Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Trading Basics
April 8, 2024
SHARE
6 Behavioral Economics Principles Every Trader Should Know
Human psychology influences decision-making in financial markets and can decide how successful your trading outcome will be. It is where the utility of behavioral economics principles and theories comes into play as they help create a more realistic picture of the economy.
Through this article, we will understand the relevance of behavioral economics and some common cognitive biases such as anchoring bias, confirmation bias, and overconfidence bias. Through real-life examples and case studies, we will illustrate how these biases have influenced trading outcomes in the past. Next, you will learn some practical strategies for recognizing and mitigating cognitive biases in trading.
Also, we’ll see how traders can incorporate behavioral economics principles into their trading strategies and use stop-loss orders, rule-based trading systems, and sentiment analysis tools to interrupt automatic thinking patterns. Let’s begin.
The Power of Behavioral Economics in Trading
Behavioral economics helps traders understand:
- Market behavior and
- Decision-making processes in trading.
It assumes that human behavior is susceptible to emotions and outside influences which is why they often end up making irrational decisions. Contrarily, traditional economic theory assumes that market participants are rational and always make decisions that maximize their utility. Let us read some stark differences below:
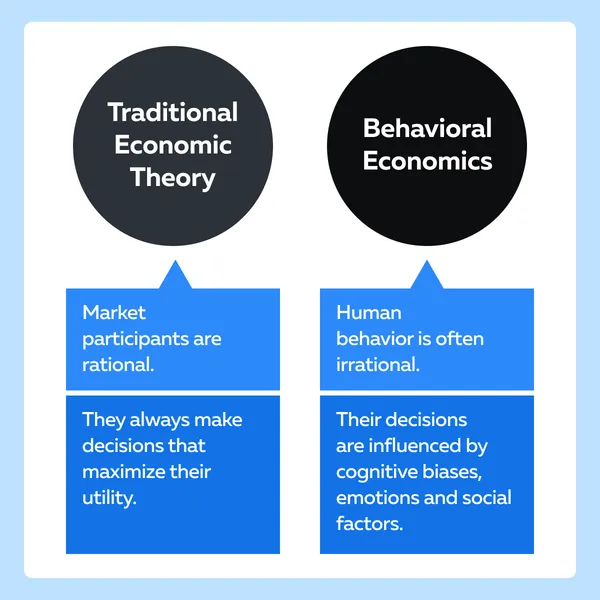
Why is Behavioral Economics Relevant in Trading?
Behavioral economics studies various biases that affect decision-making, such as:
- Loss aversion,
- Overconfidence, and
- Anchoring.
Also, it identifies market anomalies that cannot be explained by traditional economic theories. Besides, behavioral economics-
- Examines how individuals perceive and respond to risk,
- Explains how individuals often follow the crowd, which leads to herding behavior in financial markets,
- Acknowledges the impact of emotions on trading behavior, and
- Emphasizes the importance of emotional discipline. Traders who can control their emotions are better equipped to make rational decisions and avoid impulsive actions that can lead to losses.
How do Cognitive Biases and Heuristics Influence Traders’ Actions?
Cognitive biases are shortcuts or mental rules of thumb, which traders use to make quick decisions. However, they can lead to systematic errors in judgment. Let’s see how they impact trading:
- Overconfidence
-
-
- Traders often overestimate their abilities and the accuracy of their predictions.
- This bias leads to taking on excessive risk or holding onto losing positions for too long,
- They believe that the market will eventually turn in their favor.
-
- Loss Aversion
-
-
- Loss aversion refers to the tendency for individuals to prefer avoiding losses over acquiring equivalent gains.
- Traders become overly cautious and reluctant to realize losses.
- It leads to missed opportunities or holding onto losing positions longer than necessary.
-
- Anchoring
-
-
- Anchoring occurs when individuals rely too heavily on:
- Initial information or
- Reference points when making decisions.
- Traders anchor their decisions to past prices or arbitrary levels.
- This leads them to underestimate or overestimate the true value of an asset.
- Anchoring occurs when individuals rely too heavily on:
-
- Herding Behavior
-
- Herding behavior refers to traders’ tendency to follow the actions of the crowd rather than making independent judgments.
- Traders buy or sell assets based on the behavior of others.
- This creates momentum in the market and amplifies price movements.
Some Real-life Examples
Let’s study some real-life examples and understand how behavioral economics principles have affected trading outcomes:
| Event | Explanation | Trader’s Action |
| Dot-com Bubble |
|
|
| 2008 Financial Crisis | The 2008 financial crisis was fueled by excessive risk-taking and overconfidence in the housing market. |
|
| Bitcoin Bubble | The rapid rise and subsequent crash of Bitcoin prices in 2017 exemplified the impact of:
|
|
Traditional Economic vs. Behavioral Economics

Now, let’s take a look at the 6 behavioral economics principles that every trader should know:
Anchoring Bias
Anchoring bias is a cognitive bias. Following it, individuals rely too heavily on a specific piece of information, often the first one they encounter, when making decisions. In trading, anchoring bias significantly impacts traders’ perceptions of market value by making them focus on certain reference points (such as past prices or analyst recommendations).
