Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
August 12, 2024
SHARE
The Big Short Exposed: Lessons from Market Cheating and Real-Life Trading Scenarios
 One day, you noticed a heavily shorted stock suddenly surging. As the price surged, short sellers quickly bought shares to cover their positions, creating a feedback loop that pushed the price even higher. In the end, the short sellers faced significant losses. How often have you noticed such a scenario while trading in financial markets? This scenario represents the situation of a “short squeeze,” a phenomenon that drastically impacts stock prices and traders.
One day, you noticed a heavily shorted stock suddenly surging. As the price surged, short sellers quickly bought shares to cover their positions, creating a feedback loop that pushed the price even higher. In the end, the short sellers faced significant losses. How often have you noticed such a scenario while trading in financial markets? This scenario represents the situation of a “short squeeze,” a phenomenon that drastically impacts stock prices and traders.
In this article, we will understand what a short squeeze is and discuss its effects on short sellers by highlighting real-life examples like the GameStop and AMC events of 2021. You’ll learn how these squeezes occur and how they force short sellers to cover their positions at higher prices, often leading to massive losses for hedge funds.
Additionally, we will study some common market manipulation tactics through various scenes depicted in the movie The Big Short. Commonly, these tactics include spreading misleading information and delaying important financial reports, which can distort market prices. Moreover, we will analyze the regulatory failures shown in the movie and the reforms that followed, such as the Dodd-Frank Act. Let’s begin.
What is Short Selling?
Short selling is a trading strategy. Following it, an investor:
- Borrows shares of a stock,
- Sells them on the open market. and
- Buys them back when the price goes down.
This practice is used when the investor anticipates that the stock’s price will decline, which allows them to profit from the difference. For more clarity, let’s understand the process of short selling in detail:
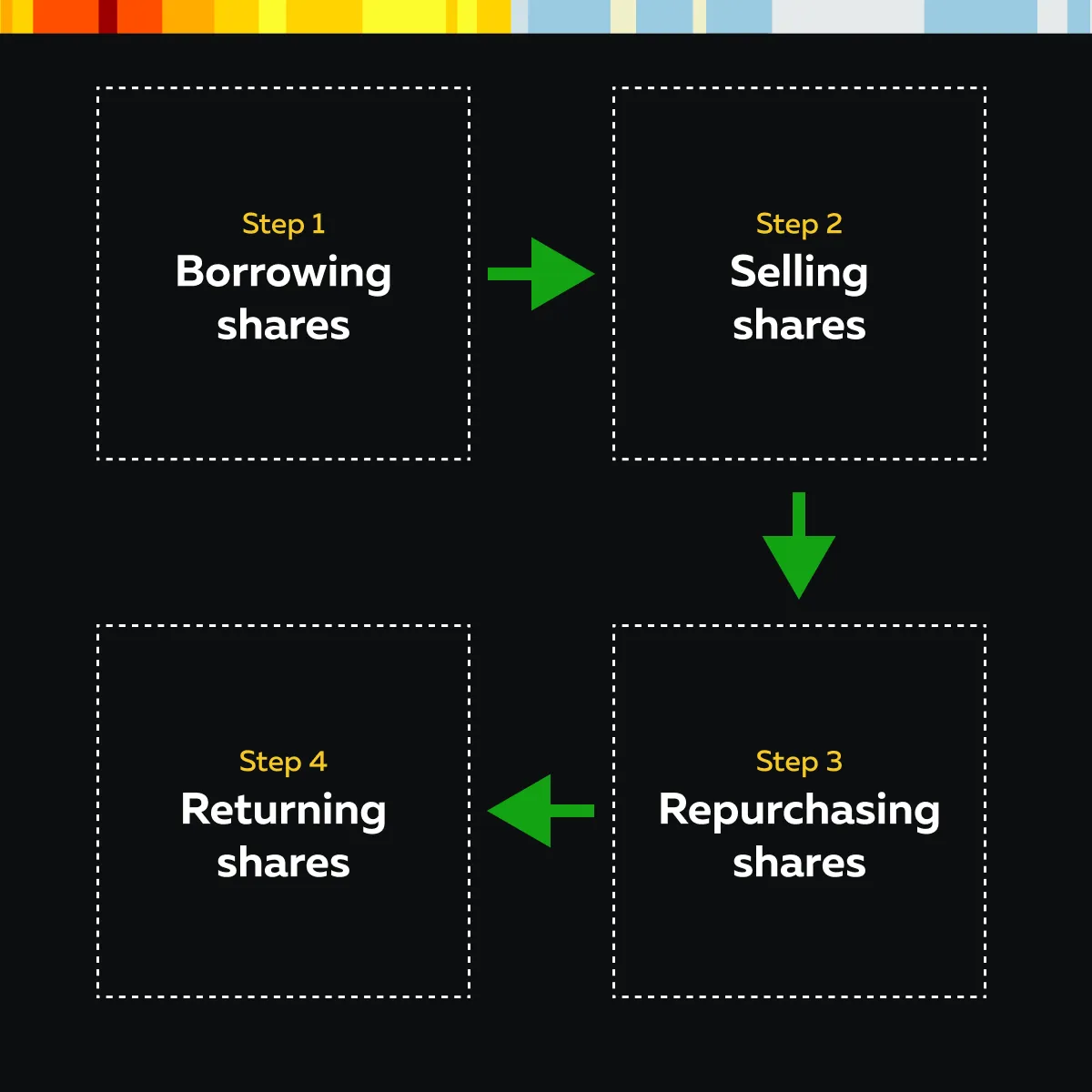
What is the Process of Short Selling?
- Borrowing Shares:
- The investor borrows shares from a broker.
- These shares mostly come from:
- The broker’s own inventory,
- Another client, or
