Our 4th of July Sale is Live
Offer Valid July 4 – July 11
Get 50% off Global+ AND data for 3 months—or save 30% on Global+ for the full year
Claim Your DealReady to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
April 8, 2024
SHARE
8 Trading Failures That Taught Us Priceless Lessons

Trading failures are not uncommon. Throughout history, certain notable cases have sent shockwaves through the financial markets. A deeper analysis of these instances allows us to identify eight significant trading failures that can severely impact your trading outcomes.
This article will provide comprehensive insights into these failures and offer practical strategies to effectively circumvent them. We have used real-life examples and expert analysis to ensure you gain a deeper understanding of the risks and complexities inherent in trading.
Additionally, we’ll understand the importance of having a sound trading strategy, the clarity of objectives, and the role of risk management in preserving capital. Let’s get started.
Learning from Mistakes: Key Lessons & Insights
Learning from past failures is crucial to avoid repeating the same mistakes in the future. Let’s explore the history and read about some famous trading failures:
1. Barings Bank Collapse
In 1995, Barings Bank, one of the UK’s oldest and most prestigious banks, collapsed due to unauthorized derivatives trading by an employee, Nick Leeson. Leeson’s speculative trades in Nikkei futures resulted in losses exceeding £800 million, leading to the bank’s bankruptcy.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
2. Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM) Collapse
LTCM, a hedge fund led by Nobel laureates and renowned financial experts, collapsed in 1998. The firm placed highly leveraged bets on interest rate spreads and convergence trades. This act failed amidst the Russian financial crisis and resulted in massive losses exceeding $4 billion.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
3. Société Générale Rogue Trader Incident
In 2008, Jérôme Kerviel, a junior trader at Société Générale, engaged in unauthorized trades amounting to €50 billion. Kerviel’s fraudulent activities led to losses of €4.9 billion.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
4. Nick Leeson and Allied Irish Banks (AIB) Incident
In 2002, Nick Leeson, infamous for the Barings Bank collapse, engaged in unauthorized trades while employed at Allied Irish Banks. Leeson’s actions resulted in losses of €691 million for AIB.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
5. Amaranth Advisors Natural Gas Losses
In 2006, Amaranth Advisors, a hedge fund specializing in energy trading, suffered massive losses exceeding $6 billion due to wrong-way bets on natural gas futures.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
6. Knight Capital Group Trading Glitch
In 2012, Knight Capital Group, a major market maker, suffered losses of $440 million in just 45 minutes due to a software glitch in its automated trading system. The malfunctioning algorithm executed numerous erroneous trades and disrupted market stability.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
7. MF Global Bankruptcy
In 2011, MF Global, a global financial services firm, filed for bankruptcy following massive losses on European sovereign debt investments. The firm’s risky bets on European bonds and excessive leverage led to its downfall.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
8. Sumitomo Copper Trading Scandal
In 1996, Yasuo Hamanaka, a trader at Sumitomo Corporation, incurred losses of $2.6 billion through unauthorized trading in copper futures. Hamanaka’s clandestine activities manipulated global copper prices and led to significant losses for Sumitomo.
| Analysis | Lessons Learned |
|
|
So, we just read about some real-life examples and understood the importance of risk management, transparency, regulatory oversight, and ethical conduct in trading and financial markets. To gain a better understanding, let’s now explore eight notable trading failures along with their complete analysis:
Overleveraging

Overleveraging refers to the practice of using borrowed funds or excessive margins to increase the size of trading positions beyond one’s capital. This act amplifies both potential profits and losses. Traders who overleverage can experience substantial losses if the market moves unfavorably, potentially leading to margin calls or even account liquidation.
Understanding Through a Hypothetical Example
The Event
- John is a novice trader.
- He decides to use 10x leverage to amplify potential profits in a volatile market.
- Despite his lack of experience, John enters a position with high leverage.
- Unfortunately, John’s market prediction turns out to be wrong.
- This event results in a significant loss that exceeds his initial investment.
- John now faces the consequences of overleveraging, including:
- Margin calls and
- Potential account liquidation.
Why Did It Happen?
The key factors that led to John’s trading failure due to overleveraging include:
- Lack of Experience
-
-
- John’s decision to use high leverage reflects his lack of experience in risk management and trading strategies.
- Novice traders often underestimate the risks associated with leverage and face significant losses.
-
- Underestimation of Risk
-
-
- John fails to appreciate the potential downside of overleveraging.
