Suppose you buy a lower-strike call.
- Simultaneously, you sell a higher-strike call on the same stock.
- This reduces your capital risk.
- At the same time, you can still capture the upside potential.
Additionally, you can use a put credit spread when expecting steady stock performance. This allows you to collect premiums while benefiting from dividend stability. Through these strategies, you can extract more value from your holdings (even in calm market environments).
3 Key Options Strategies for Dividend Stocks
Options are a powerful tool. You can use them to maximize your returns on dividend stocks. Let’s have a look at three proven options strategies for dividend stocks:
Covered Calls
In a covered call strategy, you sell call options on a stock while holding the underlying shares. This is one of the most effective options strategies for dividend stocks. That’s because it allows investors to generate additional income while maintaining ownership of high-yield stocks.
The goal here is to earn premium income from the option while continuing to collect dividends. This strategy works well for investors who believe the stock price will:
- Remain relatively stable
or
- Rise slightly but not enough to exceed the strike price of the call option sold.
How Does It Work?
By selling a covered call, an investor earns an upfront premium. This boosts total returns beyond just dividend payments. Since the investor owns the stock, the risk is lower than naked options trading.
However, the potential upside is capped. That’s because if the stock price rises above the strike price, the shares may be called away. This limits your further gains. Despite this, the combination of dividend yield and option premium makes it a preferred strategy in low-volatility environments.
For more clarity, let’s study an example:
- Suppose an investor owns 100 shares of AT&T (a well-known high-yield stock).
- They sell a call option with a strike price slightly above the current market price.
- If AT&T’s price remains below the strike price, the investor keeps both the premium and the dividends.
- If the stock surpasses the strike price, they must sell it at that level.
- However, they still benefit from the option premium and likely capital appreciation.
This approach is a great way to extract extra value from stable and high-dividend stocks.
Vertical Spreads
A vertical spread on dividend stocks is a popular options strategy. In this, you buy and sell options with different strike prices but the same expiration date. This approach is widely used to generate profits while controlling risk.
Unlike outright stock ownership, vertical spreads allow traders to speculate on price movements. You can even do so with limited capital requirements. These spreads can be bullish (bull call spread) or bearish (bear put spread), depending on the market outlook.
How Does It Work?
In this technique, you capture expected price movements while limiting downside risk. You do not make outright stock purchases. For example, a bull call spread involves:
- Buying a lower-strike call, and
- Selling a higher-strike call.
The net cost of this strategy is lower than buying a single call, making it cost-effective while benefiting from likely price increases.
On the other hand, a bear put spread works similarly. It allows you to profit from declines in high-dividend stocks by using put options.
Why It’s Effective?
Vertical spreads allow you to trade price movements within a specific range. They are beneficial for traders who want exposure to high-yield stocks without committing significant capital.
For example,
- As an investor, say you expect a dividend-paying stock to rise moderately.
- You use a bull call spread to earn profits with limited risk.
Leverage Bookmap’s tools to enhance your dividend stock strategies with advanced options insights.
Cash-Secured Puts vs. Selling Puts on Dividend Stocks
A cash-secured put is a conservative options strategy. Here, you sell a put option while holding enough cash to buy the stock if assigned. This strategy is commonly used to:
- Generate premium income and
- Acquire shares of a high-yield stock at a lower price.
Unlike selling uncovered puts, this method ensures that the investor has sufficient capital to fulfill the contract if the stock price drops below the strike price.
How Does It Work?