- Another brokerage firm.
- Selling Shares:
- The borrowed shares are sold on the open market at the current market price.
- Repurchasing Shares:
- The investor waits for the stock price to decrease.
- Once the price drops, the investor buys the same number of shares at a lower price.
- Returning Shares:
- The repurchased shares are returned to the broker.
- This completes the transaction.
- The difference between the selling price and the repurchase price (minus any borrowing costs and fees) is the investor’s profit.
Example of a Short-Selling Transaction
Alex believes that the stock of Company XYZ, currently priced at $100 per share, will decline soon. He decides to proceed with a short-selling transaction:
- Alex borrows 100 shares of Company XYZ from their broker.
- Alex sells the borrowed 100 shares at $100 each, receiving $10,000.
- After 3 hours, the price of Company XYZ’s shares falls to $90 per share.
- Alex buys back 100 shares at $90 each, spending $9,000.
- Alex returns the 100 shares to the broker.
By doing so, Alex earns a profit of $1,000 in the following manner:
- Selling price: $10,000
- Repurchasing price: $9,000
- Profit: $10,000 – $9,000 = $1,000 (excluding borrowing costs and fees)
The Cheating Depicted in The Big Short
The Big Short is a 2015 film directed by Adam McKay. The movie is based on the non-fiction book by Michael Lewis. It offers a gripping portrayal of the 2008 financial crisis by focusing on:
- The build-up of the housing bubble
and
- The eventual market collapse
Besides, the film follows several finance professionals who predict the crisis and decide to bet against the market to profit from the impending disaster. The movie also highlights the following issues:
- The irresponsible behavior of banks,
- The negligence of regulatory bodies, and
- The widespread fraud within the financial industry led to the crisis.
It shows how the housing market was inflated by risky mortgages, which were packaged into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and given high ratings by credit agencies despite their poor quality. For more clarity, let’s take a look at some specific scenes highlighting cheating and market manipulation:
Michael Burry’s Struggle with Banks
Michael Burry, played by Christian Bale, discovers the housing market bubble and decides to bet against it by purchasing credit default swaps (CDS). Despite his accurate prediction of the market collapse, he faces resistance from banks.
