Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
February 12, 2024
SHARE
The Role of Regulation in Trading: Understanding Compliance and Its Impact
In the world of financial markets, compliance is vital. It is necessary to maintain market integrity, prevent manipulations, and create a fair-trading environment.
Through this article, we will explore some major regulations like the Dodd-Frank Act, MiFID II, and the Commodity Exchange Act. We will discuss their purposes in safeguarding investors, ensuring market transparency and preventing financial malpractices. Also, we will learn about crucial regulatory bodies like the SEC, FINRA, CFTC, and NFA and their roles in overseeing securities trading.
We will also compare regulated trading with over-the-counter (OTC) trading, using examples like Forex and cryptocurrencies to illustrate the differences. By the end of this article, you will understand how technology aids compliance. Let’s get started.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape in Trading
For secure and transparent trading, all the market participants must understand the trading regulations applicable in their area of operation. Let us explore some of the key trading regulations, delineated in the table below.
| Regulations | Role |
| Dodd-Frank Act |
|
| MiFID II | The Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) is a European Union regulation that imposes rules on investment firms and trading venues. It aims to:
|
| Commodity Exchange Act (CEA) | In the U.S., the CEA regulates commodity futures and options markets. It grants the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) the authority to oversee commodity trading to ensure fair practices and protect market participants. |
| Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX) | SOX was enacted in response to corporate accounting scandals. It mandates strict governance and reporting requirements for public companies to protect investors as well as enhance the accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures. |
| Cryptocurrency Regulations | Regulations around cryptocurrencies vary globally. Some countries regulate them as securities, while others treat them as commodities. In essence, the primary goal of all cryptocurrency regulations is to:
|
Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies act as guardians of financial markets. They ensure that markets operate in a fair, transparent, and orderly manner. Some of the popular U.S. regulatory bodies are listed below:
- SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission)
-
-
- The SEC oversees securities markets and regulates securities offerings.
- Its mission is to:
- Protect investors,
- Maintain fair and efficient markets, and
- Facilitate capital formation.
-
- FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority)
-
-
- FINRA is a non-governmental organization authorized by the U.S. government to regulate brokerage firms and their registered representatives.
-
- CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission)
-
-
- The CFTC regulates commodity futures and options markets in the U.S.
- It ensures the fair and efficient functioning of these markets.
-
- NFA (National Futures Association)
-
- NFA is a self-regulatory organization overseeing the U.S. derivatives industry.
- It also works to protect investors and maintain market integrity.
Regulated Trading vs Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading
Regulated trading occurs on organized exchanges with centralized structures. Trades are executed through a transparent order-matching system. Following are some common examples of regulated trading:
- The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ for stock trading
- The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) for commodity trading
The regulated markets are subject to strict oversight by regulatory bodies like the SEC and CFTC. There is a high level of transparency with trading information, order books, and historical data, all of which are publicly accessible.
On the other hand, OTC trading involves direct transactions between parties without a centralized exchange. Trades are often negotiated privately, allowing for flexibility in deal structures. Following are common examples of OTC trading:
- The FOREX market is a prominent OTC market where currencies are traded directly between participants.
- Platforms like FTX facilitate OTC trading for cryptocurrencies, allowing for large-volume transactions.
Usually, OTC markets have varying degrees of regulatory oversights that depend on the jurisdiction. Also, the OTC trades lack the transparency of regulated exchanges due to limited availability of public information regarding the transaction details.
Let us understand this differentiation better using the following example:
| Regulated Forex Trading | OTC Forex Trading |
Forex trading on regulated exchanges follows:
|
OTC Forex trading involves decentralized transactions without a central exchange. |
| Regulatory oversight ensures fair practices and market stability. | Participants negotiate terms directly, with minimal regulatory oversights. |
Compliance and Its Importance for Traders
Compliance is a cornerstone for both individual traders and trading firms. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and stability of financial markets by:
- Promoting fair and transparent market practices,
- Ensuring that traders operate within the bounds of the law,
- Preventing legal actions, fines, and sanctions that can result from violating established rules,
- Restricting market manipulations and ensuring a level playing field for all participants.
What are the Consequences of Non-Compliance?
Regulatory bodies have the authority to enforce punitive measures for violations. In most cases, non-compliance leads to:
- Financial penalties,
- Regulatory sanctions, and
- Legal actions against traders or firms.
Additionally, non-compliance can tarnish the reputation of traders and firms, which can impact business relationships and hinder future opportunities.