Selling a cash-secured put allows traders to earn premium income upfront. If the stock remains above the strike price, the put expires worthless. In this case, the seller keeps the premium. In contrast, if the stock price falls below the strike price, the trader must buy the stock. This purchase often happens at a discount compared to its previous market price. For more clarity, check out the graphic below:
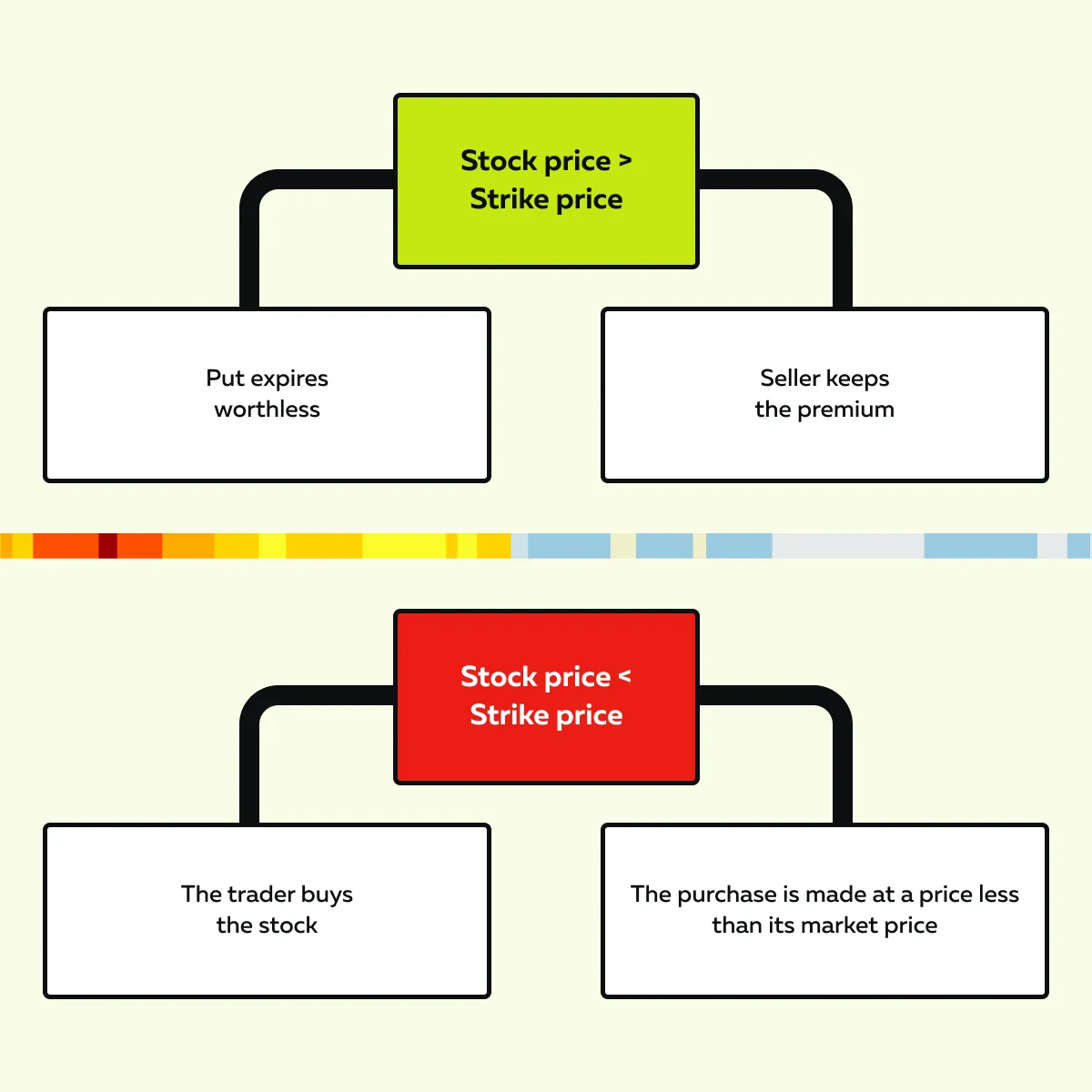
This strategy works well with high-quality dividend-paying stocks. That’s because it allows investors to accumulate shares and also benefit from option premiums.
For more clarity, let’s study an example:
- Suppose an investor wants to buy Johnson & Johnson stock but at a lower price.
- Instead of purchasing it immediately, they sell a put option with a strike price below the current market price.
- If the stock stays above the strike price, they keep the premium as profit.
- If it drops below, they buy the shares at the agreed strike price.
Important Note for Traders
Do not get confused with cash-secured calls. The term is sometimes misused. In a cash-secured put, you set aside cash to buy the stock. In contrast, a call involves selling an option on an owned stock.
Also, understand that a naked put means selling a put without the cash reserve. It exposes the trader to higher risk if the stock falls sharply. However, some investors use naked puts on stocks they already own to enhance returns with options further, though this carries additional risk.
Risks and Considerations
Most options strategies for dividend stocks provide income through premiums. But, they also limit potential gains. For example,
- Suppose you are using a covered call strategy and generating steady returns.
- But if the stock price rises significantly above the strike price, you are forced to sell at that level.
- This means you miss out on further appreciation beyond the strike price.
- This caps your upside.
While this strategy is excellent for steady income, it’s not ideal for stocks with strong growth potential. Therefore, as an investor, you should weigh the trade-off between premium income and lost gains before implementing covered calls.