Banks resist marking the value of the CDS to reflect the rising risk of mortgage defaults. Instead, they continue to demand monthly premiums from Burry. The banks refuse to acknowledge the increased risk in their valuations. This manipulation prevents Burry from profiting until the collapse is undeniable.
Mark Baum’s Revelation at the Conference
Mark Baum, portrayed by Steve Carell, attends the American Securitization Forum in Las Vegas, where he discovers the true extent of the fraud in mortgage-backed securities. He learns that the mortgage bonds are filled with subprime loans that are bound to default, yet they are still being sold as high-grade investments.
Baum’s encounter with a clueless mortgage banker reveals how lenders were giving loans to anyone, regardless of their ability to repay, contributing to the crisis.
The Florida Housing Market Investigation
Charlie Geller and Jamie Shipley, played by John Magaro and Finn Wittrock, travel to Florida to investigate the housing market and see the bubble firsthand.
They find entire neighborhoods filled with foreclosed homes. They meet mortgage brokers who brag about their unethical practices, such as selling multiple loans to unqualified buyers. This scene clearly shows how the pursuit of profits led to reckless lending practices and contributed to the inflation of the housing bubble. Synthetic CDOs and the Meeting with Georgia Hale
Jared Vennett, played by Ryan Gosling, explains synthetic collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) to Mark Baum and his team. Vennett reveals how banks created synthetic CDOs, which were essentially bets on the performance of other CDOs.
This effectively multiplied the risk and potential losses within the financial system. Baum’s meeting with Georgia Hale further uncovers the blatant disregard for risk management and ethical standards in the pursuit of short-term profits.
Getting Squeezed: The Short Squeeze Phenomenon
A short squeeze occurs when a stock with a high level of short interest (a significant number of shares sold short) experiences a rapid increase in its price. This rapid surge forces short sellers to buy shares to cover their positions. This buying activity, in turn, drives up the stock price even higher, creating a feedback loop that amplifies the price increase.
For the unaware, short sellers are investors who bet against a stock by borrowing shares and selling them. Usually, they expect to buy the shares back at a lower price to make a profit. However, when the price rises sharply instead, short sellers face potentially unlimited losses because they must repurchase the stock at a higher price.
How Does a Short Squeeze Impact Short Sellers?
The impact of a short squeeze on short sellers can be severe. They can incur substantial losses as they are forced to buy back shares at inflated prices. Furthermore:
- Brokers may issue margin calls, requiring short sellers to deposit additional funds or securities to cover potential losses, which can lead to further selling.
- The frantic buying by short sellers contributes to increased volatility and unpredictable stock price movements.
- Short squeezes shift market sentiment as dramatic price increases attract more buyers and speculative trading.
For better comprehension, let’s check out some real-life cases of short squeezes.
Real-Life Instances of Short Squeezes
Case I: The GameStop Rally of 2021
The GameStop short squeeze in January 2021 is one of the most notable examples. GameStop, a brick-and-mortar video game retailer, was heavily shorted by hedge funds, with short interest exceeding 100% of its float. Investors believed the company’s business model was outdated and its stock was expected to decline. Here’s how the event unfolded:
- Reddit’s Role
-
- A group of retail investors on the Reddit forum r/WallStreetBets identified the high short interest and began buying GameStop shares.
- Their goal was to trigger a short squeeze and profit from the subsequent price surge.
- Rapid Price Increase
- The concerted buying effort led to a dramatic increase in GameStop’s stock price.
- This increase occurred from around $20 in early January to an intraday high of $483 on January 28, 2021.
- The Dilemma of Short Sellers
- Hedge funds with large short positions, such as Melvin Capital, faced massive losses.
- They were forced to buy back shares at significantly higher prices to cover their positions, which further fueled the price surge.
- The Impact
- The GameStop rally had widespread implications.
- It led to increased scrutiny of short-selling practices and market manipulation.
- It started debates over the role of retail investors in the stock market.
