Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Futures
January 27, 2025
SHARE
Leveraged ETFs vs. Stock Index Futures: What’s the Better Play in 2025?
When it comes to trading, it’s not just about knowing the market but about using the right tools. Leveraged ETFs and stock index futures are two of the most popular instruments. Most traders use them to gain amplified exposure to market movements, but choosing the right one can be tricky!
In this article, we’ll check the differences between leveraged ETFs like TQQQ and SPXL, and index futures such as S&P 500 E-mini contracts. You’ll learn about their costs, flexibility, and the types of trading strategies they’re best suited for. From short-term momentum trades with leveraged ETFs to more precise, high-leverage opportunities with futures, we’ll explore which option might work best for your goals.
Additionally, we will see how tools like Bookmap can help you enhance your trading strategies in 2025. Let’s begin.
Understanding Leveraged ETFs and Index Futures
Leveraged ETFs and stock index futures are popular market tools. Using them, you can amplify market exposure. Leveraged ETFs (like TQQQ) allow retail investors a simple way to gain 2x or 3x the daily returns of an index. In contrast, index futures (such as S&P 500 E-mini contracts) provide high leverage and precise control. This makes them ideal for active traders.
Both have unique benefits and risks. Also, they serve different trading strategies and experience levels. Let’s understand them in detail:
What Are Leveraged ETFs?
Leveraged ETFs are specialized exchange-traded funds. They are designed to amplify the daily returns of an underlying index. See the graphic below for more clarity:
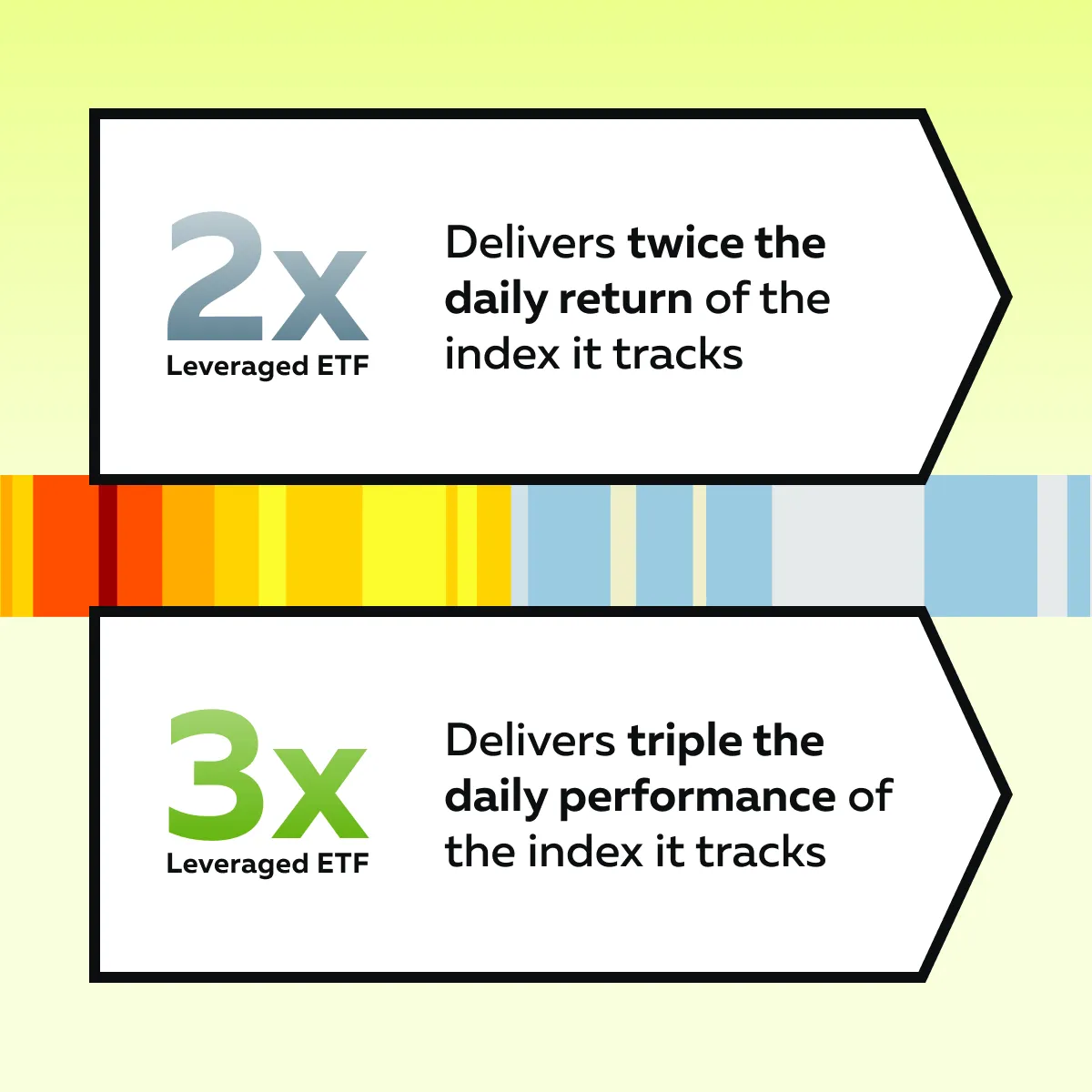
Be aware that these funds use financial instruments, such as derivatives and swaps, to achieve this leverage. These are two popular examples:
- TQQQ, which provides 3x the daily returns of the Nasdaq-100
- SPXL, which offers 3x the daily returns of the S&P 500
These leveraged ETFs are particularly appealing for short-term strategies. That’s because they can amplify gains (and losses) over a single trading day. However, they are not intended for long-term holding because compounding effects can significantly alter expected returns over time.
One Key Advantage
Leveraged ETFs are easily accessible to retail investors. It is worth mentioning that stock index futures often require:
- Significant capital
and
- Familiarity with margin requirements.
In comparison, leveraged ETFs are traded like regular stocks on exchanges. This makes them an attractive option for individuals with limited funds who want exposure to high-powered returns.
Here’s an example:
- Suppose an investor is aiming to achieve three times the daily return of the Nasdaq-100 by choosing TQQQ.
- This approach can offer substantial short-term gains.
- The gains are particularly more when paired with effective leveraged ETFs trading strategies.
However, it’s crucial to monitor these trades closely. That’s because volatility can result in quick losses if the market moves against expectations.
Why Choose ETFs Over Options or Futures?
Leveraged ETFs, such as TQQQ or SPXL, offer several advantages. They are simple and not so complex, like options and stock index futures. This makes them a preferred choice for many investors. Here’s more about the advantages ETFs have over options and stock index futures:

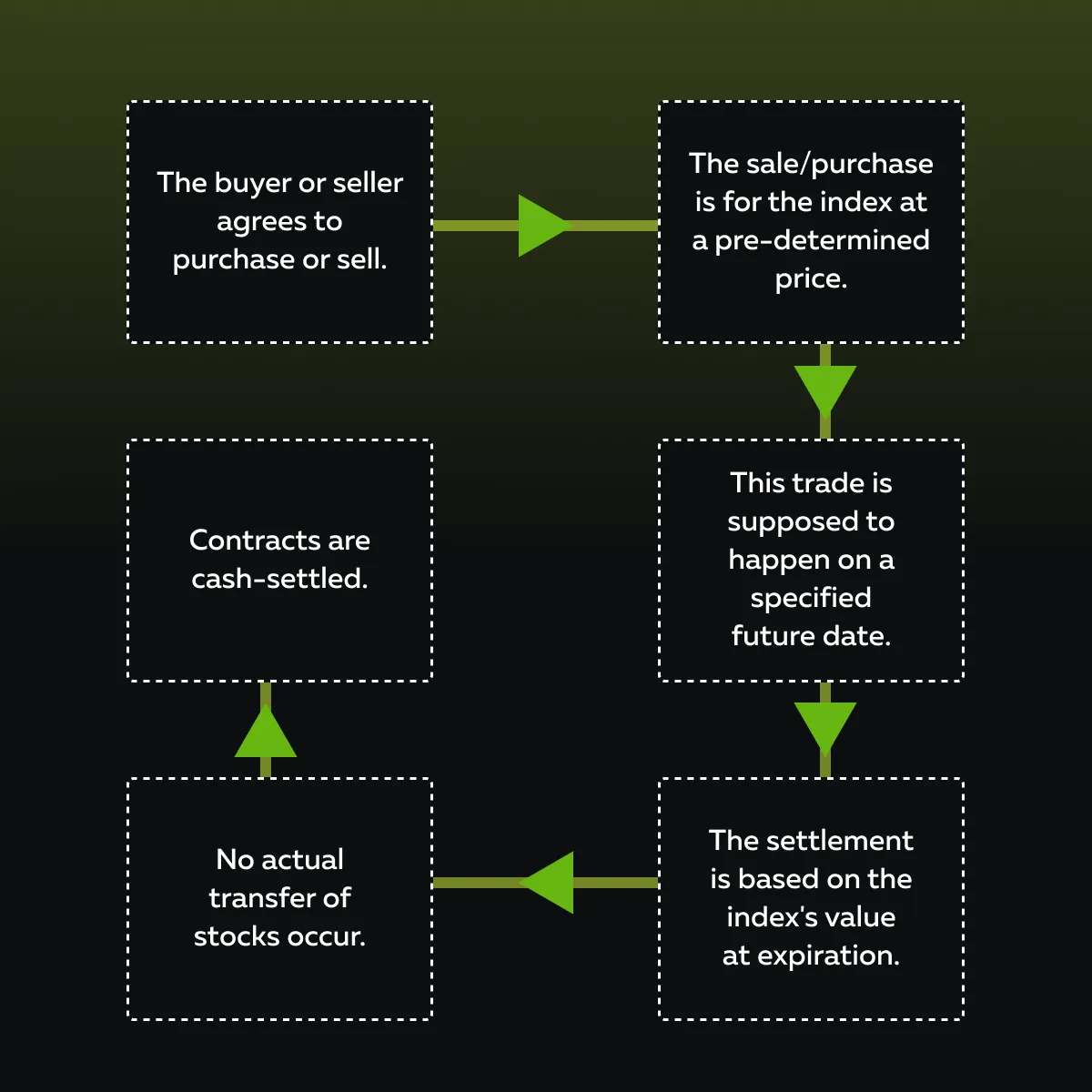
What Are Stock Index Futures?
Stock index futures are standardized contracts. They enable traders to speculate on or hedge the future value of a specific stock index.
Stay ahead in 2025 markets with Bookmap’s advanced analytics for ETFs and futures trading.
Popular Stock Index Futures Contracts