How Can Being Compliant Benefit Traders?
Compliance contributes to the overall market health. It prevents practices that could lead to market manipulations or financial crises. Traders who adhere to regulations play a vital role in maintaining stability in the financial markets. Here’s how traders who remain compliant are benefitted:
- Traders gain access to and operate in multiple global markets, which is critical for growth and diversification.
- Being compliant builds trust among investors, counterparties, and regulatory authorities.
- Traders who operate transparently and ethically build a positive reputation and attract stakeholders.
What are Short Selling Restrictions and their Impact on Trading Strategies?
The Short Sale Rule (SSR) is a regulatory measure designed to prevent excessive downward pressure on stock prices during market downturns. When a security’s price declines by a significant amount, the SSR is triggered, which imposes restrictions on short selling. Let us understand how SSR can impact trading strategies during market downturns:
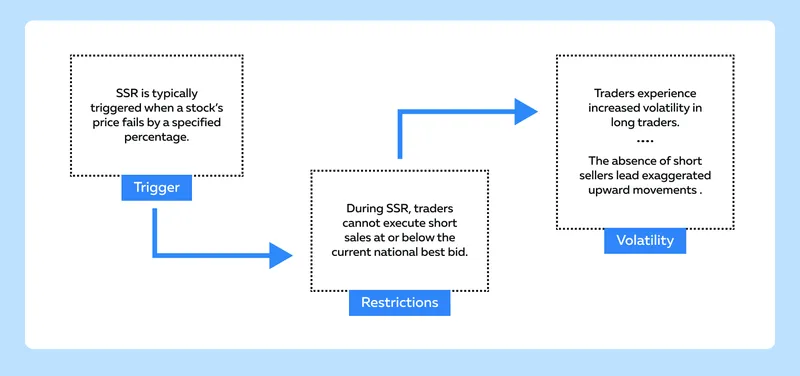
How Traders Can Adapt
With limitations on short selling, traders may shift their focus towards long positions or other strategies that capitalize on potential rebounds in the market. Long-biased strategies become more relevant when short selling is restricted.
How Regulation Affects Trading Strategies
Regulations significantly influence trading strategies and change the environment in which traders operate. Read on to understand how regulations impact trading strategies across various markets:
- Leverage Limits in Forex Trading:
-
-
- Regulations often impose leverage limits in forex trading to control risk.
- This imposition restricts the amount of borrowed capital traders can use.
- Forex traders accustomed to high leverage adjust their strategies, as the potential for amplified gains or losses is curtailed.
-
- Risk Management Emphasis:
-
-
- Traders are compelled to focus more on risk management.
- This shift happens as excessive leverage is no longer available to offset market fluctuations.
- Traders consider conservative position sizing and longer-term horizons.
-
- Reporting Requirements and High-Frequency Trading (HFT):
-
- Reporting requirements, such as real-time reporting of trades, impact the operations of high-frequency traders.
- HFT strategies must adhere to stringent reporting standards, necessitating advanced technological infrastructure.
How Regulations Influence Market Liquidity and Volatility
Effective regulations play a crucial role in preventing market manipulation and fraudulent activities. Market participants can be confident that prices are not artificially influenced, contributing to a more stable and reliable trading environment.
However, most of these regulations impose stricter capital requirements on financial institutions that can limit the capital available for trading activities. Reduced capital usually leads to a decline in market liquidity as institutions are constrained from taking large positions.
How Regulatory News Impacts Market Volatility
The announcement of new regulations or changes in existing regulations is a potent catalyst for market volatility. This is particularly true when regulatory changes impact key sectors or the broader economic outlook.
Usually, markets react swiftly and dramatically to regulatory announcements, with prices of affected assets experiencing significant fluctuations. Investors and traders quickly reassess their positions based on the perceived impact of regulatory changes.
Besides, regulatory news affecting specific sectors, such as healthcare, finance, or technology, can lead to pronounced movements in the corresponding stocks or indices.
Affect on Broader Economic Outlook:
Regulatory changes that signal shifts in the broader economic landscape trigger market-wide volatility. Investors adjust their portfolios in response to altered expectations for:
- Economic growth
- Inflation, or
- Interest rates.
Furthermore, regulatory news can influence investor sentiment and affect decisions related to asset allocation, risk management, and overall market participation.
