Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
July 19, 2024
SHARE
Understanding Rollover Periods and Open Interest: A Guide for Traders
Trends and sentiments influence price movements and are crucial in the stock market. Highlighting their importance, Warren Buffett famously said, “Be fearful when others are greedy, and greedy when others are fearful.” But do you know how to spot trends and gauge sentiments? Successful traders often track these by analyzing “rollover periods” and “open interest”.
In this article, we will explain to you both of these important concepts of futures trading: rollover period, and its significance and leveraging open interest data for making informed trading decisions. Moreover, we’ll look at how rollover periods affect market dynamics and provide strategies for managing them effectively. Additionally, we’ll discuss tools like Bookmap that help visualize and analyze open interest and rollover data. Let’s begin.
What is a Rollover Period?
A rollover period is the time when traders shift their positions from a futures contract close to expiration to a contract with a later expiration date. This process is essential for traders who wish to maintain their exposure to a particular asset without taking delivery of the physical commodity.
The Evolution of Rollover
If we talk about the historical context of a rollover, in the past, farmers would take their produce to the market without knowing the outcome of their efforts. This uncertainty was due to external factors, such as floods and droughts and this led to the development of hedging as a risk management tool.
Farmers began to buy contracts for future delivery. This purchase allowed them to:
- Lock in prices
and
- Mitigate the risk of adverse price movements.
On the other hand, speculators would take the opposite side of these trades by betting on price changes. This interplay between hedgers (e.g., farmers) and speculators gave rise to the concept of rollovers. As contracts neared their expiration dates, participants would need to shift their positions to maintain their market exposure without having to handle the physical commodity itself.
What is the Purpose of Rollovers?
The primary purpose of rollovers is to allow traders to maintain continuous exposure to an asset without taking delivery of the physical commodity. By rolling over their positions, traders can prolong their exposure to the asset without dealing with the logistical and financial challenges associated with the delivery and storage of the physical commodity.
This is particularly important in markets like crude oil, where physical delivery can be costly and impractical for most market participants. Let’s understand this concept better through an example involving “Crude Oil Futures Rollover”.
For the unaware, Crude oil futures contracts are usually traded monthly. This means that each contract represents a commitment to buy or sell a specific amount of crude oil at a predetermined price on a specified future date.
As the expiration date of the current month’s crude oil futures contract approaches, traders who wish to maintain their positions must transfer their contracts to the next month’s contract.
For example,
- Say a trader holds a contract for July delivery.
- Now, they will need to sell this contract and simultaneously buy a contract for August delivery as the expiration date of the July contract gets closer.
- This process ensures that the trader remains exposed to the price movements of crude oil without having to take delivery of the physical oil.
Similarly, let’s look at the quarterly ES (E-mini S&P 500) futures rollover. ES futures contracts expire quarterly, and traders transfer their positions from the expiring contract to the next quarter’s contract.
For example,
- As the March ES contract nears expiration, traders will:
- Sell their March contracts
and
- Buy June contracts to maintain their exposure to the S&P 500 index.
We can observe that in both cases, the rollover process enables traders to actively participate in the market and manage their risk without the need for physical settlement of the underlying assets. This way rollover contracts ensure liquidity and stability in the market.
Dynamics of Rollover Periods & Open Interest
Rollover periods are critical times in futures markets. That’s because they significantly impact:
- Open interest
and
- Market dynamics.
It is essential to note that during these periods, open interest in the expiring contract decreases while it increases in the new contract. Usually, this shift reflects traders’ transitions and signals:
- Broader market sentiment
and
- Future price directions.
Let’s understand in detail.
How Do Rollover Periods Impact Open Interest?
Open interest represents the total number of outstanding futures contracts that have not been settled.