Among the most widely traded futures contracts are the S&P 500 E-mini and Micro E-mini futures. The E-mini is a smaller-sized version of the full S&P 500 futures contract. This makes it accessible to a broader range of traders.
The Micro E-mini (introduced more recently) offers even smaller contract sizes. This feature enables greater precision in trading and risk management. Both are popular tools for gaining exposure to the S&P 500 without requiring full investment in the underlying index. Let’s learn more about them:
High Leverage and Low Margin Requirements
One of the key attractions of stock index futures is their leverage. Futures allow traders to control large positions with relatively small upfront capital (referred to as the margin). This leverage amplifies both potential gains and losses.
This makes futures an appealing choice for active traders who aim for short-term market movements. For example, trading S&P 500 futures requires as little as a few thousand dollars in margin to control contracts worth significantly more. For more clarity, let’s study an example in practice:
- Suppose a trader believes the S&P 500 will rise.
- They purchase an E-mini futures contract.
- The goal is to profit from this upward movement.
- Now, if the index rises as anticipated, the trader can sell the contract at a higher price.
- By doing so, they can realize a gain.
- Conversely, suppose the market moves against them.
- In this case, the leverage can lead to substantial losses.
Both leveraged ETFs trading strategies and stock index futures offer amplified exposure to market movements. However, experienced traders generally prefer futures due to their high leverage and lower trading costs. Futures also carry risks that require careful management, such as the possibility of margin calls.
For newer investors, instruments like TQQQ vs. S&P 500 futures might be worth comparing to determine the most suitable approach for their financial goals.
