Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Trading Basics
January 3, 2025
SHARE
Which Trading Instrument is Right for You? Options, Futures, Stocks, Crypto & More
In trading, the only constant is change!
- Prices rise and fall.
- Markets shift.
- New opportunities emerge daily.
But do you know why this happens?
Besides market conditions, this primarily happens due to the abundance of trading instruments available. While trading, you can choose from stocks to cryptocurrencies and options to forex.
How do you decide which one suits you best?
In this article, we will guide you through all these trading instruments by breaking down their unique characteristics, pros, and cons. You’ll learn about popular options like stocks, options, futures, cryptocurrencies, CFDs, and forex. Each of these instruments has its appeal depending on your capital, risk tolerance, and trading style.
By examining the costs and capital requirements associated with each option, you’ll gain valuable insights into how to choose a strategy that aligns with your financial goals. Additionally, we’ll discuss how our advanced market analysis tool, Bookmap, can enhance your trading experience. Let’s get started.
What Are the Main Types of Trading Instruments?
When engaging in financial markets, traders have a variety of instruments to choose from. It must be noted that each instrument comes with unique characteristics, benefits, and risks. They serve different trading goals and risk tolerances. Hence, most successful traders often choose instruments that align with their:
- Investment strategy
and
- Risk management approach.
Study the graphics below to gain a complete understanding:
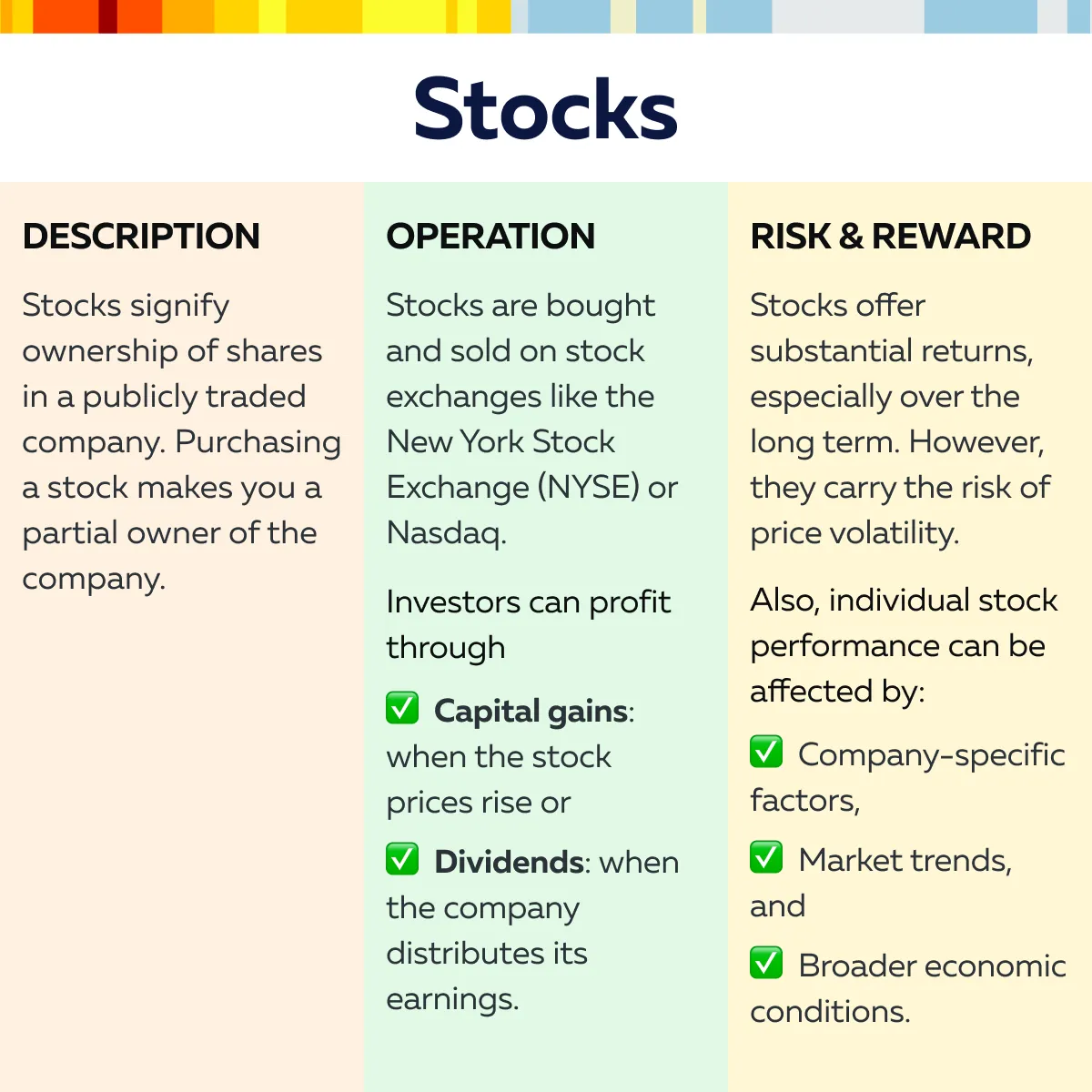
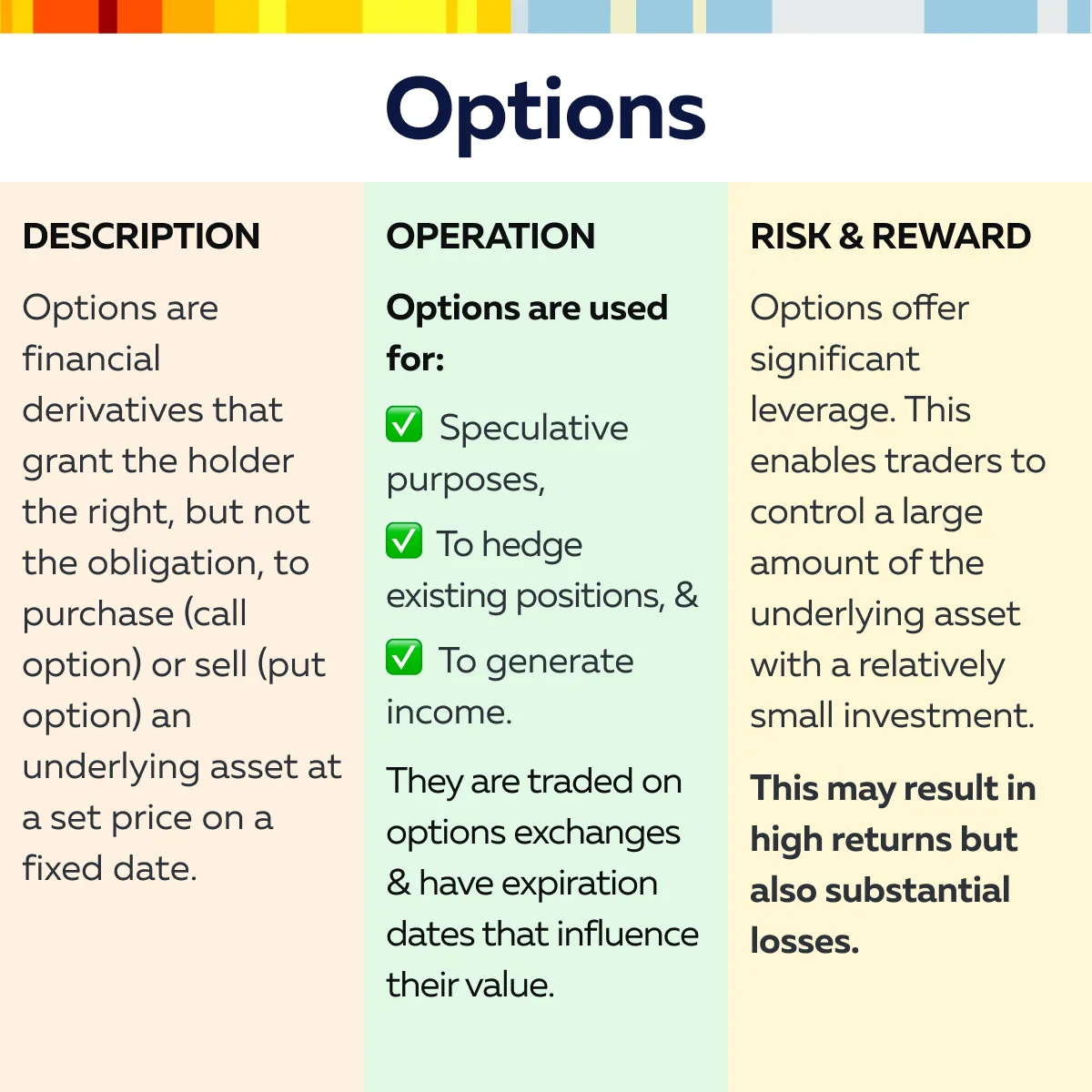




Costs and Capital Requirements Across Different Markets
Traders must note that each market has different financial barriers and costs associated with participation. Traders should carefully evaluate these factors. They must choose instruments that align with their:
- Capital,
- Risk tolerance, and
- Financial goals.
