Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Crypto
April 1, 2024
SHARE
How Blockchain Technology is Reshaping Financial Markets and Trading
Have you ever wondered how digital money works or how we can trade without banks? This article explores the world of blockchain – a modern technology – changing finance as we know it. From decentralized exchanges to tokenizing real estate, blockchain is revolutionizing how we buy, sell, and invest.
But it’s not just about money; it’s about making finance fairer and more accessible for everyone. In this article, we will explain blockchain technology in detail, delineating its advantages, key challenges, and discussing popular blockchain platforms. Let’s get started.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers. As one of its key attributes, this technology ensures the integrity and security of the data. Let’s understand the following fundamental components of this technology:
- Decentralized Ledger
-
-
- A blockchain is a distributed ledger.
- This ledger is not stored in any single location but exists across a network of computers (nodes).
- Each node maintains a copy of the ledger, and any new transactions are validated and added to the ledger through a consensus mechanism.
-
- Consensus Mechanisms
-
-
- These are protocols or rules that govern:
- How nodes agree on the validity of transactions and
- How they reach consensus about the state of the ledger.
- Examples of consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW),
- Proof of Stake (PoS), and
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
- These mechanisms ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions without the need for a central authority.
- These are protocols or rules that govern:
-
- Smart Contracts
-
-
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
- They automatically execute and enforce the terms of the agreement when predefined conditions are met.
- Smart contracts run on the blockchain and enable decentralized applications (DApps) to operate autonomously without the need for intermediaries.
-
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
-
-
- DLT refers to any system that enables the decentralized storage and management of data across a network of nodes.
- This technology ensures data integrity and immutability by recording transactions in a chronological and tamper-proof manner.
-
- Each new block of transactions is linked to the previous blocks in a chain.
-
- This linking makes it extremely difficult to alter past transactions without consensus from the majority of nodes in the network.
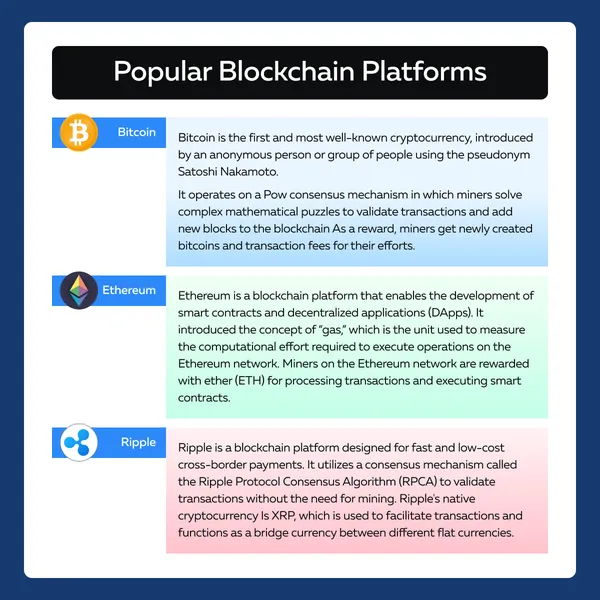
How Do Miners Earn Coins?
Most miners earn coins by processing the next block. The two major and most popular reward methods are described in the following table:
| Transaction Fees | Block Rewards |
|
a) A fixed number of newly created coins, and b) The transaction fees associated with the transactions in that block. |
Blockchain’s Impact on Financial Markets
Blockchain technology is significantly disrupting financial markets. It has completely revolutionized the way transactions are conducted by:
- Removing intermediaries,
- Reducing costs, and
- Improving efficiency.
All these effects majorly influence the financial markets. Let’s gain a deeper understanding:
- Removal of Intermediaries
-
-
- Traditionally, financial transactions involve multiple intermediaries, such as:
- Banks,
- Clearinghouses, and
- Payment processors.
- This involvement of multiple layers adds complexity, time, and costs to the process.
- Blockchain eliminates the need for these intermediaries by enabling peer-to-peer transactions.
- These peer-to-peer transactions allow individuals and businesses to transact directly with each other.
- Consequently, this disintermediation streamlines processes and reduces transaction fees.
