Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
October 23, 2024
SHARE
Spotting Insider Trading: How to Identify Unusual Market Movements
Financial markets are like humans. They soar on good news and crumble when things go wrong. But what if manipulation distorts this natural balance? “Insider trading” is a critical issue where some individuals use confidential information to gain an unfair advantage. Most losses are always faced by retail traders who do not possess that privileged information.
So how can you overcome this challenge?
In this article, we’ll help you identify red flags that could signal insider trading, such as sudden volume spikes, unusual price movements, and patterns before major announcements. Recognizing these signs can help you stay alert and avoid losses in the stock market. Additionally, you’ll also learn how illegal insider trading disrupts fairness and leads to financial losses for retail traders who don’t have access to non-public information.
We’ll also cover tools and techniques, such as real-time data analysis, order flow analysis, and footprint charts–that help detect suspicious trading behavior. These methods can give you an edge by revealing potential insider activity before it impacts stock prices. Finally, we’ll examine famous insider trading cases, including those involving Martha Stewart, Raj Rajaratnam, and SAC Capital to help you understand how authorities detect and punish illegal activities. Let’s begin.
What is Insider Trading?
Insider trading happens when individuals who have access to confidential and non-public information about the company, buy or sell its stock. This type of trading can be either legal or illegal. It depends on how the information is used and disclosed. Let’s understand legal vs. illegal insider trading in detail:
| Legal Insider Trading | Illegal Insider Trading |
|
|
How does Illegal Insider Trading Impact Market Integrity?
In the stock market, the principle of a fair and level playing field should ideally prevail where all investors have access to the same information. But illegal insider trading defeats and exploits this principle. It creates an environment where certain individuals or groups profit from confidential knowledge. Usually, this leads to:
- Market manipulation: Price movements that don’t reflect the true market conditions.
- Loss of investor confidence: When retail investors (ordinary traders) feel the market is unfair, they may pull out, reducing market participation.
- Financial losses: Retail traders are often the most affected because they unknowingly buy or sell stock without the privileged information insiders possess.
Enhance your trading strategy by learning how to spot insider trading with our tools on Bookmap. Get started here!
Identifying Unusual Market Movements Indicative of Insider Trading
To detect insider trading, market participants should focus on certain unusual market movements that are often considered “red flags.” See the graphic below to understand some of their common types:

Usually, the anomalies mentioned in the above graphic suggest that someone with insider knowledge is acting on non-public information. For more clarity, let’s understand these red flags in detail:
Red Flag I: Sudden Volume Spikes
If there is no apparent news or developments related to the company, a large volume spike may mean insider trading. This clearly implies that someone with inside information is buying or selling shares ahead of a significant event, like a merger or earnings announcement. In this red flag, volume spikes occur without any obvious news or public reason for the activity.
For example,
-
- A small company’s stock usually trades 100,000 shares per day.
- But one day, it traded 500,000 shares with no news or announcement.
- This could be a sign that insiders are trading based on information that hasn’t been made public yet.
Red Flag II: Unusual Price Movements
It is worth mentioning that a stock’s price usually reflects the market’s public knowledge. If a stock sees sharp price movements without any visible cause, it suggests that people with non-public information are influencing the price. In this red flag, the stock’s price jumps significantly up or down with no clear reason.
For Example:
- A stock surges 15% in one day.
- There is no news from the company, no analyst upgrades, and no broader market movements.
- This kind of unexplained rise could hint that insiders know about a favorable upcoming event, such as better-than-expected earnings or a major product release.
Red Flag III: Patterns Before Major Announcements
If insiders are privy to a major event, they may try to profit by buying shares ahead of good news (or selling before bad news). This creates abnormal trading activity before the event becomes public. In such cases, market participants can spot “unusual trading patterns” that are a signal of insider trading. These patterns can take the form of abnormal increases in buying or selling activity just before earnings reports, merger announcements, or other important events.
For Example,
- A company is scheduled to report earnings.
- In the days leading up to the report, there’s a sudden increase in buying activity.
- The stock price rises due to this activity, even before the public knows about an earnings beat.
- After the earnings are reported, the stock continues to rise.
- This situation benefits those who traded on the inside information.
Online Trader Tools & Techniques for Detecting Insider Trading
It might be challenging, but it’s certainly possible. By using various tools and techniques, you can identify unusual market activities. Commonly, these tools are:
- Real-time data,
- Order flow analysis, and
- Footprint charts.