For more clarity, let’s have a look at the various financial commitments and expenses traders face with various assets:
1. Stocks
| Capital Requirements | Costs |
|
|
2. Options
| Capital Requirements | Costs |
|
and
Moreover, complex strategies, such as spreads or straddles, involve multiple contracts, which further increase the cost. |
3. Futures
| Capital Requirements | Costs |
|
|
Get started with futures and options trading—Bookmap’s liquidity and order flow data can help you make informed decisions in real time.
4. Crypto
| Capital Requirements | Costs |
|
or
|
5. Forex and CFDs
| Capital Requirements | Costs |
|
|
What Type of Trader Are You?

Choosing the right trading instrument depends on a variety of factors. Commonly, this includes an assessment of your:
- Risk tolerance,
- Available Capital. and
- Preferred trading style.
The table is a complete guide that can help you identify which asset class may be the best fit for you:
| Parameters | Profile | Risk Tolerance | Capital Size | Trading Style |
| Stock Traders | You might be a stock trader if you:
and
Stock trading is ideal for those who want to invest in well-established companies or follow a long-term strategy, such as value investing or dividend investing. |
Risk tolerance is generally lower as stock traders try to minimize risk through:
However, those who engage in day trading or swing trading face more volatility. |
Significant capital is needed to generate substantial returns. This happens especially if you want to:
or
|
Long-term investors focus on fundamental analysis. In comparison, day traders and swing traders rely on:
and
|
| Options Traders | Options traders are willing to take calculated risks to benefit from price movements with less upfront capital.
They are usually drawn to options for the ability to:
|
Risk tolerance is moderate to high, depending on the strategy.
While buying options can limit risk to the premium paid, selling or writing options involves substantial risk. |
Lower capital requirements make options attractive to retail traders. However, margin requirements for some strategies, like selling uncovered calls, can be high. | Options trading is suitable for traders who enjoy using a variety of strategies, such as:
These traders must stay informed about volatility and time decay. Also, they should keep tracking the underlying asset’s behavior. |
| Futures Traders | Futures trading appeals to risk-tolerant individuals who value real-time market analysis.
Futures contracts are highly liquid. They require precise timing and a keen understanding of market trends. |
Risk tolerance is high due to the leverage involved. Futures traders must be comfortable with the possibility of significant losses. That’s because margin calls are common if the market moves against their position. | Futures trading can be done with relatively modest capital if using Micro E-mini contracts.
However, please note that larger contracts require more capital. |
Day traders and scalpers are common in the futures market. They benefit from:
|
| Crypto Traders | Crypto traders are drawn to the market for its high returns and decentralized nature.
This type of trading suits individuals:
and
|
Very high. The cryptocurrency market can experience massive price swings in a short time. Traders must be prepared for this volatility. | Relatively low barriers to entry make crypto trading accessible to most retail traders. However, proper risk management is required to avoid losses. | Crypto traders use a variety of strategies, from day trading to long-term “HODLing.”
They must stay up to date with:
|
Pros and Cons of Each Trading Instrument
Multiple trading instruments have different advantages and disadvantages. A trader must be aware of these to make an informed choice. Let’s gain a deeper understanding:
Stocks
Investing in stocks is one of the most traditional and popular ways to participate in financial markets. Let’s have a look at the advantages and disadvantages of trading or investing in stocks:
Pros
- Well-Regulated
-
- Stock markets, particularly in developed countries like the U.S., are highly regulated by authorities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
- These regulations are designed to:
- Ensure transparency,
- Protect investors, and
- Maintain a fair-trading environment.
As a result, traders and investors have access to reliable financial information, which reduces the risk of fraudulent activities.
- Ideal for Long-Term Growth
-
-
- Historically, stocks have delivered strong returns over the long term.
- They have outpaced inflation and other investment vehicles.
- This growth is fueled by factors such as:
- Company profitability,
- Overall economic expansion.