- Traditionally, financial transactions involve multiple intermediaries, such as:
-
- Cost Reduction
-
-
- Blockchain technology reduces costs associated with financial transactions by
- Eliminating intermediaries and
- Automating processes.
- Additionally, blockchain-based solutions often operate on decentralized networks.
- This feature lowers infrastructure and operational costs compared to centralized systems.
- Blockchain technology reduces costs associated with financial transactions by
-
- Improved Efficiency
-
- Blockchain enables faster and more efficient settlement of financial transactions compared to traditional systems.
- Transactions on a blockchain are processed in real time or within minutes.
- This rapid processing eliminates the delays and inefficiencies associated with traditional settlement processes that can take days to complete.
- Consequently, faster processing enables:
- Quicker access to funds and
- Greater liquidity in financial markets.
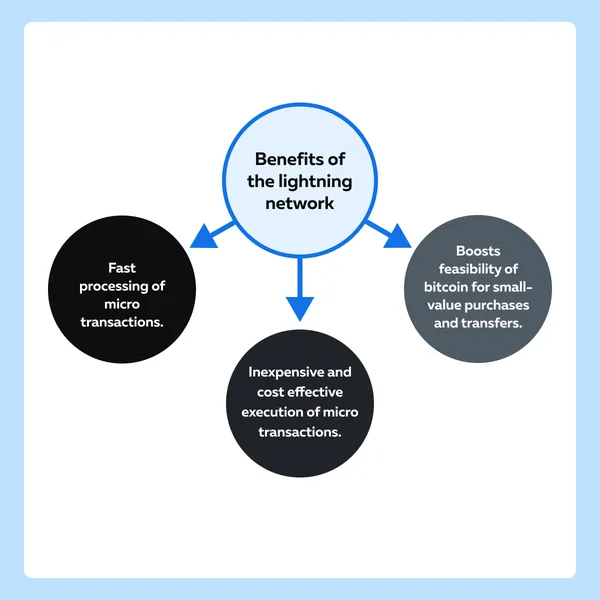
The Unique Case of El Salvador
El Salvador provides a unique example of blockchain adoption at a national level. In this country, Bitcoin (BTC) is recognized as legal tender.
Despite initial challenges and skepticism, El Salvador has embraced Bitcoin and is actively exploring innovative solutions to facilitate its use for everyday transactions. In this quest, it has developed a lightning network, which is a second-layer protocol built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain.
The Advantages of Blockchain-based Solutions
The blockchain-based solutions offer several advantages for clearing and settlement processes in financial markets. Let’s understand the two major advantages:
| Real-time Settlements | Smart Contract Automation |
a) Reduces counterparty risk and b) Improves liquidity in financial markets. |
|
The Many Benefits of Blockchain in Financial Markets
Blockchain technology is fundamentally reshaping financial markets by:
- Driving innovation,
- Improving efficiency,
- Fostering greater transparency, and
- Boosting trust in financial transactions.
It does so by providing:
- Transparent Record-keeping
-
-
- Blockchain maintains a transparent and immutable record of all transactions on a distributed ledger.
- This record remains accessible to all participants in the network.
- Such transparency reduces the risk of fraud and manipulation by providing a single source of truth for transaction data.
-
- Auditable Transactions
-
-
- Every transaction recorded on a blockchain is cryptographically secured and time-stamped.
- This recording provides an auditable trail of transactions, which can be further verified.
- An analysis of the transactions trail helps regulators, auditors, and stakeholders to verify the integrity and legitimacy of transactions.
-
- Trustless Transactions
-
-
- Blockchain technology enables trustless transactions.
-
- This means that parties can transact with each other without the need for trust or reliance on intermediaries.
