Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
June 26, 2025
SHARE
When the Fed Goes Political: How Past Chairmen Shaped Inflation (and Market Trust)
The Fed is the world’s most powerful central bank! But what if its power gets undermined? What if it gets caught between politics and policy? Veteran traders who understand the Fed’s credibility history know that when political pressure on the Fed rises, market volatility often follows.
So, should you avoid trading during Fed announcements? Never! It is one of the best times to take advantage of profitable trading opportunities. Want to learn how? In this article, we’ll first study key historical examples (from Arthur Burns’ controversial rate cuts under Nixon to Jerome Powell’s delicate balancing act during the 2021 inflation surge).
Next, you’ll learn how politically influenced decisions can lead to inflation spikes, bond market turbulence, and reduced market confidence. Also, we will check out some practical strategies for spotting early signs of Fed policy shifts. Lastly, you will learn how to use our modern market analysis tool, Bookmap, to track real-time liquidity changes and gain a valuable trading edge.
Let’s get started.
Why Political Independence Matters for the Fed
Political pressure can make institutions crumble! The Federal Reserve’s credibility relies heavily on its ability to make decisions without being swayed by political pressure. It usually backfires when political leaders push the Fed to keep interest rates low to boost economic growth (generally happens before elections).
Why? That’s because while lower rates might stimulate spending in the short term, they can also cause long-term inflation.
Now, if the Fed chairmen yield to political pressure and prioritize short-term gains over long-term stability, they risk losing credibility. Due to this loss of credibility, there are “higher risk premiums” as investors demand more returns for taking on perceived risks. Let’s see how this situation hurts the economy:
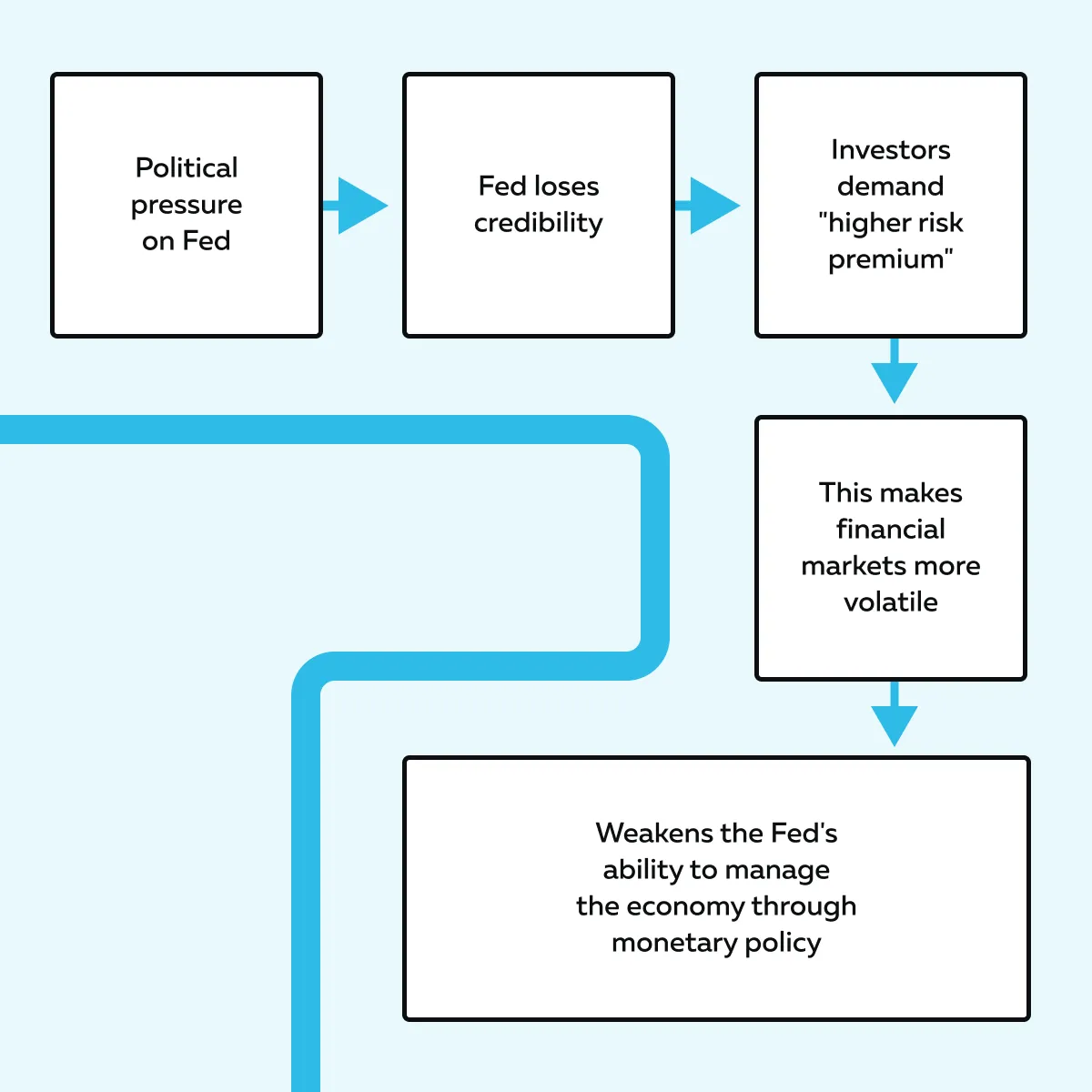
Thus, we can say that the Fed’s independence is highly important for maintaining:
- Stable inflation
and
- Strong monetary control.