-
- With stocks, investors can benefit from:
-
-
-
- Capital appreciation (the increase in stock prices),
- Dividends (income distributed by profitable companies), and
- The power of compound interest (especially when reinvesting earnings).
-
-
- Diversification Options
-
- The stock market offers a vast selection of companies.
- These companies are spread across numerous industries and sectors, including technology, healthcare, consumer goods, and finance.
- This variety enables investors to diversify their portfolios.
- They can spread risk across different areas of the economy.
- By holding a diversified portfolio, investors can mitigate the impact of poor performance by any single stock or sector, thereby protecting the overall value of their investments.
Cons
- Capital-Intensive
-
-
- Investing in stocks, especially in well-established and blue-chip companies, can be expensive.
- For retail traders with limited capital, building a well-diversified stock portfolio requires a significant financial commitment.
- For example,
- Shares of companies like Amazon or Google (now Alphabet) can be pricey.
- This makes it difficult for small investors to acquire substantial positions without a large upfront investment.
-
- Regulated Trading Patterns
-
- Active traders who wish to engage in day trading face restrictions like the Pattern Day Trader (PDT) rule in the U.S.
- As per the rule, traders must maintain a minimum account balance of $25,000.
- This balance is maintained to avoid limitations on frequent trading activities within a margin account.
- For those with smaller accounts, this requirement can be a significant barrier.
- This limits trading opportunities and flexibility.
Options
Options trading suits traders who are looking to benefit from price movements with less initial capital compared to trading stocks directly. However, the complexity and risks involved make it a strategy that requires thorough understanding and discipline. Let’s see its pros and cons:
Pros
- Lower Capital Requirement
-
-
- One of the most appealing aspects of options trading is that it requires significantly less capital than buying stocks outright.
- Traders can control a larger position in the underlying asset by paying a relatively small premium.
- This makes options an accessible choice for retail traders.
- This leverage also enhances returns on investment.
- This especially happens when the price of the underlying asset moves favorably.
-
- Flexibility with Risk/Reward
-
-
- Options offer an array of strategies.
- These strategies can be customized to fit different market outlooks and risk tolerances.
- For example,
- Traders can purchase call options when they anticipate a price increase.
- They can buy put options if they expect a decline.
- Similarly, more advanced strategies, like spreads and straddles, allow traders to limit risk.
- This flexibility makes options suitable for:
- Hedging existing positions,
- Generating income, and
- Speculating on price movements.
-
- Leverage
-
- Options enable traders to gain exposure to the price fluctuations of an underlying asset without needing to buy the asset outright.
- This leverage allows for the potential of high returns.
- Moreover, these high returns can be achieved only with a smaller investment compared to the capital needed to purchase the stock.
- However, it is worth noting that leverage also increases the risk of losses.
Cons
- Expiration Risk
-
-
- One of the major downsides of options trading is that contracts have expiration dates.
- If the underlying asset does not move as anticipated within the option’s time frame, the contract may expire, becoming worthless.
-
- This situation results in a total loss of the premium paid.
-
-
- This time sensitivity requires traders to be strategic about the timing of their trades.
-
- Complexity
-
-
- Options trading involves a steep learning curve.
- That’s because there are numerous strategies that can be employed, such as
- Spreads,
- Straddles, and
- Iron condors.
- Also, they must evaluate several factors like time decay and volatility.
- This complexity is usually overwhelming for novice traders and requires continuous education and practice.
-
- Volatility Sensitivity
-
- Be aware that option prices are significantly influenced by implied volatility.
- Even if the underlying stock moves in the expected direction, changes in implied volatility impact the value of the options contract.
- This sensitivity makes it difficult to predict outcomes.
- Therefore, traders need to be aware of how volatility fluctuations might affect their positions.
Futures

Futures trading allows us to benefit from market movements in various asset classes, from stock indices to commodities. While this market can be highly rewarding, it comes with considerable risks, especially due to the significant leverage involved. Let’s check out its pros and cons:
Pros
- High Leverage
-
-
- One of the main benefits of trading futures is the significant leverage they offer.
- With a relatively small margin deposit, traders can control large positions in:
- Commodities,
- Indices, and
- Other underlying assets.
- This leverage leads to substantial profits on favorable price moves.
- This makes futures attractive to short-term traders, such as day traders and scalpers.
-
- Liquidity
-
-
- Futures contracts for popular markets, such as the S&P 500 E-mini or major commodities like oil and gold, are known for their deep liquidity.
- This allows traders to enter and exit positions with ease, minimizing concerns about significant price slippage.