-
- Also, the inherent security and transparency of blockchain networks ensure that transactions are executed securely and reliably.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Based on rapid technological advancements, blockchain technology streamlines financial processes and reduces operational costs across various sectors. Let’s see how:
| The Benefits of Blockchain Technology | Explanation |
| Payment Processing |
|
| Cross-Border Transactions |
a) Eliminating intermediaries and b) Reducing the time and cost associated with traditional remittance services.
|
| Trade Finance |
a) Letters of credit, b) Trade finance documentation, and c) Supply chain financing.
a) Streamlined trade finance processes and b) Reduced manual paperwork. |
The Visible Impact of DeFi
Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols are disrupting traditional banking services and lending practices. They are doing so by offering decentralized alternatives to traditional financial products and services. Let’s understand how DeFi is impacting traditional banking:
- Decentralized Lending
-
-
- DeFi platforms enable individuals to borrow and lend digital assets without the need for traditional financial intermediaries such as banks.
- These platforms use smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer lending and borrowing.
- Such a facilitation allows users to:
- Earn interest on their crypto assets or
- Access liquidity through collateralized loans.
- Additionally, DeFi lending protocols like Compound and Aave are offering competitive interest rates and flexible borrowing options.
- These protocols are actively attracting users looking for alternatives to traditional banking services.
-
- Tokenization of Assets
-
-
- DeFi protocols enable the tokenization of real-world assets, such as:
- Real estate,
- Stocks, and
- Commodities.
- This tokenization allows these assets to be traded and accessed on blockchain networks.
- Trading opens up new opportunities for:
- Fractional ownership,
- Liquidity provision, and
- Cross-border investment.
- Platforms like Uniswap and SushiSwap facilitate the decentralized trading of tokenized assets.
- This facilitation enables users to trade directly with each other without the need for centralized exchanges.
- DeFi protocols enable the tokenization of real-world assets, such as:
-
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
-
- DeFi platforms offer decentralized alternatives to centralized cryptocurrency exchanges.
- These platforms allow users to trade digital assets directly from their wallets without relying on intermediaries.
- DEXs use automated market-making algorithms and liquidity pools to enable peer-to-peer trading.
- Platforms like Uniswap, PancakeSwap, and SushiSwap have gained significant traction in the DeFi space, offering users:
- Low fees,
- High liquidity, and
- Greater control over their assets.
Transparency and Trust
Blockchain technology promotes transparency and trust in financial markets through its:
- Decentralized nature and
- Cryptographic security.
Let’s see how blockchain technology ensures the integrity and immutability of transaction records:
| Decentralization | Cryptographic Security |
a) Risk of fraud, b) Manipulation, and c) Censorship. |
a) hashing and b) digital signatures.
a) Integrity, b) Authenticity, and c) Trust in the financial system. |
How Blockchain Technology Combats Fraud and Corruption?
Blockchain technology promotes transparency and combats fraud and corruption. Let’s see how:
-
- Audit and Compliance:
- Blockchain enables transparent and auditable record-keeping.
- This systematic maintenance of records makes it easier for auditors and regulators to verify the accuracy and completeness of financial data.
- Auditors can access the blockchain to:
- Trace the flow of funds,
- Verify transaction details, and
- Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Blockchain enables transparent and auditable record-keeping.
- Audit and Compliance:
- Supply Chain Traceability:
-
-
- Blockchain facilitates supply chain traceability by recording the origin, movement, and ownership of goods and products on a transparent and immutable ledger.
- Companies can use blockchain to track the entire lifecycle of products, from raw materials to finished goods.
- Thus, blockchain-based supply chain solutions:
- Enhance transparency,
- Reduce counterfeiting, and
- Improve trust among supply chain participants.
-
- Identity Verification:
-
- Blockchain enables secure and verifiable identity management systems.
- These systems allow individuals to control and share their identity information without relying on centralized authorities.
- Blockchain-based identity solutions use cryptographic techniques to
- Authenticate users and
- Protect sensitive information.
What are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
NFTs are a type of smart contract. These represent unique digital assets on the blockchain. Let’s explore some popular use cases of NFT across different blockchain platforms:
| Types of NFTs | Explanation |
| VeChain (VET) |
|
| Ethereum (ETH) |
a) Digital artwork, b) Music, and c) Virtual real estate.
|
Understanding Public vs. Private Blockchains
Public and private blockchains have different implications for transparency and data privacy. Let’s understand both of them:
- Public Blockchains (such as Bitcoin and Ethereum)
-
-
- They are open and permissionless networks.
