20% Off Just for Blog Readers — Until July 31.
Use code BLOG20-JULY for 20% off your first month of Bookmap Only valid through July 31.
Education
July 7, 2024
SHARE
What is Quantative Easing?
Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy tool used by central banks to stimulate economic growth by increasing the money supply. This is achieved through large-scale asset purchases, typically government bonds and other securities, which inject liquidity into the financial system. QE is often employed when interest rates are near zero and traditional monetary policy tools become ineffective.
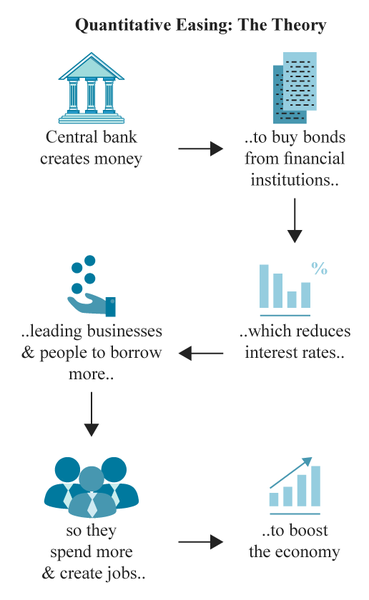
Image 1: Source
Banks can lend under more favorable conditions when interest rates are low. Because central banks use such methods as a last-resort, quantitative easing policies are often initiated when interest rates are already near zero.
To learn more about central banks in particular, have a read of our article What is a Central Bank? To learn more about QE in particular, read on.
Definition of Quantitative Easing
Quantitative easing is a strategy in which a central bank purchases long-term government securities or other assets to lower interest rates and encourage lending and investment. By increasing the amount of money circulating in the economy, QE aims to boost economic activity and prevent deflationary spirals.
How Does Quantitative Easing Work?
- Asset Purchases: The central bank buys government bonds or other financial assets from commercial banks and financial institutions.
- Increased Bank Reserves: The purchase injects money into the banking system, increasing reserves.
- Lower Interest Rates: As banks have more capital to lend, interest rates tend to decline.
- Encouraged Borrowing and Spending: Lower interest rates stimulate borrowing by businesses and consumers, leading to increased economic activity.
- Higher Asset Prices: With more liquidity in the system, investors turn to stocks and other assets, often driving prices higher.
Quantitative Easing vs. Fiscal Policy
Quantitative easing is a monetary policy tool implemented by central banks, whereas fiscal policy is controlled by the government. Fiscal policy involves government spending and tax adjustments to influence the economy. Unlike QE, which affects interest rates and liquidity, fiscal policy directly impacts demand through infrastructure projects, tax cuts, or direct stimulus payments.
Effects of Quantitative Easing on Financial Markets
Impact on Stocks
- QE often leads to increased stock prices as lower interest rates push investors toward equities for better returns.
- Corporations benefit from lower borrowing costs, enabling expansion and higher profits.
- Historical trends show stock market rallies during major QE programs, such as those initiated by the Federal Reserve post-2008 and during COVID-19.
Impact on the Housing Market
- Lower interest rates make mortgages cheaper, increasing home affordability and driving up housing demand.
- Asset price inflation can lead to housing bubbles, as seen in various economies following QE programs.
Impact on Currency and Inflation
- Currency Devaluation: An increased money supply can weaken the national currency, making exports more competitive but also increasing import costs.
- Inflationary Pressures: While QE aims to prevent deflation, excessive liquidity can lead to inflation, reducing purchasing power.
- Commodities Prices: Rising inflation often results in higher commodity prices, including oil and precious metals.
Impact on Cryptocurrency
- Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have been influenced by QE, with price surges linked to expansive monetary policies.
- The post-COVID-19 QE program saw Bitcoin reach all-time highs as investors viewed it as a hedge against inflation.
The History of Quantitative Easing
Quantitative Easing by the Federal Reserve
- 2008 Financial Crisis: The Federal Reserve introduced QE to stabilize financial markets, purchasing mortgage-backed securities and government bonds.
- 2010s Programs: QE2 and QE3 followed, expanding asset purchases and extending the program’s effects.
- COVID-19 Response: The Fed reintroduced QE, purchasing trillions in assets to prevent economic collapse.
Quantitative Easing by the Bank of England
- The Bank of England launched QE in 2009 to combat the Great Recession.
- Additional rounds of QE followed, with asset purchases increasing post-Brexit and during COVID-19.
Quantitative Easing During COVID-19
- Central banks worldwide used QE aggressively in response to pandemic-induced economic shutdowns.
- The Federal Reserve expanded its balance sheet by over $4 trillion between 2020-2021.
- The European Central Bank and Bank of England followed suit, implementing large-scale asset purchases.
Criticism of Quantitative Easing
Despite its benefits, QE has been met with significant criticism:
- Wealth Inequality: Asset purchases disproportionately benefit investors and asset holders, widening the wealth gap.
- Risk of Asset Bubbles: Prolonged QE can lead to unsustainable stock and real estate prices.
- Difficulty in Exit Strategy: Unwinding QE without destabilizing markets is a complex challenge.
- Diminished Effectiveness Over Time: Repeated QE rounds may reduce the policy’s impact as markets adjust expectations.
Quantitative Easing Alternatives
- Helicopter Money: Direct cash transfers to individuals to boost consumption.
- Yield Curve Control: Central banks cap interest rates at certain maturities to guide economic expectations.
- Fiscal Stimulus: Increased government spending to stimulate demand.
Future Predictions for Quantitative Easing
- Potential for Further QE: If economic downturns occur, central banks may resort to additional QE rounds.
- Shift Toward Digital Currencies: Central banks exploring digital currencies (CBDCs) may change monetary policy tools.
- Market Dependencies on QE: Some economists warn that financial markets have become overly reliant on central bank interventions.
Conclusion
Quantitative easing remains a powerful, yet controversial, tool in modern monetary policy. While it can stabilize economies in times of crisis, its long-term consequences, such as inflation, asset bubbles, and wealth disparities, continue to be debated. Understanding QE’s effects on financial markets, housing, currencies, and investment trends is essential for traders and investors navigating today’s economic landscape.
Did you know you can try Bookmap for free? Click here to get started.