- This ease even applies to periods of high volatility.
- Liquidity ensures that trades are executed quickly and at expected prices.
-
- Diverse Markets
-
- Futures contracts provide access to a wide array of markets.
- They allow traders to diversify their strategies.
- These markets include:
- Major stock indices,
- Agricultural products,
- Metals,
- Energy resources, and
- Currencies.
- This diversity offers traders the flexibility to capitalize on market opportunities across different economic sectors and regions.
Cons
- High Risk with Leverage
-
- The leverage that makes futures appealing can also lead to substantial losses.
- If the market moves against a position, losses can exceed the initial margin deposit.
- This leads to margin calls and potential account liquidation.
- Such a heightened risk requires traders to use strict risk management techniques, such as
and
- Position sizing.
- Complex Contract Specifications
-
-
- Each futures contract has specific details that traders must understand.
- Commonly, these include:
- Expiration dates,
- Tick sizes,
- Margin requirements, and
- Settlement methods (physical delivery or cash settlement).
- These complexities make futures trading more challenging for beginners.
-
- Requires Active Management
-
- Futures markets are highly sensitive to news and economic events.
- The leveraged nature of these contracts means that even minor market movements can significantly affect a trader’s position.
- As a result, futures trading often demands constant attention.
Cryptocurrency

Cryptocurrency trading has gained immense popularity. It has allowed traders to get high returns in a dynamic market. The decentralized and 24/7 nature of crypto markets offers unique advantages but comes with equally significant risks. Let’s check out its pros and cons:
Pros
- High Potential for Quick Gains
-
-
- A major draw of cryptocurrency trading is that it can allow you to earn substantial profits in a short period.
- Digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are well-known for their extreme price volatility.
- This volatility creates opportunities for quick gains.
- Traders who time their trades well can benefit from significant price swings.
-
- 24/7 Market Access
-
-
- Unlike traditional financial markets that have set trading hours, cryptocurrency markets operate continuously, 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- This constant access gives traders flexibility.
- They can easily act on price movements and market news at any time.
- This makes it especially appealing for those with varied schedules or those who want to monitor global market shifts.
-
- Decentralized Nature
-
- Cryptocurrencies are built on decentralized blockchain networks.
- This means they are not controlled by any central authority or government.
- This decentralization provides a sense of independence from traditional banking systems.
- Such a situation makes cryptocurrencies less vulnerable to direct government intervention and regulatory restrictions.
Cons
- Unregulated and Risky
-
-
- The cryptocurrency market is largely unregulated compared to traditional financial markets.
- This lack of regulation exposes traders to several risks.
- Some common risks are:
- Market manipulation,
- Fraud, and
- Exchange vulnerabilities.
- High-profile incidents, like exchange hacks or sudden regulatory crackdowns, can also cause severe financial losses.
- Additionally, the absence of standardized consumer protections means that investors must be extra cautious when choosing platforms for trading and storing their assets.
-
- Volatility
-
-
- While the price volatility of cryptocurrencies can lead to substantial profits, it also poses a significant risk.
- A single piece of news or market sentiment shift can cause a crypto asset to experience drastic price changes within hours or even minutes.
- This level of volatility makes crypto trading highly speculative.
- It can lead to substantial financial losses if not managed with caution.
-
- Liquidity Issues in Certain Coins
-
- Major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum generally have deep liquidity.
- This makes these cryptocurrencies easy to trade with minimal slippage.
- However, many smaller or lesser-known altcoins suffer from thin liquidity.
- This means that executing large trades in these coins leads to price slippage.
- Such a situation makes it difficult to enter or exit positions at desired prices.
- Therefore, traders focusing on niche or low-cap cryptocurrencies must be mindful of liquidity challenges and market depth.
Whether you’re trading futures, crypto, or stocks, Bookmap’s market analysis tools can help you stay ahead of the curve. Sign up now.
CFDs (Contracts for Difference)
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) provide access to a wide range of markets without the need to own the underlying assets. They offer flexibility and leverage. However, CFDs also carry unique risks, especially in terms of market exposure and broker reliability.
Pros
- Low Capital Requirement
-
-
- A significant benefit of trading CFDs is that they enable traders to speculate on the price fluctuations of various assets, including:
- Stocks,
- Commodities, and
- Forex
- A significant benefit of trading CFDs is that they enable traders to speculate on the price fluctuations of various assets, including:
-
- Importantly, there is a requirement for minimal upfront capital.