Case II: AMC Entertainment

AMC Entertainment, a movie theatre chain, experienced a similar short squeeze around the same time as GameStop. Following the success of the GameStop squeeze, retail investors turned their attention to AMC. They drove up its stock price from around $2 in January 2021 to over $20 by the end of the month. This made AMC another heavily shorted stock, with investors betting against the company due to financial struggles exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
As AMC’s stock price soared, short sellers scrambled to cover their positions, which further increased the price. AMC reached a peak of $72.62 on June 2, 2021. Such a rally led to huge losses for hedge funds with significant short positions in AMC. Moreover, it led to increased scrutiny of short-selling strategies.
Real-Life Trading Scenarios and Lessons
Market manipulation involves deliberately influencing the price or volume of a security. The primary goal of such manipulation is to create a false or misleading appearance of trading activity. Several common tactics used in real life are:

For more clarity, let’s check out some case studies related to banks and market manipulations:
In the movie The Big Short, several banks were depicted as engaging in deceptive practices. Eventually, these practices contributed to the 2008 financial crisis. Some similar tactics have been observed in real life, such as:
| Misleading Ratings | Hidden Risks |
|
|
Furthermore, the 2008 financial crisis exposed significant regulatory failures. It led to substantial reforms aimed at:
- Enhancing market transparency
and
- Reducing manipulation.
When it comes to The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the organization failed to identify:
- The risks associated with mortgage-backed securities
and
- The practices of credit rating agencies
This lack of oversight allowed the proliferation of toxic assets and the eventual market collapse. Therefore, in response to the crisis, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act was enacted in 2010. Some of the key provisions of this act include:
- Enhanced Transparency
- The act introduced stricter regulations on financial disclosures and transparency.
- These regulations ensure investors have access to accurate information.
- Volcker Rule
- This rule restricts banks from engaging in proprietary trading and limits their investments in hedge funds and private equity.
- It specifically aims to reduce risky speculative activities.
- Consumer Protection
- The creation of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) aims to protect consumers from abusive financial practices and ensure fair treatment.
Some lessons learned
From the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent reforms, investors can learn several key lessons, such as:
- Accurate and timely information is crucial for fair and efficient markets.
- Regulatory bodies must ensure transparency in financial reporting and disclosure.
- Regular observing and adjusting regulations are essential. This helps in:
- Keeping pace with evolving financial markets and
- Prevent manipulation.
- Educating investors about the risks and tactics of market manipulation can help them avoid falling victim to deceptive practices.
Trading Strategies to Avoid Getting Squeezed
To avoid getting squeezed, traders must manage risks in short selling. Traders can do so, by following several strategies, as explained in the table below:
| Technique | Explanation | Strategy |
| Setting Stop-Loss Orders | A stop-loss order is an automatic order to buy back the shorted stock if it reaches a certain price. This technique limits potential losses. |
|
| Diversifying Positions | Diversification involves spreading your investments across various assets to reduce risk. |
|
| Buying Call Options | A call option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy a stock at a specified price within a certain period. |
|
| Protective Put Options | A put option gives the holder the right to sell a stock at a specified price within a certain period. |
|
How to Identify Red Flags of Market Manipulation and Short Squeeze Scenarios?
To spot market manipulation and short squeeze scenarios, traders can look for unusual trading volumes. These unusual spikes in trading volume indicate that a stock is being heavily traded. Usually, this event is a precursor to a short squeeze. While monitoring trading volumes, if you notice a significant increase without corresponding news or events, it may signal that other traders are attempting to drive up the price.
Additionally, a sudden and rapid increase in a stock’s price can indicate a short squeeze. In such a situation, short sellers rush to cover their positions, which further drives up the price. As a strategy, keep an eye on the stock’s price movements. If you see a rapid rise, consider closing your short position or tightening your stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
Practical Example of Hedging with Options
To better understand the concept of “hedging with options,” study this hypothetical example. Say you have shorted 100 shares of Company ABC at $200 per share (you were anticipating a price drop). Now, to hedge your position:
- You purchased a call option with a strike price of $210 for $5 per option.