- Anyone can participate as a node and access the blockchain data.
- Public blockchains offer:
- High transparency and
- Censorship resistance.
- However, public blockchains may compromise data privacy as transaction details are visible to all participants.
-
- Private Blockchains
-
- Private blockchains, on the other hand, are permitted networks.
- In them, access to the blockchain data is restricted to authorized participants.
- Private blockchains offer greater control over:
- Data privacy and
- Confidentiality.
- However, they sacrifice transparency and decentralization compared to public blockchains.
- Private blockchains are commonly used in enterprise settings, where sensitive business data needs to be protected while still leveraging blockchain technology for efficiency and security.
Transforming Trading Practices

Blockchain technology is transforming trading practices and investment strategies by:
- Increasing access to global markets,
- Enabling fractional ownership,
- Enhancing liquidity,
- Ensuring transparency and security, and
- Reducing costs.
As blockchain adoption continues to grow, its impact on trading and investing is expected to deepen, leading to further innovation in the financial industry. Blockchain technology enables investors to access global markets seamlessly besides allowing investors to purchase and trade fractional shares of high-value assets, such as real estate, art, and stocks.
Also, blockchain provides transparency and security in trading practices by maintaining a decentralized and immutable ledger of transactions.
The Emergence of Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
The DEXs have emerged as innovative platforms that enable peer-to-peer trading of digital assets without intermediaries or central authorities. They operate on blockchain networks and provide several advantages over traditional centralized exchanges (CEXs), including increased security and user control. Let’s discuss some major advantages below:
- Security
-
-
- One of the key advantages of DEXs over CEXs is enhanced security.
- DEXs operate on decentralized networks, where transactions are executed directly between users’ wallets.
- There is no need for a central authority to hold custody of funds.
- This benefit eliminates the risk of:
- Centralized exchange hacks,
- Exit scams, or
- Insider manipulation.
- Since users retain control of their private keys and funds at all times, the risk of unauthorized access or theft is significantly reduced on DEXs.
-
- User Control
-
-
- DEXs offer users greater control over their assets and trading activities compared to CEXs.
- On DEXs, users have full control of their private keys and funds.
- They can execute trades directly from their wallets without the need to deposit funds onto the exchange platform.
- This benefit eliminates the risk of funds:
- Being frozen or
- Seized by the exchange operator.
- All the users on DEXs maintain ownership and control of their assets throughout the trading process.
- Additionally, DEXs typically do not require users to undergo lengthy KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures.
-
- Censorship Resistance
-
-
- DEXs are censorship-resistant platforms.
- These cannot be easily shut down or controlled by external authorities.
-
- Since DEXs operate on decentralized networks, there is no single point of failure and no central authority that can censor transactions or restrict access to the platform.
-
- This benefit makes DEXs particularly attractive to users in jurisdictions with strict financial regulations or censorship.
What is the Tokenization of Assets?
Tokenization refers to the process of representing real-world assets, such as real estate, stocks, commodities, or artwork, as digital tokens on a blockchain. These tokens are programmable, divisible, and can be traded or transferred easily on blockchain networks. Let’s understand two of its major benefits as explained in the given table:
| Fractional Ownership | Liquidity |
|
|
The ETH404 chain
The ETH404 chain is a relatively new blockchain platform. It introduces innovative mechanisms for:
- Fractional ownership and
- Asset tokenization.
The ETH404 chain interrelates fractional ownership with NFTs by allowing users to tokenize real-world assets and represent ownership stakes as NFTs. These NFTs can then be fractionally divided and traded on the ETH404 chain, enabling investors to buy and sell fractional shares of high-value assets.