-
-
- This is because CFDs don’t require the full purchase of an asset.
- Only a margin deposit is required.
- As a result, retail traders can access diverse markets even with a smaller account size.
-
- Leverage
-
-
- CFDs provide higher leverage compared to traditional stock or futures trading.
- This leverage allows traders to amplify gains from market movements with a relatively small investment.
- For example, by using leverage, traders can control a large position for a fraction of the total asset value.
- However, you must understand that while leverage can increase profits, it can also significantly magnify losses.
-
- Flexibility
-
- CFDs offer the ability to:
- Go long (speculating that the price will rise),
- Short (speculating that the price will fall).
- This flexibility permits traders to capitalize on market trends, whether they are upward or downward.
- This can be done without having to deal with the complexities of physically owning the underlying instrument.
- This feature makes CFDs an attractive choice for short-term traders who want to capitalize on price fluctuations.
- CFDs offer the ability to:
Cons
- High Leverage Risk
-
-
- Please note that the leverage that makes CFDs attractive can also be a double-edged sword.
- In highly volatile markets, leveraged positions lead to rapid and significant losses.
- They can even wipe out a trader’s account.
- Hence, it is important for CFD traders to use stop-loss orders.
- Also, they should practice disciplined risk management to avoid substantial financial setbacks.
-
- No Ownership of Underlying Asset
-
- When trading CFDs, you do not actually own the underlying asset.
- Hence, traders miss out on certain benefits associated with asset ownership, like:
- Dividends from stocks
or
- The right to vote at shareholder meetings
- Additionally, because CFDs are purely speculative contracts, there is no physical delivery or inherent value associated with the trade.
- Broker Risk
CFDs are offered by brokers who may not be regulated as strictly as traditional exchanges, leading to risks in terms of liquidity and transparency.
- Regulatory Oversight: Some CFD brokers operate in jurisdictions with less stringent regulatory oversight, increasing the risk of fraud.
- Liquidity Issues: Since CFDs are not traded on centralized exchanges, Broker-provided liquidity can vary, complicating trade execution.
- Transparency Concerns: The lack of transparency in pricing and execution can result in unfavorable trading conditions, such as wider spreads or slippage.
- Counterparty Risk: Trading CFDs involves a direct contract with the broker, meaning that trader funds are at risk if the broker faces financial issues.
- Conflict of Interest: Brokers acting as market makers may create biased trading conditions by taking the opposite side of trades.
What’s Right for You? Tailoring a Trading Strategy

To choose the right trading instrument, your strategy must align with your:
- Financial goals,
- Risk tolerance, and
- Capital availability.
To help you develop a trading strategy that suits you, below is a set of questions you must answer:
Do You Have a Large Capital Base?
If you have a significant amount of capital, investing in stocks can provide:
- Long-term growth
and
- Stability.
On the other hand, futures offer substantial exposure to market movements. With a larger capital base, you can manage bigger positions and diversify your investments across various assets. This also allows you to withstand market fluctuations more comfortably.
Are You Risk-Averse?
For traders who want to control risk, options are an appealing choice. Buying options (such as calls or puts) limit your maximum loss to the premium paid (due to predefined risk). This feature makes options an excellent choice for those who prefer to know their maximum exposure upfront. Furthermore, strategies like covered calls or spreads provide additional risk mitigation.
Looking for High-Frequency Trading Opportunities?