How Anchoring Bias Leads Traders to Misinterpret and Make Suboptimal Decisions
Anchoring bias makes traders disregard new information that contradicts their anchored value, resulting in suboptimal decision-making. In most cases, traders anchor their valuation of a stock to its previous high price, even when the company’s fundamentals have changed significantly since that time.
For Example,
- A stock was previously trading at $100 per share and has since dropped to $50 per share.
- Traders anchored to the $100 price.
- They perceived the $50 price as a bargain without checking if the fundamentals justify the current valuation.
Similarly, if an analyst issues a price target of $150 per share for Company Y based on outdated information, traders anchored to this target may buy or sell the stock based solely on the analyst’s recommendation without conducting their analysis.
How to Overcome Anchoring Bias
| Use Multiple Valuation Metrics | Seek Diverse Sources of Information |
Instead of relying solely on past prices or single valuation metrics, traders can use a variety of indicators, such as:
|
To avoid fixating on a single reference point, traders should gather information from a diverse range of sources, including:
|
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion is a cognitive bias where individuals prefer to avoid losses rather than acquire equivalent gains. In trading, loss aversion influences traders’ risk preferences by causing them to experience the pain of losses more intensely than the pleasure of gains. This bias leads to:
- Irrational decision-making and
- Affect trading outcomes significantly.
How Loss Aversion Results in Irrational Decision-making
Traders who are loss-averse tend to be more risk-averse. They prefer to avoid potential losses even if it means sacrificing potential gains. Loss aversion can lead traders to hold onto losing positions for too long, hoping that the market will reverse, and they can avoid realizing the loss.
Conversely, loss aversion prompts traders to sell winning positions prematurely to secure profits. Following it, most traders fear that the gains will erode if they continue to hold the position.
Let’s understand this through a hypothetical example:
- A trader purchased shares of Company A at $50 per share.
- The stock price subsequently dropped to $40 per share.
- Instead of selling and cutting losses, the trader holds onto the position.
- They hope for a rebound despite mounting evidence of further decline.
How to Mitigate Loss Aversion
- Set Predetermined Stop-Loss Levels
-
-
- Establish specific price levels.
- At this level, automatically sell a position to limit potential losses.
- This removes the emotional aspect of decision-making and ensures that losses are kept within a predetermined tolerance.
-
- Diversify the Portfolio
-
-
- Reduce losses on the overall portfolio by spreading investments across different:
- Asset classes,
- Sectors, and
- Securities.
- Diversification helps mitigate the fear of significant losses from any single investment.
- Reduce losses on the overall portfolio by spreading investments across different:
-
- Maintain a Disciplined Approach
-
- Develop a trading plan with clear entry and exit criteria based on objective analysis.
- Discipline helps traders:
- Stick to their strategy and
- Avoid making impulsive decisions.
Overconfidence Bias
Overconfidence bias is a cognitive bias where individuals have an inflated belief in their own:
- Abilities,
- Knowledge, or
- Judgments.
In trading, overconfidence leads traders to overestimate their accuracy and success in tasks or decisions. They often take excessive risks and ignore warning signs in the market.
How Overconfidence Effects Traders’ Assessment
Traders affected by overconfidence bias believe that they are better than average at:
- Predicting market movements or
- Identifying profitable trading opportunities.
They underestimate the complexity of financial markets and overestimate their ability to generate consistent profits. Let’s grasp the concept better through an example:
- A trader believes they have superior analytical skills and can accurately predict short-term market movements.
- As a result, they frequently engage in high-frequency trading
- They take multiple positions based on their predictions, despite the high transaction costs and increased risk of losses.
How to Overcome Overconfidence Bias
- Maintain a Trading Journal
-
-
- Keep a detailed record of trades, including:
- Entry and exit points,
- The rationale for trade decisions, and
- Trade outcomes.
- Journaling allows traders to objectively evaluate their performance over time.
- It counteracts overconfidence by providing concrete evidence of strengths and weaknesses in trading strategies.
- Keep a detailed record of trades, including:
-
- Seek Feedback from Peers or Mentors
-
-
- Actively seek feedback from experienced traders or mentors
- This act provides valuable insights and perspectives that challenge overconfident beliefs.
- Also, such a peer review helps identify blind spots.
-
- Use Risk Management Techniques
-
- Implement risk management strategies, such as:
- Setting risk limits,
- Diversifying portfolios, and
- Using stop-loss orders.