The Role of Technology in Ensuring Compliance
Technology plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance through automated reporting tools. These tools enhance the efficiency and accuracy of regulatory reporting by reducing manual errors and streamlining the process.
The automated systems enable real-time monitoring of transactions, positions, and market activities. This helps traders and firms to respond quickly to changing regulatory requirements.
Adapting Trading Practices to Regulatory Changes
Adapting trading practices to regulatory changes is integral to sustained success in financial markets. Staying updated through various channels, including direct regulatory sources, financial news outlets, and online communities, provides the necessary information. Read the table below to explore some popular strategies:
| Strategies | Explanation |
| Regularly Monitor Regulatory Websites |
|
| Utilize Financial News Outlets |
|
| Leverage Regulatory Technology (Regtech): |
|
| Join Online Trading Communities |
|
| Regularly Review Trading Strategies |
|
The Importance of Flexibility and Adaptability
Flexibility in trading strategies enables traders to promptly adjust to new compliance requirements. A quick ability to adapt ensures that traders can continue operations without disruption while adhering to the latest regulatory standards.
It also allows traders to:
- Incorporate new risk management measures in response to regulatory changes.
- Optimize trading strategies taking advantage of market opportunities
- Quickly find innovative ways to thrive in changing market conditions.
- Develop resilient trading practices in the face of market volatility triggered by regulatory changes.
- Capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Differences Between OTC and Regulated Trading
Over-the-counter (OTC) trading and regulated trading represent two distinct concepts in financial markets. Regulated trading occurs on organized exchanges where transactions are executed through transparent and centralized systems. In contrast, OTC trading involves decentralized transactions, negotiated directly between parties without the intermediation of an exchange. Read the table below to gain better clarity:
| Parameters | OTC Trading | Regulated Trading |
| Market Structure |
|
|
| Popular Examples |
|
|
| Market Transparency |
|
|
| Liquidity |
|
|
The Implications of OTC Trading
OTC trading brings both advantages and challenges to the financial markets. While it offers efficiency for large transactions and provides a platform for innovation, the trade-off includes potential challenges in market transparency, liquidity, and regulatory oversight. Let’s study this in detail.
-
- Market Transparency:
- OTC markets are often characterized by limited transparency compared to regulated exchanges.
- The negotiation and execution of trades occur privately between parties.
- This privacy leads to a lack of publicly available information on:
- Pricing
- Order books, and
- Transaction details.
- This reduces transparency and poses challenges for investors in assessing the true market value of assets.
- Market Transparency:
- Liquidity:
-
-
- OTC markets are known for providing liquidity for large-volume trades without causing significant price movements in public markets.
- This is particularly advantageous for institutions and high-net-worth individuals seeking to execute substantial transactions efficiently.
- However, the lack of standardized contracts and centralized clearinghouses in OTC markets leads to illiquidity for certain assets, especially during periods of market stress or economic uncertainty.
-
- Regulatory Oversight:
-
- OTC markets operate with varying degrees of regulatory oversight.
- Cryptocurrency OTC markets, for instance, face diverse and evolving regulatory landscapes globally.
- The absence of a centralized exchange presents challenges for standardizing regulatory practices across OTC markets.
- This lack of standardization leads to regulatory arbitrage, a practice of exploiting the difference between jurisdictions.
The Future of Trading Regulation
In the future, increasing digitization and global interconnectedness are likely to prompt regulatory adjustments. One anticipated trend in regulatory processes is the further integration of advanced technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence. This could enhance surveillance capabilities while providing regulators with more effective tools to monitor and enforce compliance. Let’s explore some emerging trends explained in the table below:
| Trends | Explanation |
| Cryptocurrency Regulation |
|
| ESG Compliance |
|
| Digital Securities and Tokenization |
|
| Focus on Market Manipulation Prevention |
|
| Increased Cross-Border Cooperation |
|
Conclusion
Compliance with trading regulations is not only a legal necessity but a foundation for responsible and successful trading. Traders who prioritize understanding and compliance position themselves for long-term success.
Also, governments across the world aim to protect investors by enforcing regulations such as the Dodd-Frank Act, MiFID II, and the Commodity Exchange Act. Thus, traders need to remain compliant and operate sustainably in a secure trading environment.
Ready to navigate the complex world of trading regulations and make informed decisions? Explore essential tips for crypto trading beginners to get started with confidence and compliance. Learn how understanding regulations can impact your trading success. Explore Essential Tips for Crypto Trading and trade smarter today!