During rollover periods, traders close their positions in the expiring contract and open new positions in the contract with a later expiration date. As a result, open interest in the expiring contract declines while it rises in the new contract. See the graphic below:
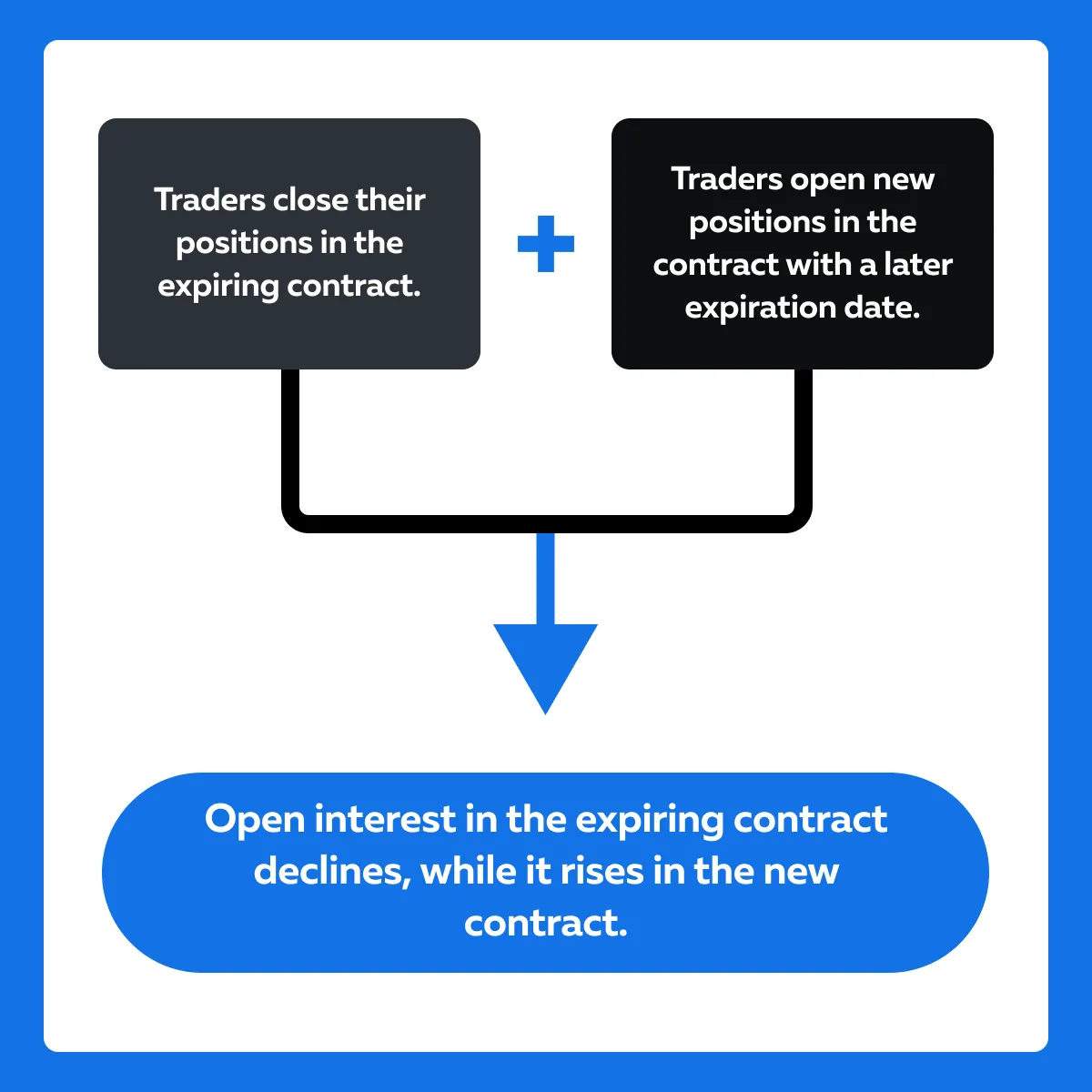
Now, let’s understand this “impact” better through a scenario involving agricultural commodities.
Consider an agricultural commodity, such as corn. As the June corn futures contract approaches expiration, traders begin to roll over their positions to the July contract. During this time, we might observe the following:
- Open Interest in June Contract: Decreases as traders close out their positions.
- Open Interest in July Contract: Increases sharply as traders establish new positions.
This pattern is often seen in agricultural markets where participants are keen to maintain their exposure due to:
- Seasonal factors,
- Weather conditions, and
- Other market-moving events.
A sharp rise in open interest in the new contract, in this case, the July contract, indicates the bullish outlook of traders on corn prices.
How to Interpret Shifts in Market Sentiment Using Roll-Over Periods?
Changes in open interest during rollover periods are a strong indicator of shifts in market sentiment. Let’s see how:
| Significant Increase in Open Interest in New Contract | Example |
|
or
|
How are Bullish Sentiment and Open Interest Related?
Let’s understand this relation through a situation where rising open interest in a new contract correlates with increasing bullish sentiment.