- Risk management mitigates the adverse effects of overconfidence bias by:
- Limiting potential losses and
- Maintaining discipline in trading decisions.
- Implement risk management strategies, such as:
Herding Behavior
Herding behavior refers to the tendency of individuals to follow the actions or beliefs of a larger group. Following this behavior, they do not conduct:
- Independent analysis or
- Critical thinking.
In trading, herding behavior amplifies market trends and volatility. This amplification happens because large numbers of investors or traders collectively move in the same direction based on perceived market sentiment rather than objective fundamentals.
How Herding Behavior Impacts Market Dynamics
Herding behavior is shown when a large group of investors buy or sell securities based on the actions of others rather than their analysis. When a significant number of market participants engage in herding behavior, it can create momentum in a specific direction. This directed momentum leads to:
- Exaggerated price movements and
- Increased volatility.
Conversely, herding behavior contributes to market bubbles or crashes as investors follow the crowd without considering the underlying fundamentals of the assets. Let’s understand better through a real-life example:
- During periods of market euphoria, such as the dot-com bubble in the late 1990s, investors flocked to technology stocks.
- This herd behavior was based on the belief that they were guaranteed to generate huge returns.
- However, this inflated the valuations of technology companies, ultimately resulting in a market crash when the bubble burst.
How to Avoid Herding Behavior
- Conduct Independent Research
-
-
- Rely on your own analysis and due diligence.
- Don’t follow the crowd blindly.
- Conduct thorough research into the fundamentals of securities.
-
- Maintain A Contrarian Mindset
-
-
- Look for opportunities to go against the prevailing market trend
- Buy when others are selling.
- Sell when others are buying.
-
- Diversify the Portfolio
-
- Diversify investments across different asset classes.
- Don’t follow the crowd into a single investment or market trend.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is a cognitive bias where individuals tend to seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs or hypotheses while ignoring or dismissing evidence that contradicts them. In trading, confirmation bias influences traders’ decision-making by leading them to selectively interpret information in a way that reinforces their preconceived notions.
How Does Confirmation Bias Influence Traders’ Tendency?
Traders affected by confirmation bias selectively focus on:
- News articles,
- Analyst reports, or
- Market Commentary.
While doing so, they align with their existing beliefs or biases and overlook or downplay contradictory evidence. They ignore alternative viewpoints that challenge their convictions. This ignorance leads to:
- A distorted perception of market conditions and
- Increased susceptibility to making biased decisions.
Let’s study an example:
- A trader holds a bullish outlook on a particular stock.
- Their opinion is based on positive earnings reports and optimistic analyst forecasts.
- They only seek out news articles or opinions that support their bullish thesis.
- They ignore warnings of potential downside risks or unfavorable market conditions.
How to Mitigate Confirmation Bias
- Actively Seek Out Dissenting Opinions
-
-
- Deliberately expose yourself to alternative viewpoints and dissenting opinions that challenge your existing beliefs.
- This exposure encourages a more balanced and objective assessment of market information.
-
- Regularly Challenge Assumptions
-
-
- Regularly question your assumptions and hypotheses through rigorous analysis and critical thinking.
- Actively seek to disconfirm your beliefs rather than confirm them.
-
- Keep A Trading Journal
-
- Maintain a detailed record of trades.
- Include the rationale behind each decision and the outcomes.
- Journaling will allow you to reflect on their past decisions objectively.
- You will also identify instances where confirmation bias has influenced trading decisions.
Sunk Cost Fallacy
The Sunk Cost Fallacy is a cognitive bias where individuals continue to invest in a losing proposition. This happens because they have already incurred irrecoverable costs. Following this fallacy, they ignore the rational analysis that suggests it’s best to cut losses.
In trading, the sunk cost fallacy influences traders’ decisions to hold onto depreciating assets or investments. Most often, they are driven by the desire to recoup past losses rather than objectively evaluating prospects.
How Does Sunk Cost Fallacy Impact Traders’ Decisions?
Traders affected by the sunk cost fallacy focus on past investments, such as:
- The purchase price of a stock or
- The time and effort spent researching a particular investment.
They do not consider future potential and market conditions. Further, they hesitate to sell a losing position because doing so would mean accepting that the past investments are irrecoverable losses, leading to a reluctance to realize losses and move on.
Thus, it is commonly said that the sunk cost fallacy can trap traders in a cycle of throwing good money after bad. This happens as traders continue to invest additional resources in an attempt to justify past decisions.
Let’s understand with an example:
- A trader purchases shares of Company X at $100 per share.
- But the stock price subsequently drops to $50 per share.
- Despite deteriorating fundamentals and market conditions suggesting further downside, the trader continues to hold onto the stock, hoping to recoup the initial $100 investment.