- If the stock price rises to $250, the call option’s value will offset the losses from your short position.
- Alternatively, you can buy put options on a correlated but not identical stock or index.
- If your short position faces a squeeze, the gains from the put options can partially or wholly offset the losses.
Case Study: Learning from Real-Life Events
The GameStop short squeeze is one of the most notable and recent examples of a short squeeze. This event precisely shows the:
- Power of retail investors
and
- Impact of social media on the stock market.
For more clarity, let’s have a look at the timeline of key events:
- Early 2020
- GameStop, a struggling video game retailer, sees its stock price hovering around $4 per share.
- This happened due to declining sales and the pandemic’s impact on brick-and-mortar stores.
- Mid-2020
- Michael Burry of The Big Short fame discloses a significant long position in GameStop.
- He argues that the stock is undervalued.
- August 2020
- Ryan Cohen, co-founder of Chewy, announces a substantial stake in GameStop.
- By doing so, he fuels optimism about the company’s future.
- December 2020
- GameStop’s stock starts gaining attention on Reddit’s r/WallStreetBets (WSB) community.
- Here, users notice the high short interest in the stock.
- January 2021:
- January 11: Ryan Cohen joins GameStop’s board. This sparked further enthusiasm.
- January 13-19: The stock price surges from $20 to $40 as retail investors on WSB rally to buy shares and options.
- January 22: GameStop’s stock closes at $65. This attracts media attention and more retail investors.
- January 25-29:
- The stock price skyrockets, peaking at $483 on January 28.
- The massive buying pressure forces short sellers to cover their positions.
- This event further drives up the price in a classic short squeeze.
- February 2021
- The stock price stabilizes but remains volatile.
- It fluctuates between $50 and $100 as retail and institutional investors continue to battle.
How did this event impact short sellers?
Short sellers, including prominent hedge funds like Melvin Capital, face significant losses. Melvin Capital reportedly loses over 50% of its assets in January alone due to its large short position in GameStop. Moreover, several short sellers are forced to cover their positions at much higher prices. This situation leads to substantial financial damage and liquidations.
The Aftermath:
| Market Volatility | Regulatory Scrutiny | Retail Investor Empowerment |
| The GameStop saga highlights the potential for extreme volatility in the stock market, particularly with the influence of retail investors and social media. | The event prompts scrutiny from regulators and policymakers. This led to discussions about:
|
The episode underscores the growing influence of retail investors and the power of collective action. Some similar movements were also observed in other heavily shorted stocks. |
How Traders Could Have Better Prepared or Mitigated the Impact?
- Traders should have kept an eye on social media platforms and forums for unusual activity or discussions about specific stocks.
- Be aware that early detection of coordinated buying efforts could provide a warning.
- Short sellers could have diversified their positions to avoid overexposure to any single stock.
- Diversification should have been preferred as it reduces the risk of significant losses from a short squeeze in one stock.
- Stop-loss orders should have been implemented to limit losses if a stock’s price rises rapidly.
- Short sellers could have used call options to hedge their positions.
Conclusion
The Big Short and several real-life trading scenarios teach us valuable lessons about market dynamics and the risks of short selling. The movie clearly illustrates how misleading information and delayed reporting can manipulate market prices. Eventually, this led to massive financial crises. It also highlights regulatory failures and the importance of reforms like the Dodd-Frank Act.
For traders, these insights are crucial. It’s important to stay informed, understand the risks, and be vigilant against market manipulation. Learning from past events also helps traders develop better strategies and avoid the negative effects of short selling. Hence, always verify the information before making investment decisions and be aware of the potential for short squeezes, as it can lead to significant losses.
By applying these lessons, traders can better manage the market and protect their investments. Additionally, staying updated on regulatory changes and market trends is important to respond to risks promptly.
For more detailed strategies on short selling, check out this guide: How to Profit from a Falling Market with Short Selling.