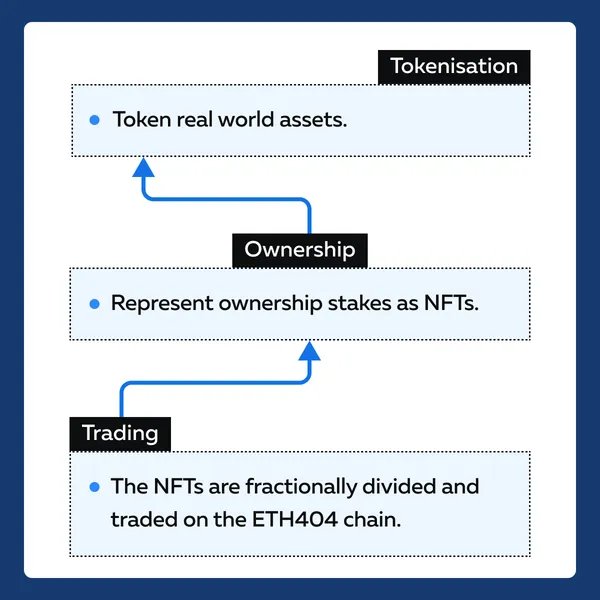
ETH404 follows a unique mechanism and represents unique and indivisible assets. It comes loaded with the advantages of fractional ownership and allows for greater accessibility and liquidity in investment opportunities.
Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) play a crucial role in facilitating peer-to-peer trading of digital assets by operating on blockchain networks without the need for intermediaries or centralized control. These exchanges offer:
- Censorship resistance,
- Transparency, and
- Financial autonomy.
Additionally, popular DEXs like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap provide users with efficient trading mechanisms and additional features, such as yield farming and liquidity provision. Let’s perform an in-depth analysis of DEXs and their role in the cryptocurrency ecosystem:
The Role of DEXs
DEXs enable users to trade cryptocurrencies and digital assets directly with each other without relying on a centralized intermediary. They operate on decentralized networks, allowing users to:
- Retain control of their funds and
- Trade assets securely and transparently.
DEXs utilize smart contracts and automated market-making algorithms to facilitate trades and ensure liquidity on the platform. These provide a censorship-resistant and permissionless environment for trading digital assets.
Comparison of Popular DEXs
| DEXs | Explanation |
| Uniswap |
a) Swap ERC-20 tokens directly from their wallets and b) Earn fees by providing liquidity to the platform.
|
| SushiSwap |
|
| PancakeSwap |
|
| Opensea |
|
Challenges Facing DEX Adoption
- Liquidity Concerns
-
-
- DEXs rely on liquidity providers to maintain sufficient liquidity in trading pairs.
- However, liquidity can be fragmented across different DEXs.
- This fragmentation leads to:
- Lower liquidity and
- Higher slippage for less popular tokens.
- Automated market makers (AMMs) help mitigate liquidity concerns but may still face challenges in maintaining optimal liquidity for all trading pairs.
-
- Regulatory Uncertainty
-
-
- Most often, DEXs face regulatory scrutiny or enforcement actions.
- This enhanced vigilance leads to restrictions or shutdowns in certain jurisdictions.
-
- User Experience
-
- User experience is a significant barrier to entry for DEX adoption.
- While DEXs offer decentralized and non-custodial trading, the user interface and onboarding process may be complex for beginners.
- Additionally, when trading on DEXs, users need to be mindful of:
- Gas fees,
- Slippage, and
- Impermanent loss.
Tokenization of Assets
Asset tokenization is the process of representing traditional assets, such as:
- Real estate,
- Art,
- Commodities, and
- Securities, as digital tokens on a blockchain.
These tokens are programmable, divisible, and can be traded or transferred easily on blockchain networks. Asset tokenization helps in the following:
- Digitizing ownership,
- Increasing liquidity, and
- Expanding investment opportunities.
Some Common Tokenized Assets
| Tokenized Assets | Explanation |
| Real Estate |
|
| Art |
|
| Commodities |
|
What are Some Benefits of Asset Tokenization?
- Fractional Ownership
-
-
- Asset tokenization allows for fractional ownership of high-value assets.
- It democratizes access to investment opportunities.
- It allows investors to purchase and trade fractional shares of assets.
- Such fractional trading promotes diversification and reduces barriers to entry for individual investors.
-
- Increased Liquidity
-
-
- Tokenized assets can be traded 24/7 on blockchain-based platforms.
- This enhanced trading improves liquidity in traditionally illiquid markets.
- By facilitating secondary market trading, asset tokenization improves:
- Price discovery and
- Market efficiency.