Furthermore, let’s check out some other risks and considerations:
Assignment Risk & Ex-Dividend Date Timing
Investors using covered calls on dividend stocks must consider the timing of the ex-dividend date. That’s because it impacts early assignment risk. Many traders buy dividend stocks just before the ex-dividend date to capture dividends and then sell immediately after.
Now, if a trader has sold a covered call and it’s in the money (ITM) near the ex-dividend date, early assignment becomes more likely. This is because option holders might exercise early to claim the dividend, leaving the seller without the stock and the dividend payment.
For more clarity, let’s study an example:
- Suppose you sell a covered call on ABC Inc. a few days before its ex-dividend date.
- Now, if the stock price rises above the call’s strike price, there’s a high chance of early assignment.
- This means you will be forced to sell the stock before the ex-dividend date.
- If this happens, you will miss out on the dividend payment.
To mitigate this risk, you can adjust strike prices or use vertical spread on dividend stocks. Alternatively, you can roll the covered call to a later expiration. This will help you retain the stock.
Tax Implications & Long-Term Holding Risks
Investors using options strategies for dividend stocks should be aware of tax consequences. They should be particularly cautious when selling covered calls on long-term holdings. If a stock is held for years, it usually qualifies for favorable long-term capital gains tax rates.
However, repeatedly selling covered calls can trigger short-term taxable income. It is taxed at a higher rate.
Additionally, covered calls limit portfolio appreciation over time. Let’s see how through the graphic below:
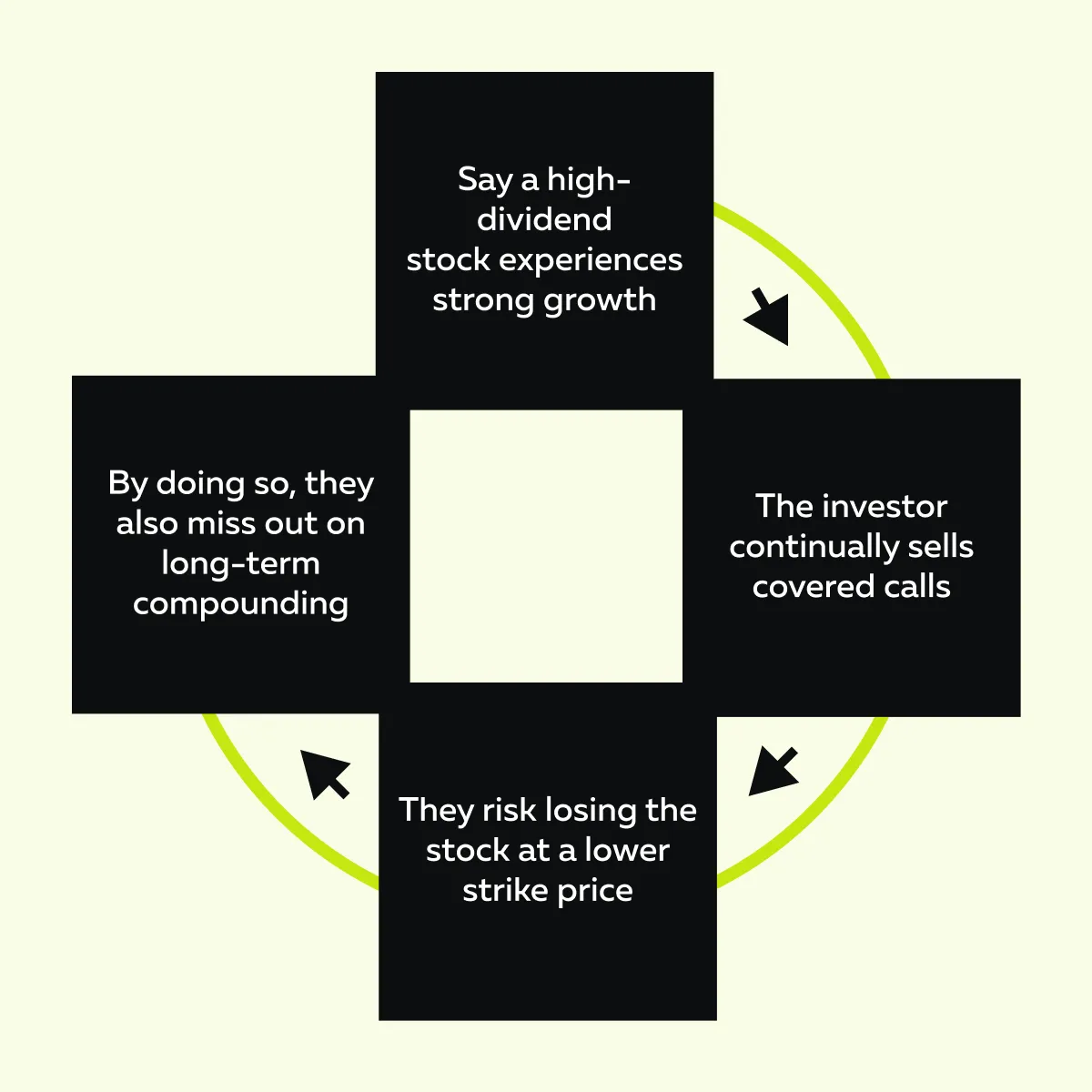
For example,
- Suppose a long-term investor in Coca-Cola repeatedly sells covered calls.