- By amplifying his position size with borrowed funds, he exposes himself to higher levels of risk.
-
- Unfavorable Market Movements
-
- Despite the potential for increased profits, overleveraging magnifies losses when market movements are adverse.
- In John’s case, his wrong market prediction resulted in significant.
What Can You Learn from John?
Traders can learn several lessons from John’s trading failure:
- Always prioritize risk management strategies.
- Implement proper position sizing and leverage control to mitigate the impact of adverse market movements.
- Invest in education and gain experience in trading before utilizing leverage.
- Understand the risks and complexities of leverage.
- Adopt a conservative approach to leverage, especially when you are a beginner.
- Start with lower leverage ratios and gradually increase exposure as you gain experience.
Ignoring Risk Management
Neglecting risk management principles in trading can lead to severe consequences. Traders who do so expose themselves to unnecessary risk by failing to implement proper risk management techniques, such as:
- Setting stop-loss orders or
- Diversifying their portfolio.
Such ignorance usually leads to substantial losses that can wipe out trading capital.
Understanding Through a Hypothetical Example
The Event
- Sarah, a seasoned trader, fails to set stop-loss orders on her trades.
- Confident in her analysis, she disregards risk management principles despite warnings from fellow traders and market volatility.
- She continues to hold onto losing positions without an exit strategy.
- A sudden market downturn catches her off guard.
- Sarah suffers significant losses as she watches her position deteriorate.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to Sarah’s trading failure are:
- Overconfidence
-
-
- Sarah is overconfident in her analysis and her trading decisions.
- She neglects risk management principles and assumes that her trades will always turn in her favor.
-
- Lack of Discipline
-
-
- Sarah’s failure to set stop-loss orders demonstrates a lack of discipline in her trading approach.
- Without predefined risk limits, she exposes herself to unlimited losses.
-
- Failure to Adapt
-
- Despite market volatility and warnings from fellow traders, Sarah disregards the importance of protecting her capital and managing downside risk.
- She fails to:
- Adapt her trading strategy or
- Implement risk management measures.
What can you learn from Sarah?
Traders can learn several lessons from Sarah’s trading failure:
- Remain humble and objective in trading.
- Recognize that no analysis is infallible.
- Adopt a realistic assessment of risk and volatility in the markets.
- Maintain discipline and consistency in implementing risk management techniques.
- Stay adaptable and flexible in response to changing market conditions.
- Be willing to adjust trading strategies and risk management measures accordingly to protect capital and minimize losses.
Chasing the Market
Chasing the market refers to the act of entering trades based on fear of missing out (FOMO) rather than sound analysis or strategy. This behavior often leads to impulsive decision-making and can result in losses when traders enter positions at:
- Inflated prices or
- Late stages of a trend.
Most traders who chase the market overlook critical factors, such as market fundamentals or technical indicators, exposing themselves to unnecessary risk.
Understanding Through a Hypothetical Example
The Event
- Mike is an impulsive trader who sees a rapid price increase in a cryptocurrency.
- Fearing he will miss out on potential profits, Mike decides to buy in without considering the underlying fundamentals.
- He enters the trade at the peak of the market.
- Shortly after, he witnesses a sharp price reversal.
- Mike’s impulsive decision to chase the market leads to significant losses.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to Mike’s trading failure due to chasing the market include:
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
-
-
- Mike’s fear of missing out on potential profits drives him to make impulsive trading decisions.
- He prioritizes short-term gains over sound analysis or strategy.
- This prioritization leads to reckless behavior.
-
- Lack of Analysis
-
-
- Mike fails to conduct a proper analysis of the market.
- He overlooks critical indicators and enters the trade based solely on price movement.
-
- Late Entry
-
- By chasing the market, Mike enters the trade at the peak of the market cycle.
- By doing so, he exposes himself to the risk of a sharp price reversal.
- His late entry diminishes potential profits and increases the likelihood of significant losses.
What can you learn from Mike?
Traders can learn several lessons from Mike’s trading failure:
- Maintain patience and discipline in trading.
- Avoid impulsive decisions driven by FOMO.
- Develop a systematic approach to trading based on thorough analysis and strategy.
- Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the market, including:
- Fundamental,
- Technical, and
- Sentiment analysis.
- Consider multiple factors before entering a trade to assess potential risks and rewards accurately.
- Prioritize risk management techniques, such as:
- Setting stop-loss orders and
- Defining risk-reward ratios.