Key Differences: Leveraged ETFs vs. Index Futures
By using leveraged ETFs and stock index futures, you can gain amplified exposure to market movements. However, they work in different ways. See the graphic below:
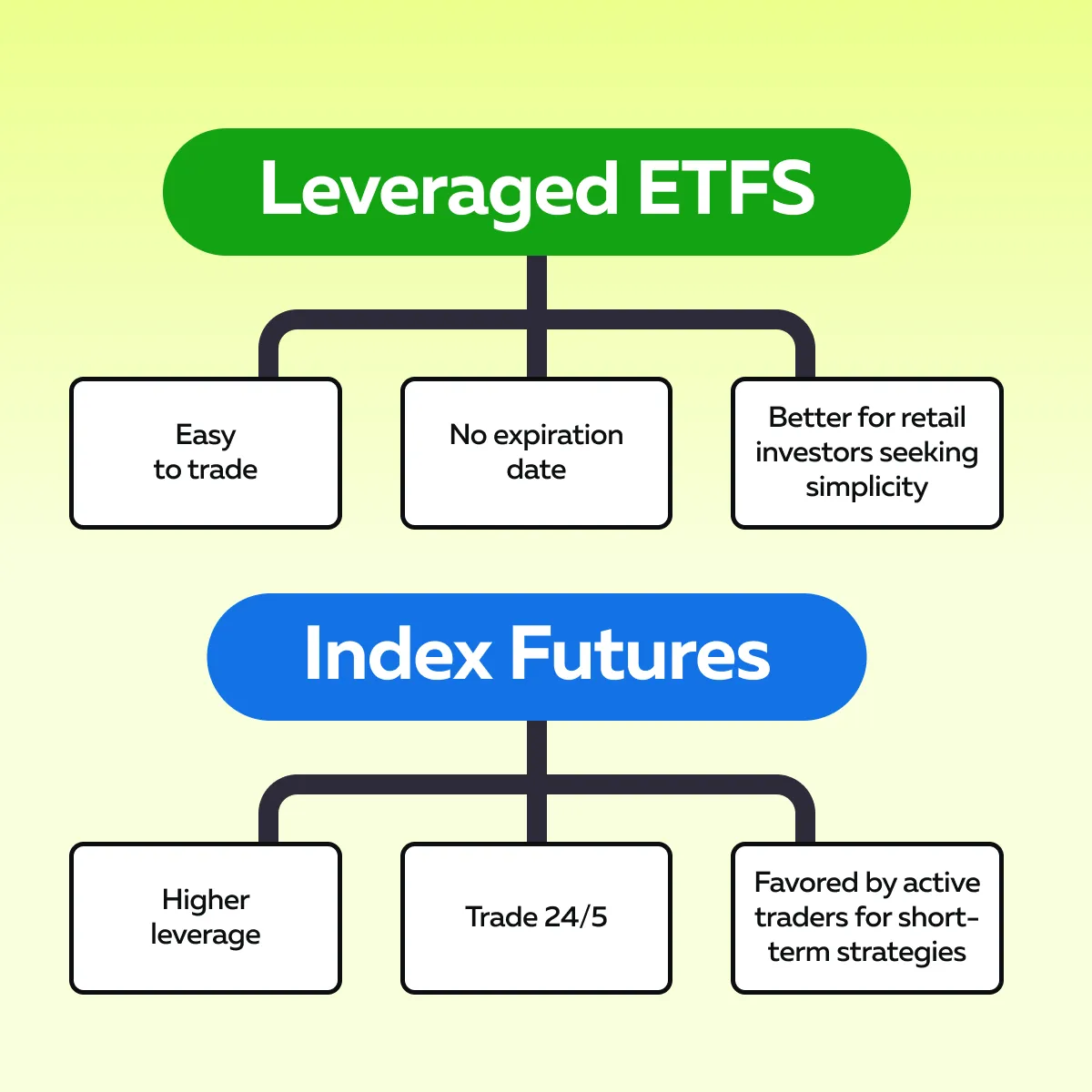
To make a smart choice, you must understand their costs, risks, and flexibility. Let’s understand several key differences in detail:
Cost Comparison
When comparing leveraged ETFs like TQQQ and stock index futures, such as the S&P 500 Micro E-mini, traders need to evaluate costs. Commonly, this includes the following expenditure:
- Management fees,
- Tracking accuracy, and
- Leverage-related expenses.
Both instruments offer leveraged exposure to market movements. But they do so with distinct cost structures. Let’s see how:
| Leveraged ETFs | Stock Index Futures |
|
|
However, please note that the leverage in futures comes with its own risks. A small unfavorable price movement can lead to significant losses. It can potentially wipe out the initial margin and trigger a margin call.
Unlike ETFs, futures traders are also required to manage contract expirations and rollover costs. They must do so if they want to maintain positions over time.
How to Choose the Right Tool?

The decision between leveraged ETFs vs. futures depends on an investor’s-
- Goals,
- Experience, and
- Risk tolerance.