When political pressure on the Fed increases, it compromises the central bank’s credibility, ultimately harming the economy. Want to see how markets react to policy uncertainty? Track real-time volatility with Bookmap.
Key Historical Examples of Politically Influenced Fed Decisions
The political pressure on the Fed is not a new concept! Throughout its history, the Federal Reserve has made controversial monetary policy decisions due to political pressure. These decisions influenced both inflation and the Fed’s credibility.
Let’s check out some popular examples:
Arthur Burns (1970–1978): Inflation Fueled by Political Compliance

Arthur Burns served as Federal Reserve chairman from 1970 to 1978. His tenure is a well-known example of how political pressure on the Fed can undermine economic stability.
Before the 1972 election, President Nixon urged Burns to keep interest rates low to boost the economy. Despite clear signs of rising inflation, Burns complied. He maintained a loose monetary policy.
This politically driven decision backfired! The prolonged period of low interest rates led to excessive spending. As a result, inflation surged throughout the 1970s. Later, the situation even worsened and led to stagflation. For the unaware, it is a period of high inflation combined with stagnant economic growth.
The credibility of the Fed was severely damaged during Burns’ tenure. Nixon’s recorded conversations revealed direct political interference. It was confirmed that Nixon was pressuring Burns to support his economic agenda.
Paul Volcker (1979–1987): Breaking the Cycle at Political Cost

Paul Volcker became Federal Reserve chairman in 1979. He took over after the turbulent periods under Arthur Burns and G. William Miller (both of whom struggled with inflation). Unlike his predecessors, Volcker made the tough decision to aggressively raise interest rates to combat soaring inflation, despite knowing it would cause short-term economic pain.
His bold actions triggered a severe recession. It pushed unemployment higher and drew intense political backlash. Many politicians criticized Volcker for causing widespread economic hardship. However, he refused to give in to political pressure. Instead, he focused solely on:
- Restoring the Federal Reserve’s credibility
and
- Curbing inflation.
Volcker’s commitment paid off! By maintaining his course, he successfully reanchored inflation expectations. He proved that a determined Fed chairman could restore economic stability (even at a significant political cost).
This episode became a defining moment in the Fed’s credibility history. You can observe from this example that enduring short-term pain can lead to long-term economic stability.
Alan Greenspan (Late 1990s–2000s): Independence Blurred by Market Accommodation

Alan Greenspan was one of the most influential Federal Reserve chairmen. He is often credited with managing economic crises effectively. However, his actions during the early 2000s raised concerns about the Fed’s independence.
After the 2001 recession, Greenspan kept interest rates exceptionally low for an extended period. Critics argue that this dovish stance favored an easy monetary policy and created excessively loose credit conditions. Political pressure on the Fed was not explicitly present during his tenure. However, market expectations likely influenced Greenspan’s decisions.
Now, let’s understand what this prolonged period of low rates led to through the graphic below:

Greenspan’s tenure shows that even perceived market-driven decisions can blur the line between:
- Independent monetary policy
and
- Market accommodation.
Although he intended to stabilize the economy, the long-term consequences clearly show the risks of maintaining low rates for too long.
Jerome Powell (2018–Present): Modern Pressure in a Political Spotlight

Jerome Powell became the Federal Reserve chairman in 2018. He stepped into a highly politicized environment. Early in his term, Powell raised interest rates to prevent the economy from overheating. However, this drew direct criticism from President Trump, who publicly pressured Powell to keep rates low.
From 2018 to 2019, Powell faced intense political pressure on the Fed. However, he initially resisted and maintained the rate hikes. In 2019, the Fed reversed course. It paused and eventually started cutting rates. The rationale for the rate cuts was global economic risks.
Powell’s stand? He stated that the decisions were data-driven. However, some critics speculated that political pressure influenced the timing.
Later in 2021, the Federal Reserve said the rising inflation would only be temporary or short-lived (transitory). However, many people now believe that this view caused the Fed to wait too long before:
- Raising interest rates
or
As inflation, measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), kept rising rapidly, people started to doubt the Fed’s ability to control it. Critics say the Fed didn’t fully realize how serious inflation was, which made the rise even worse.