How to Overcome the Sunk Cost Fallacy
- Emphasize Rational Decision-Making
-
-
- Focus on future potential and market conditions.
- Ignore past expenditures when evaluating investment decisions.
- Adopt a forward-looking approach.
- Don’t get influenced by sunk costs.
- Make more objective decisions.
-
- Set Predetermined Exit Criteria
-
-
- Establish clear criteria for when to exit an investment, such as:
- Predefined stop-loss levels or
- Target price thresholds.
- By setting pre-determined exit criteria, traders can mitigate the influence of the sunk cost fallacy by providing a systematic framework for decision-making.
- Establish clear criteria for when to exit an investment, such as:
-
- Foster a Mindset of Acceptance
-
- Recognize that losses are an inevitable part of the trading process.
- Accept losses when necessary.
- Try reframing losses as learning experiences rather than failures.
- Overcome the emotional attachment to sunk costs.
Implementing Behavioral Economics Principles in Trading

Most traders improve their trading performance by mitigating the effects of cognitive biases. Here is a compilation of some popular strategies and practical tips for addressing cognitive biases:
| How to Recognize Cognitive Biases? | How to Mitigate Cognitive Biases? |
Education and Awareness
|
Pause and Reflect
|
Keep a Trading Journal
|
Consider Alternative Viewpoints
|
Seek Feedback
|
Use Decision-Making Frameworks
|
How to Incorporate Behavioral Economics Principles
Incorporating behavioral economics principles into trading strategies significantly improves trading outcomes. Here are some practical ways traders can integrate these principles:
- Place Stop-Loss Orders
-
-
- Set up stop-loss orders to counteract loss aversion and prevent emotional decision-making during market volatility.
- These orders automatically execute a trade when a predefined price level is reached.
-
- Implement Rule-Based Trading Systems
-
-
- Develop and follow rule-based trading systems or checklists.
- Following such systems minimizes the influence of gut feelings or impulsive actions.
- In most cases, rule-based trading systems, outline specific entry and exit criteria based on objective factors such as:
- Technical indicators,
- Fundamental analysis, or
- Predefined trading rules.
-
- Leveraging Sentiment Analysis Tools
-
-
- Use sentiment analysis tools or market sentiment indicators to gauge the collective psychology of market participants.
- Using these tools helps in identifying potential trading opportunities.
-
- Adopting a Systematic Approach
-
- Adopt a systematic approach to decision-making to minimize emotional biases.
- Perform data-driven analysis over intuition or emotion.
- By doing so, you can make objective decisions based on empirical evidence and statistical probabilities.
Developing Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is crucial for traders to recognize and overcome cognitive biases in trading. They tend to make more rational and informed decisions by understanding their own:
- Thought processes,
- Emotions, and
- Biases.
Let’s understand why self-awareness is important:
How to Cultivate Self-Awareness
- Maintain a trading journal to record your thoughts, emotions, and decisions before, during, and after each trade.
- Review your journal regularly and identify patterns of behavior and cognitive biases influencing your trading.
- Incorporate mindfulness practices into your daily routine to increase self-awareness and emotional regulation.
- Take breaks during trading sessions to check in with yourself.
- Continuously monitor your own biases and cognitive tendencies during trading activities.
- Pay attention to instances where you may be:
- Anchoring to past prices,
- Seeking confirmation of existing beliefs, or
- Overestimating your abilities.
- Set realistic and achievable goals for your trading performance and progress.
Using Behavioral Prompts
Behavioral prompts or cues are techniques that traders use to:
- Interrupt automatic thinking patterns and
- Promote more rational decision-making.
These prompts serve as reminders to consider alternative perspectives and adhere to trading strategies. Let’s explore some proven tactics using which traders can implement behavioral prompts to reduce the influence of cognitive biases:
| Techniques | Explanation |
| Set Alarms or Reminders |
|
| Implementation Intentions |
|
| Visualization Techniques |
|
| Pre-Trade Checklists |
|
Conclusion
A deep analysis of the principles of behavioral economics in trading offers valuable insights for traders. By understanding how human psychology influences decision-making, traders can make better choices and improve their performance in the market.
Behavioral economics teaches us that the decisions we make are not always as rational as we think. Cognitive biases like anchoring, confirmation bias, and overconfidence, cause us to make mistakes in trading. However, by recognizing these biases and actively working on them, traders can make more rational decisions.
Most traders use techniques like setting stop-loss orders, implementing rule-based trading systems, and leveraging sentiment analysis tools to interrupt automatic thinking patterns and reduce the influence of cognitive biases. Additionally, by incorporating behavioral prompts into their trading strategies, traders can make more objective decisions based on data and analysis rather than emotion.
Explore how understanding these revolutionary behavioral economics principles can transform your trading strategies. For a comprehensive guide on implementing these principles, check out our article here.