-
- Automated Compliance
-
- Smart contracts can be used to automate compliance with regulatory requirements, such as:
- Know Your Customer (KYC) and
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
- Tokenized assets enforce compliance rules programmatically and reduce administrative burden.
- Smart contracts can be used to automate compliance with regulatory requirements, such as:
Challenges and Considerations

Efficient integration of blockchain technology into financial markets and trading practices requires addressing several issues such as scalability, regulatory hurdles, interoperability challenges, and much more. Let’s understand them in depth as explained in the table below:
| Scalability Issues | Regulatory Hurdles | Interoperability Challenges |
a) Sharding, b) Layer-2, and c) Protocol upgrades. |
|
a) Cross-chain bridges and b) Interoperability protocols. |
Additionally, privacy and data security are paramount considerations in blockchain implementations, especially in financial markets, where sensitive financial data is involved.
While blockchain offers transparency and immutability, ensuring data privacy and confidentiality is essential to protecting user information and preventing unauthorized access or data breaches. Privacy-enhancing technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs and secure multi-party computation can help address privacy concerns in blockchain implementations.
Governance issues such as centralization of decision-making power, conflicts of interest, and lack of transparency also impact the stability and trustworthiness of blockchain networks. Thus, transparent and inclusive governance mechanisms should be established to ensure the long-term sustainability and decentralization of blockchain networks.
The Role of Vampire or Sandwich Bots and Slippage
Vampire or sandwich bots are automated trading algorithms that exploit price discrepancies and liquidity imbalances across decentralized exchanges (DEXs). These bots mine available liquidity by:
- Front-running trades and
- Arbitraging fractional differences across liquidity pools.
These tactics lead to slippage and reduced profitability for retail traders. Let’s understand the modus operandi with a hypothetical example:
What happened? – The Event
- Suppose a trader wants to buy 1 Ethereum (ETH) using a decentralized exchange like Uniswap.
- They checked the current market price of ETH and saw that it was $2,000.
- However, when they went to execute their trade on Uniswap, they noticed that the price had suddenly increased to $2,050.
- This unexpected price movement is known as slippage.
Why did it happen? – The Cause
- This sudden surge in price was caused due to the operations of vampire/sandwich bots.
- These bots exploited price discrepancies and liquidity imbalances on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap.
How did it happen? – The Process
- Before you execute your trade, vampire or sandwich bots detect your intention to buy ETH.
- They quickly place their buy orders ahead of yours, causing the price of ETH to increase before your trade is executed.
- By front-running your trade, these bots can profit from the price increase at your expense.
- Additionally, vampire or sandwich bots monitor liquidity pools on Uniswap and other DEXs for any discrepancies in prices.
- If they detect a lower price for ETH on one liquidity pool compared to another, they exploit this difference by:
- Buying ETH at a lower price and
- Selling it at a higher price.
What have we got to learn? – The Outcome
- As a result of the activities of vampires or sandwich bots, the price of ETH on Uniswap was higher than expected when the traders went to execute their trade.
- This caused slippage, and the trader ended up paying a higher price for ETH than what was initially anticipated.
- So, the presence of these bots exacerbates slippage and reduces profitability for retail traders.
What is “jared from subway.eth,”?
The vampire or sandwich bots are named after notable figures or humorous aliases like “jared from subway.eth,”. During the rise of certain assets or meme coins like PEPE, these bots become particularly active and take advantage of:
- Heightened volatility and
- Trading volumes to execute profitable trades.
In the case of “jared from subway.eth”, these bots reportedly made 50 ETH every few hours.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has significantly transformed financial markets and trading. It offers numerous benefits, such as enhanced accessibility, transparency, and efficiency. Through blockchain, financial processes have become more accessible and affordable for everyone.
It records transactions in a secure and immutable ledger, thereby boosting transparency and trust. This technology has democratized access to financial services, allowing individuals from all backgrounds to participate in trading and investing.
As blockchain continues to evolve, it will further streamline financial operations and promote inclusivity in the global economy. Dive deeper into the conversation about blockchain, smart money, and trading volume with an experienced trader by clicking here.
