Education
January 10, 2024
SHARE
Understanding Arbitrage: How Traders Profit from Market Inefficiencies
In the world of financial markets, it is common to observe disparities in prices across exchanges, time zones, and financial instruments. For some traders, these inefficiencies become pathways to profit.
Arbitrage is a strategic maneuver that offers an opportunity to exploit temporal disparities in valuations. Following this practice, several quick-witted traders often leverage technology, algorithms, and strategic finesse to exploit market inefficiencies.
In this article, we will first begin with the evolution of arbitrage and gradually understand the strategies that turn price differentials into golden opportunities. Let’s get started.
Understanding Arbitrage Across Markets
Arbitrage, often referred to as statistical arbitrage or stat trading, is a sophisticated financial strategy that capitalizes on price differentials. These inefficiencies exist in several markets, including cryptocurrency, forex, stocks, and commodities. Let’s begin with the crypto market.
What is Crypto Market Arbitrage?
The cryptocurrency market is infamously known for its volatility. These swift price variations create arbitrage opportunities, prompting most arbitrageurs to exploit price differentials. Several factors contribute to these disparities:
- Different levels of trading activity: Some exchanges have higher trading volumes than others, which leads to more efficient price discovery and lower spreads. Conversely, some exchanges have lower trading volumes, which results in price lags and wider spreads.
- Different levels of liquidity: Liquidity varies across different crypto exchanges. A lack of liquidity on a particular exchange leads to wider bid-ask spreads, providing arbitrage opportunities.
- Different geographical locations: The crypto market is global and decentralized, which means that there are no central authorities or regulators that control the prices. Therefore, the prices of cryptocurrencies may vary depending on the location, demand, and supply of each exchange.
Let’s understand better using a hypothetical example.
The Research
Based on thorough analysis, a trader conducted a detailed analysis and found a significant price gap in Bitcoin between two exchanges operating in different regions. The trader collected the following data and presented it in a table:
| Aspects | Stock Exchange A | Stock Exchange B |
| Trading Volume/ Demand | High | Low |
| Price | Increasing at a significant rate | Increasing at a normal rate |
The Action
- The trader swiftly bought Bitcoin on Exchange B at a lower price.
- They simultaneously sold it on Exchange A at a higher price.
- This resulted in a quick and profitable arbitrage trade.
What is Forex Market Arbitrage?
Forex (foreign exchange) arbitrage is a strategy that takes advantage of price differences for the same currency pair on different exchanges or markets. The basic idea is to exploit inconsistencies in exchange rates to generate profits. One of its most important concepts is triangular arbitrage, which involves three currency pairs.
Triangular Arbitrage
This technique works by taking advantage of discrepancies between the cross rates of three different currency pairs that share a common currency. For instance, if there’s a discrepancy between the direct exchange rates of USD/EUR and USD/GBP, a trader can perform triangular arbitrage using EUR/GBP.
Let’s elaborate on this example using a hypothetical scenario.
The Rates
- Direct Rates:
- USD/EUR = 0.85
- USD/GBP = 0.75
- Calculate Cross Rates:
- EUR/GBP = 1USD/EUR x USD/GBP
- EUR/GBP = 10.85 x 0.75=0.8824
The Discrepancy
It must be noted that if the actual market rate for EUR/GBP is higher than 0.8824, an arbitrage opportunity exists.
The Arbitrage Execution
- Buy GBP with USD at a better rate
- Convert GBP to EUR at a more favorable rate
- Convert EUR back to USD at the initial rate
The Profit
The resulting profit is the difference between the starting and ending USD amounts.
How Important is Rapid Execution and Cost Considerations?
In the highly liquid forex market, timing is crucial for successful arbitrage. Prices can change rapidly, and delays in execution may lead to missed opportunities or reduced profits. Additionally, traders must be aware of transaction costs, which can erode arbitrage profits. These costs include:
- Spreads (the difference between buying and selling prices) and,
- Any fees associated with trading.
Given the tight spreads in the forex market, traders need to factor in these costs to accurately assess the profitability of an arbitrage opportunity.
