20% Off Just for Blog Readers — Until July 31.
Use code BLOG20-JULY for 20% off your first month of Bookmap Only valid through July 31.
Futures
June 23, 2024
SHARE
What is Arbitrage Trading?
Profitable trading is about buying and selling at a better price, whether buying low and selling high, or buying high and selling higher (or vice versa for shorts).
Arbitrage trading, however, is slightly different. A strategy that seeks to profit from price differentials between related instruments, trades are typically quick and for small returns. If executed consistently and accurately, it can be one of the most profitable strategies around.
Theoretically, “arb” trading is riskless since the strategy takes advantage of market inefficiencies. However, the reality is that there is always risk in financial markets, as the great story of Long-Term Capital Management entails in Roger Lowenstein’s great book When Genius Failed.
Types of Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage can be categorised into four main types: pure arbitrage, merger arbitrage, statistical arbitrage, and convertible arbitrage.
Pure Arbitrage
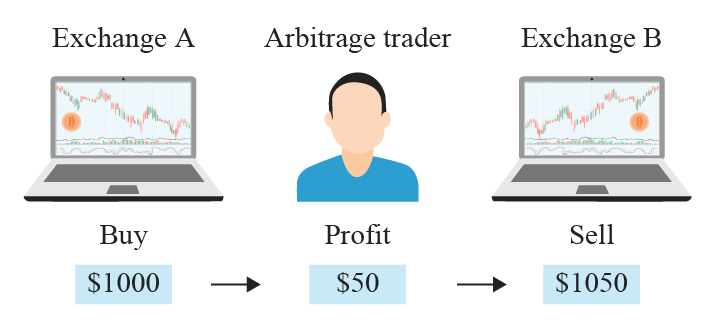
Pure arbitrage is what most people think of when talking about arbitrage trading. As a result, the phrases “arbitrage” and “pure arbitrage” are frequently interchanged. This is when a trader buys and sells an asset on two marketplaces or exchanges to capitalize on a price discrepancy.
Merger Arbitrage
Merger arbitrage is the sort of arbitrage that can be exploited when two publicly traded companies merge.
A merger involves two groups: the buying corporation and the targets. If the target company is a publicly listed corporation, the acquiring company must acquire the company’s outstanding shares. In most cases, this is at a premium to the stock’s current trading price, resulting in a profit for owners. As the transaction becomes public, traders seeking to profit from it buy the target company’s shares, bringing it closer to the offer price.
Convertible Arbitrage
Convertible arbitrage is a strategy that utilizes convertible bonds (also known as convertible notes or convertible debt). A convertible bond is fundamentally the same as any other bond: it is a business debt that pays interest to the bondholder. The only significant distinction between a convertible bond and a standard bond is that a convertible bond allows the bondholder to exchange it for stock of the underlying firm at a later period, sometimes at a reduced cost. Companies issue convertible bonds to provide reduced interest payments.
If the arb trader takes two simultaneous long and short positions in a convertible bond and its underlying stock, the trader is looking to profit from any movements in the market, assuming the hedge ratio is accurately calculated.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage (or stat arb) is essentially a mean reversion strategy that seeks to exploit correlations of thousands of assets in diverse portfolios. Since this strategy usually involves up to thousands of assets and is traded over very short timeframes, it is a highly quantitative strategy.
Like the other forms of arbitrage trading, stat arb is a market neutral strategy, meaning that delta of the strategy will be close to 0.
How Arbitrage Trading Works
Arbitrage trading operates because—despite the assumptions of most economic models—financial markets have inherent inefficiencies. Markets are a function of supply and demand, but sometimes things like excessive leverage or crowd behavior can lead to prices being pushed further away from any equilibrium or “fair” price.
Arbitrage Examples
Futures Spread Arbitrage
A futures spread requires taking two positions with different expiration dates. The two positions are traded as a single unit, with each side considered a “leg” of the unit trade.
There are different types of futures spread arbitrage, such as inter-commodity futures spread trades (where the trade is spread across two separate, but highly correlated commodities), as well as the more common intra-commodity calendar spread, whereby the trader takes positions spread across different expiration dates.
Public Company Merger Arbitrage
Merger arbitrage is the practice of trading equities in firms undergoing mergers. The most basic transactions include purchasing shares in the targeted firm at a discount to the acquisition price to sell them at a higher price once the deal is completed. However, betting on mergers is a tricky game with many pitfalls, and is often better left to the more connected hedge funds.
How Do HFTs Do Arbitrage Trading?
Organizations in the high frequency trading industry use a variety of trading tactics to make money. Arbitrage strategies include benchmark arbitrage, volatility arbitrage, statistical arbitrage, merger arbitrage, etc.
High-frequency trading enterprises rely on ultra-fast algorithms and direct connections to the exchanges.
Arbritarge: More Efficient Markets?
Arbitrage trading is one of the trading strategies that arguably makes financial markets more efficient, which is a good thing for everyone. Strategies like momentum and trend following are sometimes accused of pushing prices further away from equilibrium, potentially destabilizing markets under certain circumstances.
Since arbitrage trading is all about buying and selling identical or similar assets until their prices converge, it can be considered an aid in the price discovery process of financial markets overall.
Wrap-up
Arb trading is buying the same or similar instrument and looking to profit from (usually small) price differencials across markets. It can also be done across expiries of futures contracts on the same exchange.
One of the oldest and most popular forms of trading, arbitarge is considered risk-free, but it does come with its caveats. Maybe forms of arb trading can only be conducted by the bigger players such as hedge funds.
Even if you aren’t going to be implementing this method of trading in your strategy, it is still important to know about, since it is so widespread. Who knows, perhaps the person on the other side of your next trade will be arbing.
Bookmap comes with tools for making some of the above discussesd forms of arbitarge trading easier. For example, Multibook will show you the different prices of an instrument across multiple exchanges on a single chart. Try Bookmap for free today.