Lack of Discipline
Discipline is essential for successful trading. It helps traders to:
- Stick to their strategies and
- Avoid impulsive decisions driven by emotions.
A lack of discipline and deviation from trading plans leads to inconsistent results and missed opportunities.
Understanding Through a Hypothetical Example
The Event
- Emily is a disciplined trader who develops a robust trading plan based on:
- Technical analysis and
- Risk management principles.
- However, during a losing streak, Emily becomes frustrated and abandons her strategy.
- She seeks to recoup losses through impulsive trades.
- As a result, she exacerbates her losses and further damages her trading psychology.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to Emily’s trading failure due to lack of discipline include:
- Emotional Decision-Making
-
-
- Emily’s frustration during a losing streak leads to emotional decision-making.
- This act causes her to abandon her disciplined approach to trading.
-
- Loss Aversion
-
-
- In an attempt to recoup losses quickly, Emily engages in impulsive trade.
- She did not adhere to her trading plan or risk management principles.
- This behavior is driven by a desire to avoid the pain of realizing losses, known as loss aversion.
-
- Short-Term Focus
-
- Emily’s lack of discipline results in a short-term focus on recouping losses rather than adhering to her long-term trading strategy.
- By deviating from her proven approach, she sacrifices consistency and exposes herself to further losses.
What can you learn from Emily?
Traders can learn several lessons from Emily’s trading failure due to lack of discipline:
- Maintain discipline by adhering to your trading plan and strategy, even during periods of drawdown or losses.
- Avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions or short-term fluctuations in the market.
- Develop emotional resilience and learn to manage emotions, such as fear, greed, and frustration.
- Regularly review and evaluate your trading performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Learn from past mistakes and refine your approach to trading to enhance consistency and profitability.
Poor Timing
Timing is critical in trading. When traders, enter the market at the wrong time, it leads to significant losses or missed opportunities. They usually enter positions:
- During unfavorable market conditions or
- When they fail to capitalize on profitable opportunities.
Poor timing results in losses due to being caught on the wrong side of the market or missing out on potential gains.
Understanding a Through Hypothetical Example
The Event
- David is an inexperienced trader.
- He enters a long position in a stock without waiting for a confirmation signal from his technical indicators.
- Shortly after entering the trade, the stock experiences a sharp price decline due to negative news.
- David incurs substantial losses.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to David’s trading failure due to poor timing include:
- Lack of Patience
-
-
- David’s impatience leads him to enter a trade prematurely.
- He does not wait for confirmation from his technical indicators or market analysis.
- He fails to assess the current market conditions and potential risks associated with his trade.
-
- Ignoring Signals
-
-
- David disregards warning signs and fails to consider external factors, such as negative news or market sentiment.
- He enters the trade based on incomplete information.
- This act increased his vulnerability to adverse market movements.
-
- Inexperience
-
- As an inexperienced trader, David lacks the knowledge and expertise to:
- Properly time his entries and
- Assess market conditions accurately.
- His failure to recognize the importance of timing contributes to his trading failure.
- As an inexperienced trader, David lacks the knowledge and expertise to:
What can you learn from David?
Traders can learn several lessons from David’s trading failure due to poor timing:
- Practice patience and discipline when entering trades.
- Wait for confirmation signals.
- Assess market conditions thoroughly before taking action.
- Avoid impulsive decisions based on emotions or incomplete information.
- Utilize technical analysis tools and indicators to identify high-probability trading opportunities.
- Time entries effectively.
- Incorporate multiple factors, such as:
- Trend analysis,
- Support and resistance levels, and
- Momentum indicators.
- Implement robust risk management strategies.
- Set stop-loss orders and adhere to risk-reward ratios.
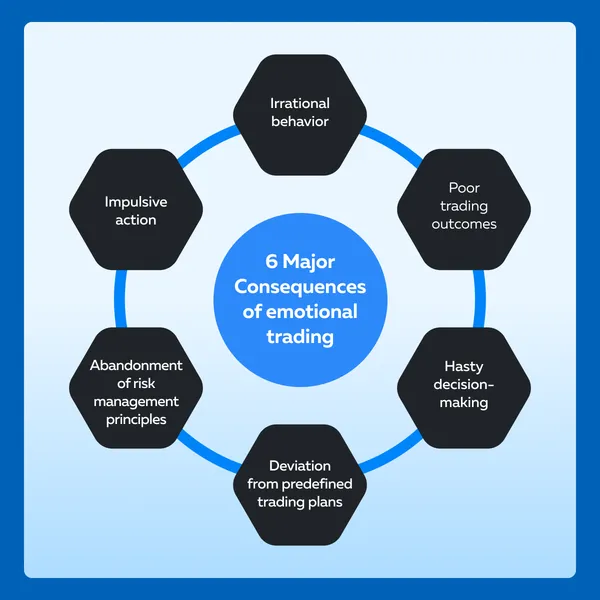
Emotional Trading
Emotional trading occurs when traders allow emotions, such as fear, greed, or anxiety to influence their decision-making process.