Arbitrage in Stock and Commodity Markets
Arbitrage strategies are not limited to forex and cryptocurrencies. They also play a significant role in stock markets. Here, opportunities arise through various financial instruments, such as:
- ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) and Index funds:
- These investment vehicles track the performance of a specific index or sector.
- Usually, price discrepancies arise between the ETF or index fund and the underlying assets.
- Traders exploit these arbitrage opportunities by simultaneously buying and selling.
- Futures Contracts:
- Arbitrage in stock markets also involves futures contracts.
- Arbitrageurs exploit price disparities between the current stock price and the futures price.
- They buy the underlying stock while simultaneously selling the equivalent futures contract (or vice versa) to capture the price differential.
Commodity Arbitrage Across Global Markets
Not only stocks, but arbitrage opportunities also exist in commodity markets. Let’s understand using a hypothetical scenario involving gold:
The Price Discrepancy
| In the New York Market | In the London Market | |
| Price of Gold (per ounce) | $1,800 | $1,780 |
Transport Costs and Time Delays
-
- Traders can take advantage of the $20 per ounce price difference between London and New York gold markets by buying gold in London and selling it in New York.
- However, transport costs and time delays need to be factored in.
- Transporting physical commodities involves expenses and takes time, during which market conditions may change.
Arbitrage Execution
The traders need to calculate whether the potential profit from the price difference:
- Covers the transport costs and,
- Compensates for any potential price changes during transit.
Risk Mitigation
- To mitigate risk, traders use financial instruments like futures contracts.
- These instruments establish a hedge against potential losses due to price fluctuations during transportation.
The Final Action
The trader exploited the available arbitrage opportunity by taking the following actions:
| Action 1: Buy Futures Contract in London | Action 2: Sell Futures Contract in New York |
| To secure a future delivery of gold at the current lower price in London, the trader initiated a buy position in a futures contract. | The trader also sold an equivalent futures contract in the New York market, where the price is higher. |
The Role of Technology in Arbitrage Trading
From manual tracking to automated algorithms, arbitrage trading has come a long way. The integration of technology has significantly enhanced speed, accuracy, and efficiency. The evolution of arbitrage software has been instrumental in the success of modern traders. Let’s understand in-depth.
The Evolution of Arbitrage Software
Understand the evolution through the table below:
| What are the benefits of evolution? | How did arbitrage happen in the early days? | How does arbitrage happen now? |
| Increased Automation and Speed |
|
|
| Cross-Exchange Bots in Cryptocurrencies |
|
|
| Integrated Analysis Platforms in Forex |
|
|
Automation and Algorithmic Arbitrage
The evolution of algorithmic trading has made the arbitrage process more efficient and responsive. Algorithmic arbitrage strategies enable the following:
What are the Different Algorithmic Trading Strategies?
Currently, there are multiple arbitrage processes. Each one of them is tailored to exploit specific market inefficiencies efficiently. Let’s see notable algorithmic trading strategies and understand their benefits as well as potential pitfalls.
| Algorithmic Trading Strategy | What does the Strategy do? | What is the Pitfall? |
| Statistical Arbitrage |
|
|
| Pairs Trading |
|
|
| Latency Arbitrage |
|
|
How Important is Backtesting in Algorithmic Arbitrage?
Markets evolve, and backtesting helps traders adapt algorithms to changing conditions. It plays a crucial role in refining algorithms to prevent unintended exploitation of market inefficiencies. It helps identify scenarios where the algorithm may perform sub-optimally.
Additionally, backtesting allows traders to integrate risk management strategies into algorithms. This integration ensures that the automated system:
- Considers potential downsides and
- Operates within predefined risk parameters
Let’s understand the importance of backtesting taking the example of latency arbitrage.
- Backtesting involves applying the algorithm to historical market data to assess its performance.
- It helps traders:
- Refine the algorithm by identifying potential pitfalls and
- Ensuring that it reacts appropriately to varying market conditions.
Arbitrage Strategy & Execution
Developing a successful arbitrage strategy requires a comprehensive approach. By carefully developing and executing your arbitrage strategy while prioritizing risk management, increase the likelihood of achieving consistent profits. Let’s understand how you can make your arbitrage strategy.