Leveraged ETFs (costlier in the long term) are simpler to use. They don’t require margin management. In comparison, futures (cheaper in terms of ongoing costs) demand a higher level of expertise. Whether one opts for leveraged ETFs trading strategies or 2025 futures trading, understanding these cost factors is important for maximizing returns.
Flexibility and Trading Dynamics
When comparing leveraged ETFs vs. index futures, flexibility and trading dynamics are key factors to consider. Both offer distinct advantages. Also, they cater to different trading styles and objectives. Let’s see how:
Leveraged ETFs are Easy to Use for Retail Investors

Leveraged ETFs, such as SPXL (3x S&P 500), are designed for simplicity. They are highly accessible to retail investors. They can be traded during regular market hours, just like individual stocks, through any standard brokerage account. This ease of trading eliminates the need to deal with the complexities associated with
- Margin calls,
- Rollover costs, and
- Expiration dates.
Leveraged ETFs are also a popular choice for investors who prefer straightforward strategies or have longer-term goals. Here’s an example:
- Say a retail investor is looking for leveraged exposure to the S&P 500.
- Now, they might use SPXL instead of S&P 500 futures.
- This approach allows for leveraged market participation.
- Also, there is no added responsibility for monitoring margin requirements or overnight trading risks.
Stock Index Futures Allow For Greater Flexibility and Precision
Stock index futures, such as the S&P 500 Micro E-mini, offer unmatched flexibility for active traders. This flexibility increases even further for those engaged in short-term or high-frequency trading. Be aware that futures markets operate 24 hours a day, five days a week (24/5). This allows traders to respond to global market events outside of regular stock exchange hours.
Furthermore, futures also provide precise control over contract sizes. They allow traders to tailor their exposure to their portfolio and risk tolerance. Read the given example:
-
- Suppose a day trader is using our advanced market analysis tool like our Bookmap.
- Using it, they closely monitor liquidity levels in S&P 500 futures.
- This monitoring allows them to time entries and exits with pinpoint accuracy.
- Bookmap allows traders to actively manage trades in real time.
- This gives the trader a significant edge for intraday trading strategies.
Monitor order flow and liquidity dynamics in index futures with Bookmap.
Choosing Between ETFs and Futures
For those seeking simplicity and long-term exposure, leveraged ETF trading strategies with instruments like SPXL or TQQQ can be an ideal choice. Conversely, active traders who require more flexibility and control may prefer 2025 futures trading with tools like Micro E-mini contracts.