| Scenario | Outcome |
|
|
Key Strategies for Managing Rollover Periods
It is worth mentioning that effective management of rollover periods is important for traders. See the graphic below to understand how it helps:
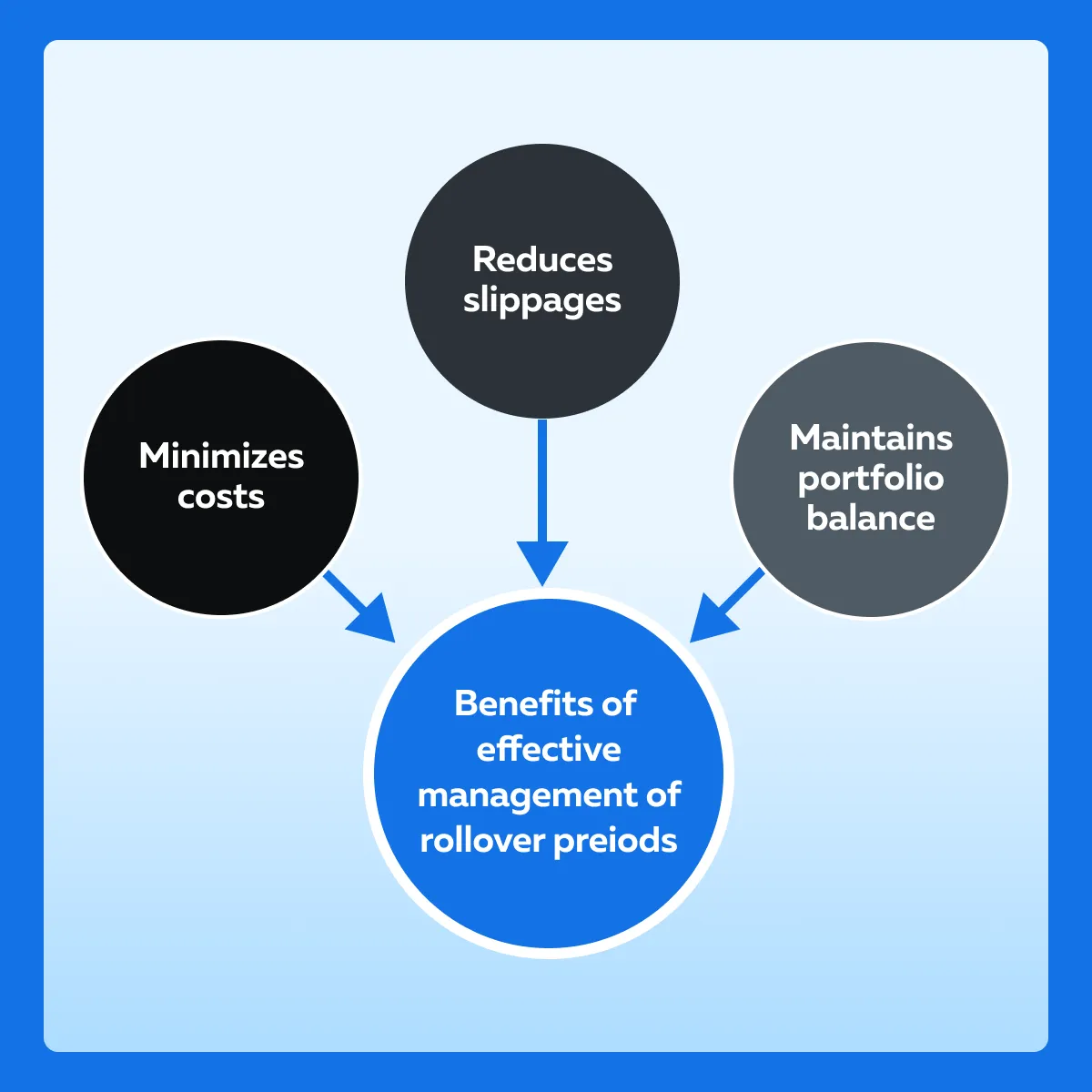
Traders can effectively manage the rollover period by:
- Timing the rollover
and
- Adjusting position sizes during these periods.
Let’s understand both these strategies in detail:
- A) How to Time the Rollover?
- Monitor Open Interest
- Track the open interest in both the expiring and new contracts.
- A decrease in the open interest of the expiring contract and a simultaneous increase in the open interest of the new contract indicate that the rollover process is in progress.
- Track Volume
- High trading volume in the new contract suggests increased liquidity.
- This is an optimal time for executing the rollover in order to minimize slippage.
- Spread Analysis
- Analyze the price spread between the
- Expiring contract
- Analyze the price spread between the
and
- New contract.
- A narrow spread indicates a favorable time to roll over.
- That’s because it minimizes the cost of transitioning between contracts.
- Timing
- Execute the rollover before the expiration date, which is usually within the last week of trading for the expiring contract.
- This helps avoid last-minute rushes and potential liquidity issues.
Let’s understand better through an example involving the rolling over of S&P 500 Futures:
- Say a trader observes that:
- Open interest in the expiring June S&P 500 futures contract is decreasing.
- While the open interest in the September contract is rising.
- Volume in the September contract has significantly increased, which indicates higher liquidity.
- The trader checks the price spread between the June and September contracts.
- Finding it narrow, the trader determines it’s a suitable time to execute the rollover.