What Happens When the Fed Breaks With Policy Discipline
Please note that when the Federal Reserve deviates from its established policy discipline, the consequences usually extend far beyond just hyperinflation. Even if inflation doesn’t spiral out of control, the Fed’s credibility can suffer! This may result in various adverse effects, including:
1. Bond Market Volatility
Investors lose confidence in the Fed’s ability to control inflation. It leads to unpredictable bond yields. If the Fed is seen as inconsistent, bond traders will start demanding higher yields to compensate for increased risk, causing market volatility.
2. Currency Weakness
If the Fed’s credibility is in question, foreign investors may lose confidence in the US dollar. This will cause it to weaken. A weaker dollar can increase import costs and further increase inflation.
3. De-anchoring of Inflation Expectations:
When the Fed signals mixed messages, businesses and consumers start to expect higher inflation. This leads to:
- Higher wage demands
and
- Price increases.
4. Start front-running the Fed
Additionally, traders may also start to front-run the Fed. They will start making investment decisions based on anticipated policy changes rather than actual data. This behavior again undermines the Fed’s monetary control, as markets begin to move based on speculation rather than fundamentals.
A modern example occurred in 2021–2022 when some investors questioned Powell’s dovish stance. They stated that this stance was more influenced by fear of market stress than by actual economic data. Such a perception weakened confidence in the Fed’s ability to tighten policy without causing economic harm.
Understand how inflation shocks unfold—use Bookmap to follow live futures flows.
Why This Matters for Traders Today
The Federal Reserve is the driver of market movements, particularly in:
- Futures,
- Bonds, and
- Foreign exchange (FX) markets.
When the Fed makes a policy move, it usually ripples through these markets. It also impacts both prices and investor behavior.
Even today, political pressure on the Fed still exists! Though it’s often more subtle than in the past. Let’s see where this pressure can come from:
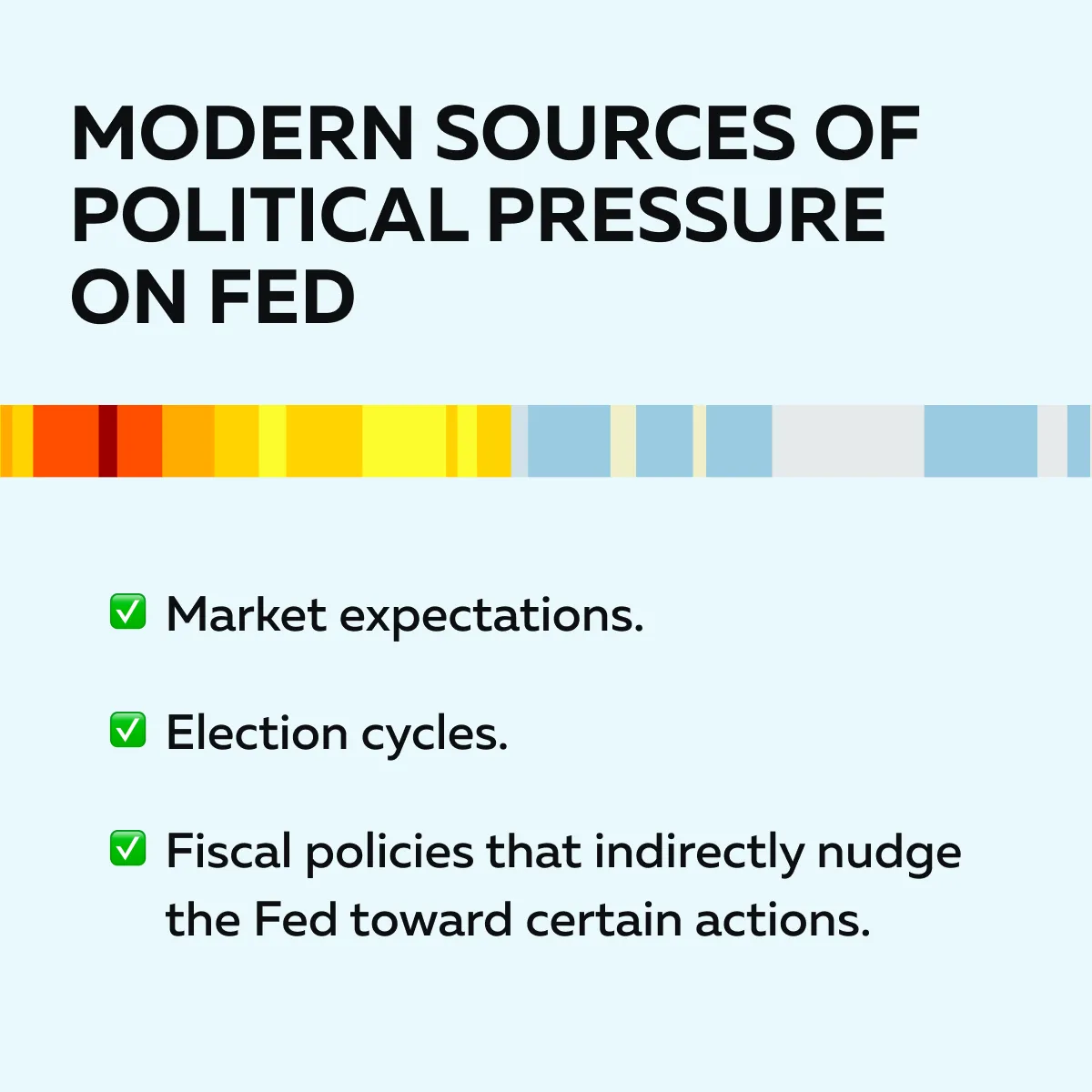
Prepare for macro shifts with real-time liquidity insight—explore Bookmap’s tools.