Trading Strategies for Leveraged ETFs and Futures
Leveraged ETFs and stock index futures offer different opportunities for traders. Check the graphic below to learn the ideal usage of each tool:
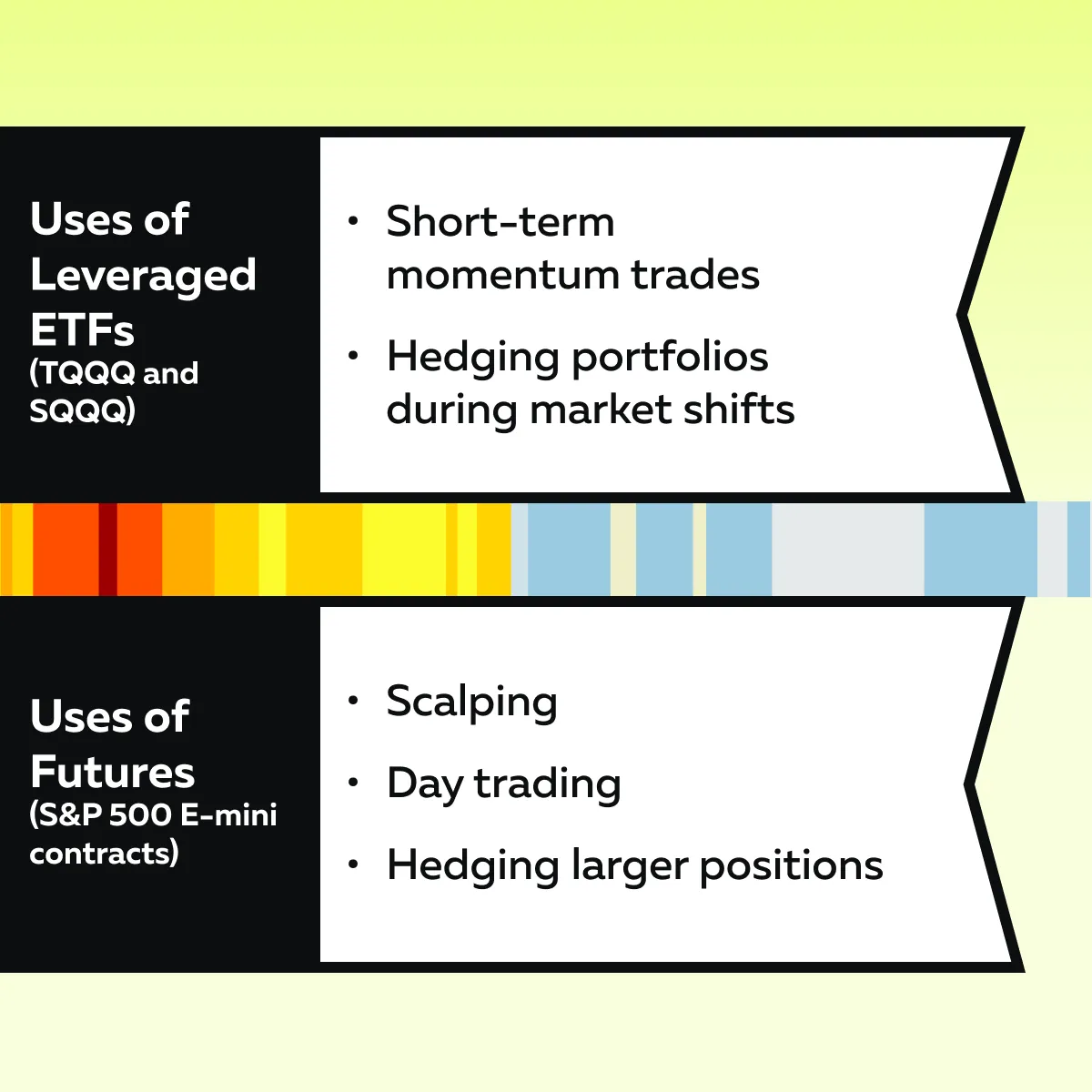
In this way, each tool has unique benefits and uses. So, you must choose strategies as per your experience, market outlook, and trading style.
Leveraged ETF Strategies
Leveraged ETFs, such as TQQQ (3x Nasdaq-100) or SQQQ (inverse 3x Nasdaq-100), are ideal tools for short-term and hedging strategies. They deliver amplified performances. This makes them attractive for capturing market movements quickly. Let’s understand the relevant strategies in detail:
| Short-Term Momentum Trades | Hedging Portfolios |
|
|
Index Futures Strategies
Stock index futures, such as the S&P 500 E-mini or Micro E-mini futures, offer flexibility and precision. They are ideal for active traders and institutions. Futures are particularly popular in scenarios requiring high leverage and low transaction costs. Let’s understand the relevant strategies in detail:
| Scalping and Day Trading | Hedging Large Positions |
|
or
|
Choosing the Right Strategy
Whether you opt for TQQQ vs. S&P 500 futures or combine both tools, you must align your strategy with:
- Your risk tolerance
and
- Prevailing market outlook.
Please note that leveraged ETFs work well for straightforward and short-term plays. In contrast, futures provide advanced traders with the flexibility and precision needed for active market management.
Conclusion
Both leveraged ETFs and stock index futures allow traders to gain exposure to the market. But they come with distinct advantages and drawbacks. Leveraged ETFs (like TQQQ and SPXL) are easier to use, especially for retail investors. They are traded like stocks and don’t expire. This makes them ideal for short-term trades or hedging. However, the compounded effects and tracking errors make them less effective for long-term investments.
On the other hand, stock index futures, such as the S&P 500 E-mini, provide high leverage. With them, you get the ability to trade 24/5. This feature makes them attractive to active traders and day traders. Also, futures offer precise control over positions. They are useful for strategies like scalping and hedging large portfolios. However, they require margin maintenance and a good understanding of market dynamics. This can be a challenge for beginners.
To optimize and make the most of 2025, you should also start using real-time market analysis tools like our Bookmap. Using it, you can easily track liquidity and identify price trends. This allows you to fine-tune entry and exit points. Gain a competitive edge with Bookmap’s real-time futures analysis tools.