- The trader sells the June contract and simultaneously buys the September contract.
- This way, they complete the rollover with minimal slippage and cost.
- B) How to Adjust Position Sizes?
- Risk Management
- Adjust position sizes to manage risk and maintain portfolio balance.
- Consider market volatility and potential changes in market conditions during the rollover period.
- Maintain Proportional Exposure:
- Ensure the new positions maintain the same proportional exposure to the market as the expiring positions.
- This helps in preserving the intended risk-reward profile of the portfolio.
Let’s understand better through an example:
- A trader notices that
- Open interest in the expiring crude oil futures contract is decreasing, while
- The new contract’s open interest is increasing sharply, indicating a bullish sentiment.
- The trader anticipates higher volatility due to geopolitical tensions impacting crude oil prices.
- To manage the risk, the trader decides to adjust the position size.
- The trader reduces the size of the new contract position by 10% to accommodate the increased volatility and potential risk.
- This adjustment helps in:
- Maintaining the overall portfolio balance
and
- Mitigating excessive risk.
- The trader sells the expiring contract and buys a smaller-sized new contract, aligning with the revised risk management strategy.
Analyzing Open Interest for Trading Decisions

Most traders use open interest data to identify the market. For the unaware, “open interest” represents the total number of outstanding futures contracts that are not yet settled. It provides insights into the strength and direction of market trends. Let’s explore how to interpret it:
| Increasing Open Interest in a Rising Market | Decreasing Open Interest in a Rising Market |
|
|
Let’s understand through an example how a trader identified a bullish trend using open interest data:
- Market Observation
-
-
- A trader is monitoring the wheat futures market.
- Over the past few weeks, the price of wheat has been steadily increasing.
-
- Analyzing Open Interest
-
-
- The trader observes that open interest in wheat futures has also been increasing alongside the rising prices.
- This suggests that new long positions are being established and reinforces the bullish trend.
-
- Trading Decision
-
- Based on the rising prices and increasing open interest, the trader concludes that the bullish trend is likely to continue.
- The trader decides to enter a long position in wheat futures to capitalize on the anticipated upward movement.
How to Visualize and Analyze Open Interest?
To gain a competitive advantage and precisely visualize the open interest, most traders prefer using analytical tools like Bookmap, which helps them visualize market data, including:
- Open interest
and
- Rollover data.
It provides a heatmap visualization of the order book and allows traders to see:
- Where liquidity is concentrated?
- How market participants are positioning themselves?
Let’s check out the modern features offered by Bookmap:
| Heatmaps | Volume and Price Analysis |
|
|
By using open interest data and advanced analytical tools like Bookmap, traders can identify and capitalize on bullish trends, as well as anticipate potential reversals.
Conclusion
For successful futures trading, it is critical to analyze rollover periods and open interest. Rollover periods allow traders to maintain continuous market exposure without taking delivery of the physical commodity. In contrast, open interest data provides insights into market trends and sentiment. By monitoring these factors, traders can time their rollovers to minimize costs and slippage, adjust position sizes, and manage risk effectively.
Additionally, by incorporating open interest analysis, traders can identify the strength and direction of trends, facilitating informed trading decisions. Advanced market analysis tools like Bookmap can further enhance this analysis by providing clear visualizations of market data.
Therefore, by paying attention to rollover periods and open interest, traders can perform better in the futures markets and increase their chances of trading success. To learn more about open interest, check out this article here.
FAQ
What is a rollover period in futures trading?
A rollover period refers to the time when traders shift their positions from a futures contract nearing expiration to a contract with a later expiration date. This allows them to maintain exposure to the asset without dealing with physical delivery. Rollovers are essential for continuous trading and are particularly common in markets like crude oil, agricultural commodities, and stock index futures.
How does open interest change during a rollover period?
During rollover periods, open interest in the expiring contract typically decreases while it increases in the next active contract. This shift reflects traders closing out positions in the old contract and opening new ones in the new contract. Monitoring open interest patterns during rollovers helps traders gauge market sentiment and potential price direction.
How can traders use rollover and open interest data to improve trading decisions?
By analyzing open interest trends during rollovers, traders can identify shifts in sentiment, such as growing bullish or bearish outlooks. Timing the rollover based on liquidity, adjusting position sizes based on volatility, and tracking open interest alongside price movements can help traders manage risk and strengthen trade setups.
What tools can help traders visualize open interest and rollover activity?
Advanced trading platforms like Bookmap offer powerful visualizations, including heatmaps and volume analysis tools. These allow traders to monitor changes in liquidity, spot shifts in open interest, and better understand how market participants are positioning themselves. Using such tools can provide a significant edge during rollover periods and beyond.