Why does this matter for traders?
As a trader, you should watch carefully for hints that show the Federal Reserve is making decisions based on
- Political pressure or events (like elections or government actions)
instead of
- Focusing purely on real economic numbers.
That’s because if politics rather than data influence the Fed decisions, it could cause unexpected market reactions, which you must be ready for. Below are three key indicators you should watch for:
| Sudden Policy Pivots | Softened Forward Guidance | Verbal Contradictions |
|
or
|
|
Level Up Your Trading Game with Bookmap!

By using our avant-garde real-time market analysis tool, Bookmap, you can track real-time liquidity around key Fed events, such as:
- FOMC meetings
or
- Major policy speeches.
Also, using our advanced market analysis tool, Bookmap, you can learn about the market sentiment. It shows how traders are positioning based on perceived Fed credibility or policy direction. For more clarity, let’s study how you can practically use our modern real-time market analysis tool, Bookmap:
| Signal to Watch | What It Indicates | Impact on Markets | How It Appears on Our Bookmap |
| Sudden Policy Changes | Political influence | Increased volatility in bonds and FX. |
|
| Softened Guidance | Uncertainty about future policy | Traders adjust rate hike expectations. |
|
| Verbal Contradictions | Confusion about the Fed’s stance | Market distrust and likely sell-offs. |
|
By observing these patterns on our advanced market analysis tool, Bookmap, you can spot:
- Early signs of market uncertainty
or
- Shifts in sentiment related to Fed credibility.
Conclusion
History demonstrates that when there is political pressure on the Fed, the consequences are severe! Usually, it leads to rising inflation, shaken market confidence, and heightened volatility.
From Arthur Burns’ accommodative stance under Nixon to Jerome Powell’s perceived dovishness during the 2021 inflation surge, the pattern is clear – when politics overrides economic data, traders should take notice!
During these times, you, as a trader, must recognize early signs of policy divergence. This gives you a trading edge. But how? You can start using a modern real-time market analysis tool, Bookmap. Using it, you can understand how institutions are positioning themselves around key Fed events.
So, the secret? Stay vigilant for major macroeconomic announcements and understand how policy decisions impact market sentiment. This will let you trade profitably and effectively in volatile periods. Want more insights? Visit the Bookmap’s Learning Center for strategies on trading during policy shifts.
FAQ
1. What does it mean for the Fed to be politically independent?
The Federal Reserve is politically independent when it makes monetary policy decisions based solely on economic data. It does not get influenced by political agendas or election timing. Also, it does not crumble under the pressure of government leaders who are only looking for short-term economic boosts.
When politically independent, the Fed can better control inflation and unemployment. This allows it to maintain strong:
- Economic stability
and
- Credibility.
2. Who was the most politically influenced Fed chair?
Arthur Burns is often seen as the most politically influenced Fed chairman. In the early 1970s, he kept interest rates low under President Nixon despite clear signs of rising inflation. This decision was mainly due to political pressure to boost the economy before the 1972 election. It even contributed to the stagflation crisis of the 1970s.
3. Has modern Fed policy been influenced by politics?
It is not as obvious as it was in the past! However, some argue that recent Fed decisions, particularly in 2021, were influenced by political or market pressure. Critics say the Fed was too slow to raise rates despite rising inflation. This stance was possibly due to concerns about triggering a:
- Market downturn
or
- Economic instability.
4. How can traders track credibility shifts in real-time?
As a trader, you can begin utilizing our real-time market analysis tool, Bookmap. Using it, you can monitor:
- Real-time volume
and
- Liquidity shifts during major Fed announcements.
If markets react sharply or move unexpectedly, it signals that traders doubt the Fed’s policy intentions or credibility. Using this valuable insight, you can predict the likely market shifts.