- They face unexpected tax burdens.
- Also, it limits the likely stock price gains.
- If the stock is consistently called away, it disrupts the benefits of buy-and-hold investing with dividends.
Transaction Costs and Market Volatility
When enhancing returns with options, be cautious of transaction costs, as they can erode profitability. Please note that options trading involves:
- Bid-ask spreads,
- Brokerage commissions and
- Contract fees.
All of these reduce net returns. Frequent trading (such as rolling covered calls or adjusting vertical spread on dividend stocks) can lead to increased expenses. Thus, you should keep monitoring costs.
Additionally, market volatility also plays a significant role in:
- Options pricing
and
- Execution.
High volatility increases option premiums. This makes covered calls more lucrative. However, it also raises the risk of early assignment. If a stock price fluctuates significantly, a call option might be exercised earlier than expected. Thus, you are forced to sell the stock.
For more clarity, let’s study an example:
- Suppose you sell covered calls on a high-yield stock in a highly volatile market.
- Now, the stock price jumps suddenly due to earnings or macroeconomic news.
- You exercise the call option unexpectedly.
- You sell your stock at the strike price, even if you plan to hold it for the long term.
Combining Dividend Investing with Market Trends
Be aware that dividend stocks react differently to various market cycles. Hence, you should try to align them with the right options and strategies for dividend stocks to optimize returns. Let’s see how:

For example:
- Suppose, during a recession, investors turn to consumer staples stocks.
- These stocks usually retain value.
- This makes them ideal for cash-secured puts.
- Here, investors sell puts at a lower strike price.
- By doing so, they can buy the stock at a discount while earning a premium in the process.
Integrating Economic Indicators
Macroeconomic trends directly impact dividend stocks. Also, they influence their corresponding options strategies for dividend stocks. Let’s see how through the graphic below:
Similarly, inflation can affect dividend stocks differently. Companies with strong pricing power can:
and
- Continue paying dividends.
In contrast, others struggle with rising costs. In such cases, enhancing returns with options becomes essential. Selling covered calls during inflationary periods allows you to supplement income when stock appreciation slows.