Understanding Through a Hypothetical Example
The Event
- Lisa is a trader with a fear of missing out.
- She enters a position in a volatile market without conducting a proper analysis.
- Despite the trade initially moving in her favor, she becomes anxious as the market fluctuates.
- Consequently, she decides to exit prematurely, missing out on potential profits.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to Lisa’s trading failure due to emotional trading include:
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
-
-
- Lisa’s fear of missing out on potential profits drives her to enter a trade without:
- Conducting proper analysis or
- Adhering to her trading plans.
- She succumbs to impulsive decision-making driven by the fear of missing out on market opportunities.
- Lisa’s fear of missing out on potential profits drives her to enter a trade without:
-
- Anxiety and Impatience
-
-
- As the market fluctuates, Lisa becomes anxious and impatient.
- It becomes impossible for her to tolerate uncertainty or volatility.
- Her emotional response leads her to exit the trade prematurely.
- She ignores her initial analysis and potential profit targets.
-
- Lack of Discipline
-
- Lisa lacks discipline and control over her emotions.
- Instead of sticking to her trading plan and risk management principles, she allows fear and anxiety to dictate her actions.
What can you learn from Lisa?
Traders can learn several lessons from Lisa’s trading failure due to emotional trading:
- Develop emotional resilience.
- Learn to effectively manage emotions, such as fear, greed, and anxiety.
- Maintain discipline by adhering to your trading plan and strategy.
- Ignore emotional impulses or market fluctuations.
- Avoid making impulsive decisions based on fear or greed.
- Prioritize consistency and risk management.
- Cultivate mindfulness and self-awareness.
- Take steps to mitigate emotional biases.
- Adopt a rational and objective approach to trading.
Overtrading
Overtrading occurs when traders execute an excessive number of trades, often beyond their risk tolerance or trading plan.
Understanding Through a Hypothetical Example
The Event
- Alex is a day trader.
- He becomes addicted to the adrenaline rush of trading.
- He executes multiple trades throughout the day, regardless of market conditions.
- Despite incurring high brokerage fees and slippage costs, Alex fails to generate consistent profits due to his impulsive trading behavior.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to Alex’s trading failure due to overtrading include:
- Addiction to Action
-
-
- Alex executes multiple trades throughout the day.
- He seeks constant action in the market.
- He prioritizes quantity over quality and disregards the importance of patience and discipline in trading.
-
- Impulsive Behavior
-
-
- Alex’s overtrading behavior reflects impulsivity and a lack of self-control.
- He fails to adhere to his trading plan or risk management principles.
- He makes hasty decisions based on emotional impulses rather than rational analysis.
-
- High Transaction Costs
-
- Alex’s frequent trading activity results in high transaction costs, including:
- Brokerage fees and
- Slippage costs.
- These costs eat into his profits.
- Despite his active trading approach, he fails to generate consistent returns due to the negative impact of transaction costs.
- Alex’s frequent trading activity results in high transaction costs, including:
What can you learn from Alex?
Traders can learn several lessons from Alex’s trading failure due to overtrading:
- Prioritize quality over quantity in trading.
- Focus on high-probability trading setups.
- Avoid unnecessary trades deviating from your plan due to emotional impulses
- Exercise patience and discipline to wait for favorable opportunities that align with your trading strategy.
- Maintain discipline by adhering to your trading plan and risk management principles
- Set predefined criteria for trade entry and exit.
- Be mindful of transaction costs and their impact on trading profitability.
- Limit overtrading to minimize transaction costs.
Analysis Paralysis
Analysis paralysis refers to the tendency of traders to become overwhelmed by information and analysis. It leads to indecision and inaction. Traders who suffer from analysis paralysis spend excessive time analyzing market data and searching for the perfect entry or exit point but struggle to execute trades effectively.