Creating an Arbitrage Strategy
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Perform Market Research:
- Identify potential arbitrage opportunities by:
- Analyzing historical price data and
- Monitoring current market conditions
- Focus on markets where price discrepancies are likely to occur.
- Considering multiple factors such as:
- Liquidity
- Trading volumes, and
- Geographical influences.
Step 2: Risk Assessment:
- Evaluate the potential risks associated with identified arbitrage opportunities, including:
- Slippage
- Execution risk, and
- Counterparty risk
- Determine the risk tolerance for each trade
- Establish clear risk management parameters.
Step 3: Tool Selection:
- Choose appropriate tools, such as algorithmic trading software or platforms.
- The selection must be based on the type of arbitrage strategy you plan to implement.
- Ensure that selected tools provide:
- Real-time market data
- Execution capabilities, and
- Risk management features.
Step 4: Set Up Alerts:
- Implement alerts to notify you of potential arbitrage opportunities.
- These alerts should be based on predefined criteria, such as:
- Percentage price differences or
- Specific market conditions.
Step 5: Optimal Size and Speed of Trades:
- Calculate the optimal size of trades based on risk tolerance and available capital.
- Consider the speed at which trades need to be executed to capitalize on arbitrage opportunities,
- Take into account market conditions and latency considerations.
Execute an Arbitrage Trade
Executing an arbitrage trade requires precision timing and a clear understanding of order types. Here’s how you can do it:
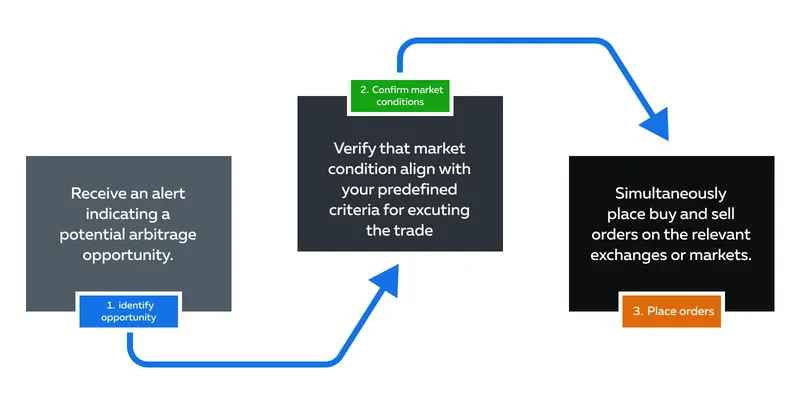
Important Points to Consider:
- Execute trades with precision timing to minimize the impact of market fluctuations.
- Monitor the execution of orders in real time.
- Ensure that the arbitrage strategy is being implemented as intended.
- If market conditions change rapidly, be prepared to adjust or cancel orders as needed.
Risk Management in Arbitrage
Effective risk management is crucial in arbitrage strategies. Read the table below to understand popular strategies:
| Risk Management Strategies | Meaning |
| Slippage | Set slippage limits to control the maximum acceptable deviation between expected and actual execution prices. |
| Execution Risk |
|
| Counterparty Risk | Assess and mitigate counterparty risk by choosing reputable exchanges or counterparties for your trades. |
| Diversification | Diversify across different assets or markets to reduce the impact of adverse events on a single trade. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Regularly reassess market conditions and adjust risk management parameters accordingly. |
Conclusion
Arbitrage, whether in crypto, forex, or other markets, continues to present lucrative opportunities for traders. The dynamic nature of these markets, coupled with the integration of advanced technologies, has changed the way arbitrage trading is performed.
Traders who combine a thorough understanding of market dynamics with the benefits of technology can seize opportunities and maintain profitability. However, traders must always remember that markets evolve and unforeseen events can impact prices.
Successful arbitrage requires continuous monitoring, adaptation of strategies, and a disciplined approach to risk management. Discover more strategies and in-depth analyses by exploring our definitive guide on ‘What is Arbitrage Trading’.