For more clarity, let’s study an example:
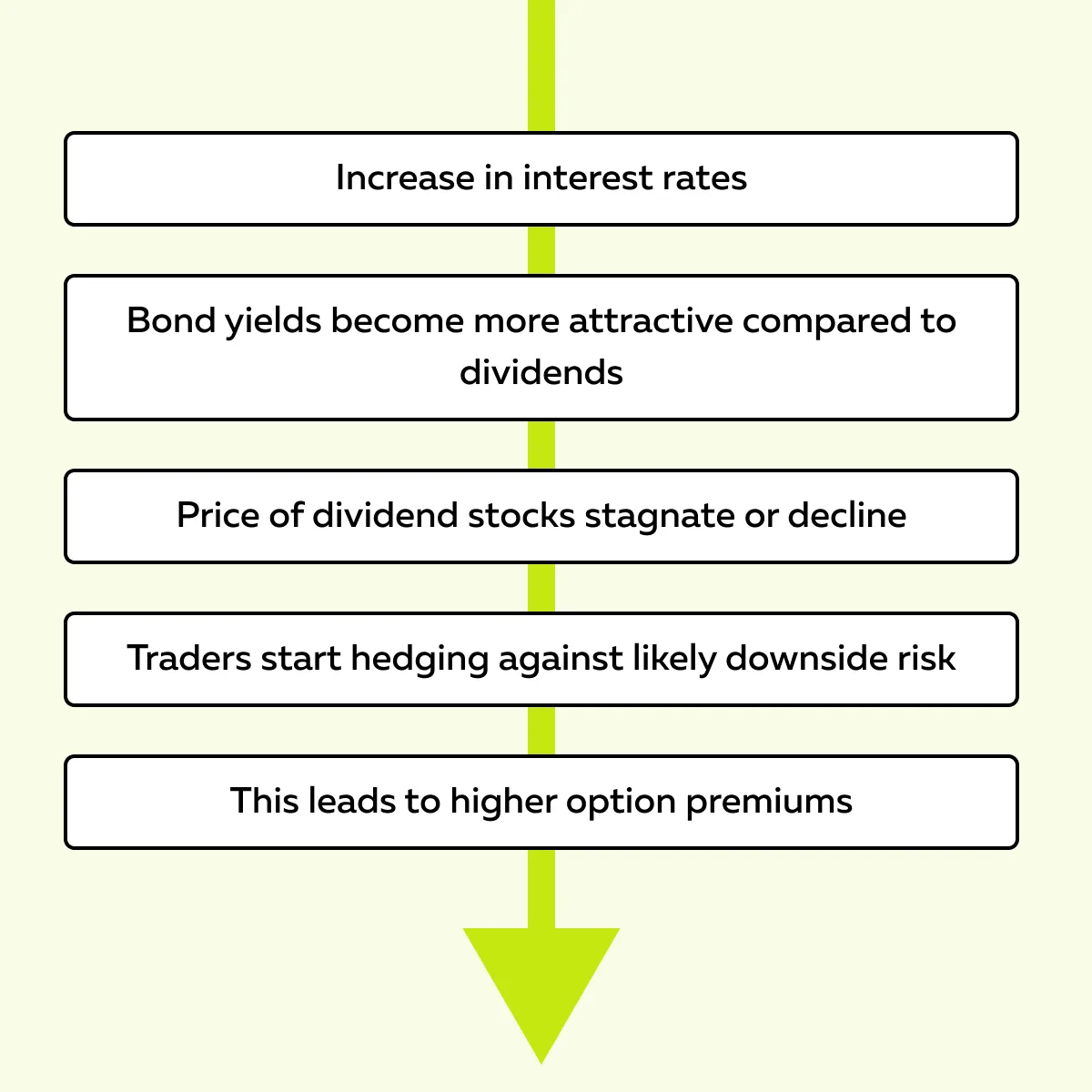
- Suppose a Federal Reserve increases interest rates.
- Dividend stocks (like Verizon or AT&T) experience reduced demand.
- That’s because investors shift toward bonds.
- However, this scenario can also create higher implied volatility.
- This makes covered calls more profitable as premiums rise.
- In such cases, investors use cash-secured puts.
- Through it, they can:
- Acquire stocks at lower prices,
and
- Earn additional income from the premium.
Adapting Strategies Based on Volatility
Market volatility significantly impacts options pricing. Higher volatility increases option premiums. This increases benefits strategies like covered calls and cash-secured puts. However, it also raises the risk of early assignment or unexpected price swings.
For example:
- Suppose before a company’s earnings announcement that implied volatility often spikes.
- This provides an opportunity for dividend investors to sell covered calls at higher premiums.
- Now, assume that the stock price remains stable post-earnings.
- Here, investors keep the option premium and continue to collect dividends.
Conclusion
Options strategies for dividend stocks provide investors with multiple advantages. It can:
- Enhance your income,
- Reduce risk, and
- Optimize stock positions.
Strategies like covered calls allow investors to collect option premiums while continuing to receive dividends. This makes it ideal for stable and high-yield stocks. Similarly, a vertical spread on dividend stocks allows you to manage risk while capturing upside potential (especially in low-volatility markets). Cash-secured puts offer another way to generate income. It will enable you to acquire dividend stocks at a lower price.
To maximize the effectiveness of these strategies, you should use our advanced market analysis tool, Bookmap. Using it, you get real-time market visualization and liquidity analysis. For example, when selling a covered call, Bookmap can help you spot price ceilings where the stock may face resistance. This allows you to choose the right strike price. Similarly, when using a vertical spread on dividend stocks, real-time data ensures your positions are accurate and within the expected price range.
Want better insights into options strategies? Use Bookmap to track key liquidity zones and time your trades effectively.