Understanding a Through Hypothetical Example
The Event
- Sophia is an aspiring trader.
- She spends hours each day:
- Analyzing charts,
- Studying technical indicators, and
- Reading market news.
- However, she becomes paralyzed by the sheer volume of information and struggles to make confident trading decisions.
- As a result, Sophia misses out on profitable opportunities.
- She fails to capitalize on her market analysis.
Why did it happen?
The key factors that led to Sophia’s trading failure due to analysis paralysis include:
- Overwhelmed by Information
-
-
- Sophia becomes overwhelmed by the abundance of:
- Market data,
- Technical indicators, and
- News sources available to her.
- She struggles to filter out irrelevant information and prioritize key factors relevant to her trading strategy.
- Sophia becomes overwhelmed by the abundance of:
-
- Perfectionism
-
-
- Sophia seeks the perfect entry or exit point in her trades.
- This leads her to:
- Spend excessive time analyzing market data and
- Search for optimal trading opportunities.
- However, her pursuit of perfection prevents her from taking decisive action and executing trades effectively.
-
- Lack of Confidence
-
- Sophia’s analysis paralysis erodes her confidence in her trading decisions.
- Lack of confidence leads to indecision and inaction.
- She second-guesses her analysis and hesitates to pull the trigger on trades.
- She fears the potential for losses or missed opportunities.
Why can you learn from Sophia?
Traders can learn several lessons from Sophia’s trading failure due to analysis paralysis:
- Prioritize key factors relevant to your trading strategy.
- Filter out irrelevant information to avoid feeling overwhelmed by market data.
- Develop a structured approach to analysis.
- Focus on identifying high-probability trading opportunities.
- Establish clear criteria for trade entry and exit based on your analysis and risk management principles.
- Define predefined triggers for taking action.
- Avoid getting bogged down in excessive analysis or indecision.
- Build confidence in your trading decisions by backtesting your strategies.
- Trust your analysis and decision-making process.
- Be prepared to act decisively when opportunities arise.
The Importance of a Sound Trading Strategy
Having a sound trading strategy is crucial for traders. It avoids the major trading failures discussed above and promotes trading discipline. Let’s see why sound trading strategies are important:
| Prevents Common Trading Mistakes | Adopts Risk Management Techniques |
|
|
How Bookmap Can Help?
Traders can use advanced market analysis tools like Bookmap for enhanced decision-making. Bookmap offers visual representations of market liquidity and order flow. These visualizations allow traders to:
- Identify key support and resistance levels,
- Detect market trends, and
- Anticipate potential price movements.
Read the table below to understand how Bookmap can help you develop a robust trading approach:
| Bookmap’s Benefits | Explanation |
| Eliminates Emotional Trading |
|
| Prevents Overtrading |
|
| Overcoming Analysis Paralysis |
|
| Improving Trade Timing |
|
Why Focus on Consistency and Long-Term Success?
Traders need to develop and follow a robust trading strategy that aligns with their:
- Goals,
- Risk tolerance, and
- Market analysis.
Building and sticking to such a strategy helps in:
- Establishing clear goals for trading activities,
- Incorporating risk management techniques,
- Adhering to a trading strategy that promotes consistency in decision-making, helping traders,
- Avoiding impulsive actions driven by emotions or short-term market fluctuations, and
- Executing trades based on rational analysis rather than emotional impulses.
It is important to note that a robust trading strategy is flexible and adaptable to changing market conditions. Thus, traders must continuously review and refine their strategy in response to new information or market trends. By doing this, traders can stay ahead of the curve, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and minimize risks.
Conclusion
In trading, failures are often the greatest teachers. By examining trading failures closely, traders can gain valuable insights and significantly improve their trading strategies. Each failure provides an opportunity to reassess strategies, refine approaches, and enhance decision-making processes.
Firstly, it’s crucial to understand the common pitfalls in trading, such as overleveraging, emotional trading, and poor timing. These mistakes often lead to substantial losses if not addressed effectively.
Secondly, adopting a proactive approach to risk management is paramount. Implementing robust risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, diversifying portfolios, and adhering to predefined risk limits, can help protect capital and minimize losses during adverse market conditions.
Lastly, continuous learning is essential for traders to stay ahead. They must stay informed about market trends and utilize advanced market analysis tools like Bookmap to maintain a competitive advantage.
Explore further insights on common trading mistakes and solutions in our companion article: Trading Mistakes 101: Common Pitfalls and Finding Solutions.