If you thrive on the fast-paced nature of trading and are interested in strategies like scalping or day trading, both futures and cryptocurrency markets offer ample opportunities. These instruments are known for a variety of features. Check the graphic below:
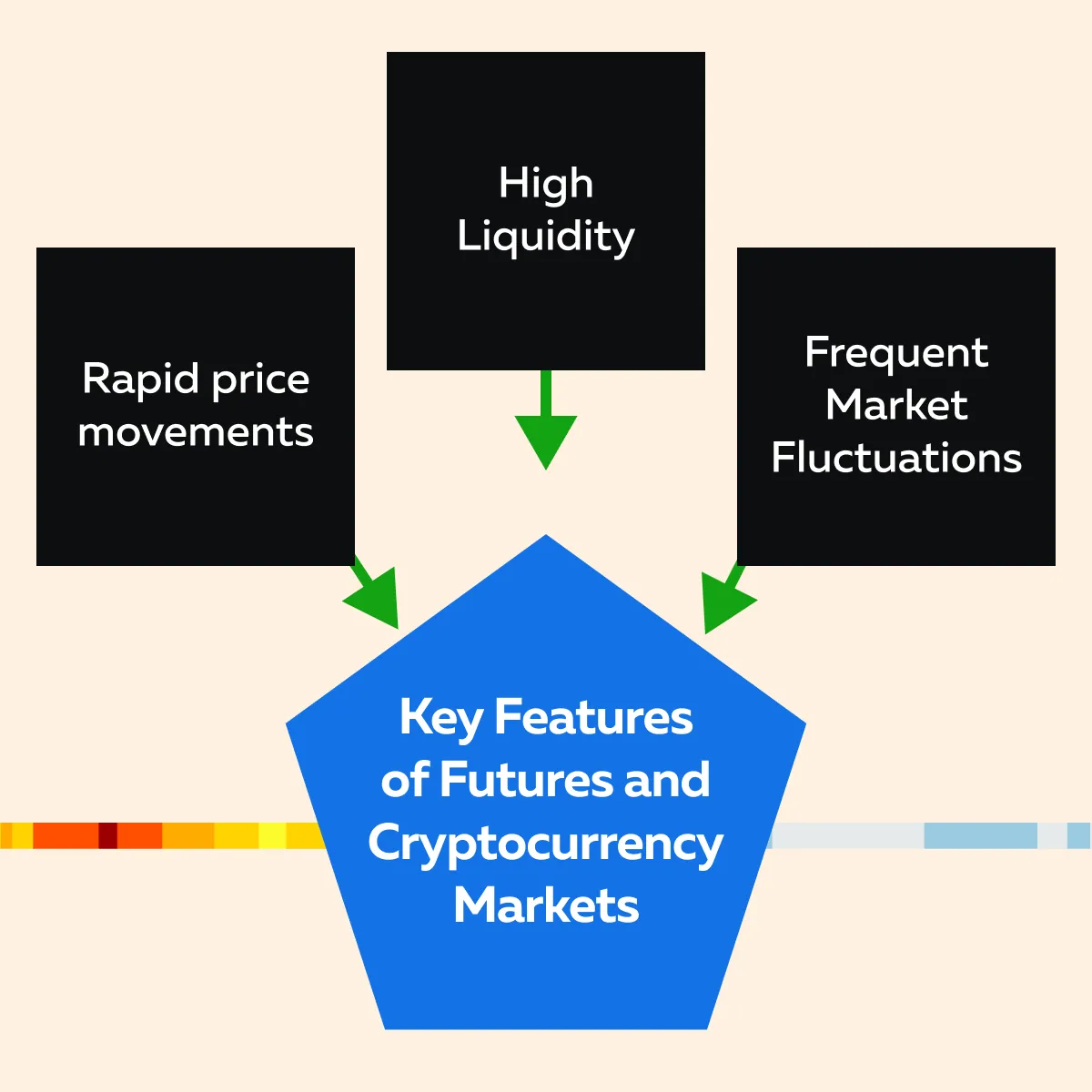
These features make them suitable for active traders who monitor markets closely and execute trades quickly.
It’s important to consider the following factors when choosing your trading instrument:
- Your availability for active management,
- Your understanding of market mechanics, and
- Your financial goals (long-term wealth building or short-term speculative gains).
Understanding your risk tolerance and financial objectives will guide you to the most appropriate trading strategy.
Conclusion
Each trading instrument comes with its own set of advantages and risks. Stocks are ideal for those with substantial capital looking for long-term growth, while options appeal to traders seeking to control their risk exposure and use strategic leverage.
On the other hand, futures offer high leverage and liquidity. They are more suitable for experienced and active traders, while cryptocurrencies provide around-the-clock trading opportunities but come with extreme volatility. Lastly, CFDs offer flexibility and low capital requirements but also carry significant broker and leverage risks.
To make a smart choice of instruments, you should always understand your:
- Financial goals,
- Risk tolerance, and
- Capital limitations.
Ideally, you should take time to evaluate how each market fits into your overall trading strategy. Also, remember that having the right tools can make a big difference. Our advanced market analysis tool, Bookmap, can provide you with a competitive edge over others in the market. By using Bookmap, you can get better insights into market depth, order flow, and real-time trading activity. These insights would allow you to stay ahead and trade better!
Ready to dive into trading? Bookmap’s advanced visualization tools can give you the edge across futures, stocks, options, and more.