Let’s explore in detail how they provide clues about potential insider actions:
A) Real-Time Market Data
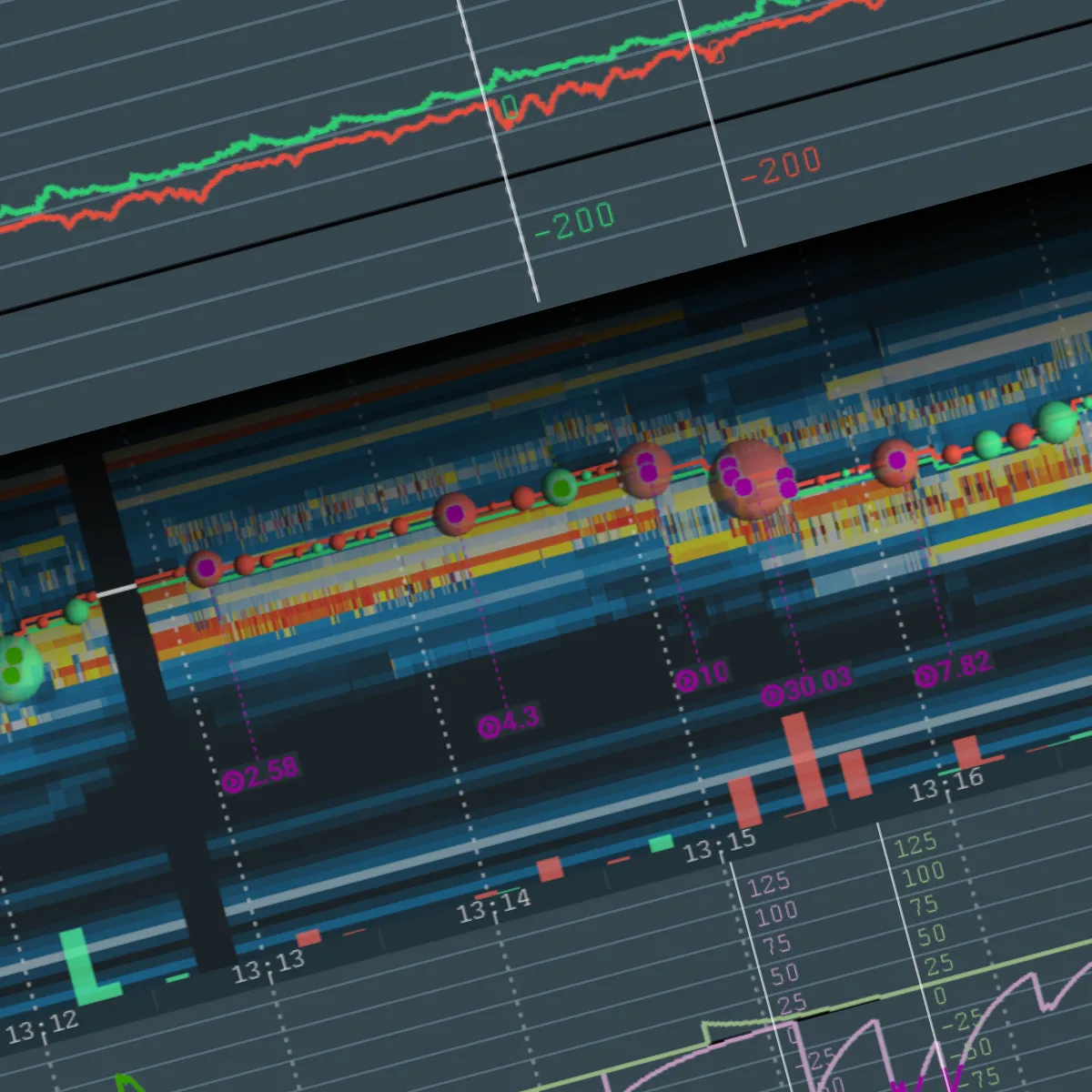
Traders can use real-time data and advanced analytics to detect unusual trading. This detection can be made by constantly monitoring live data. Such monitoring helps traders spot patterns or sudden shifts in the market, like a surge in large buy orders for a particular stock before any public news is released.
For example,
- A trader notices an unexpected influx of large buy orders on a relatively dormant stock.
- This situation raises suspicions of potential insider trading before a major announcement.
B) Analyzing Order Flow
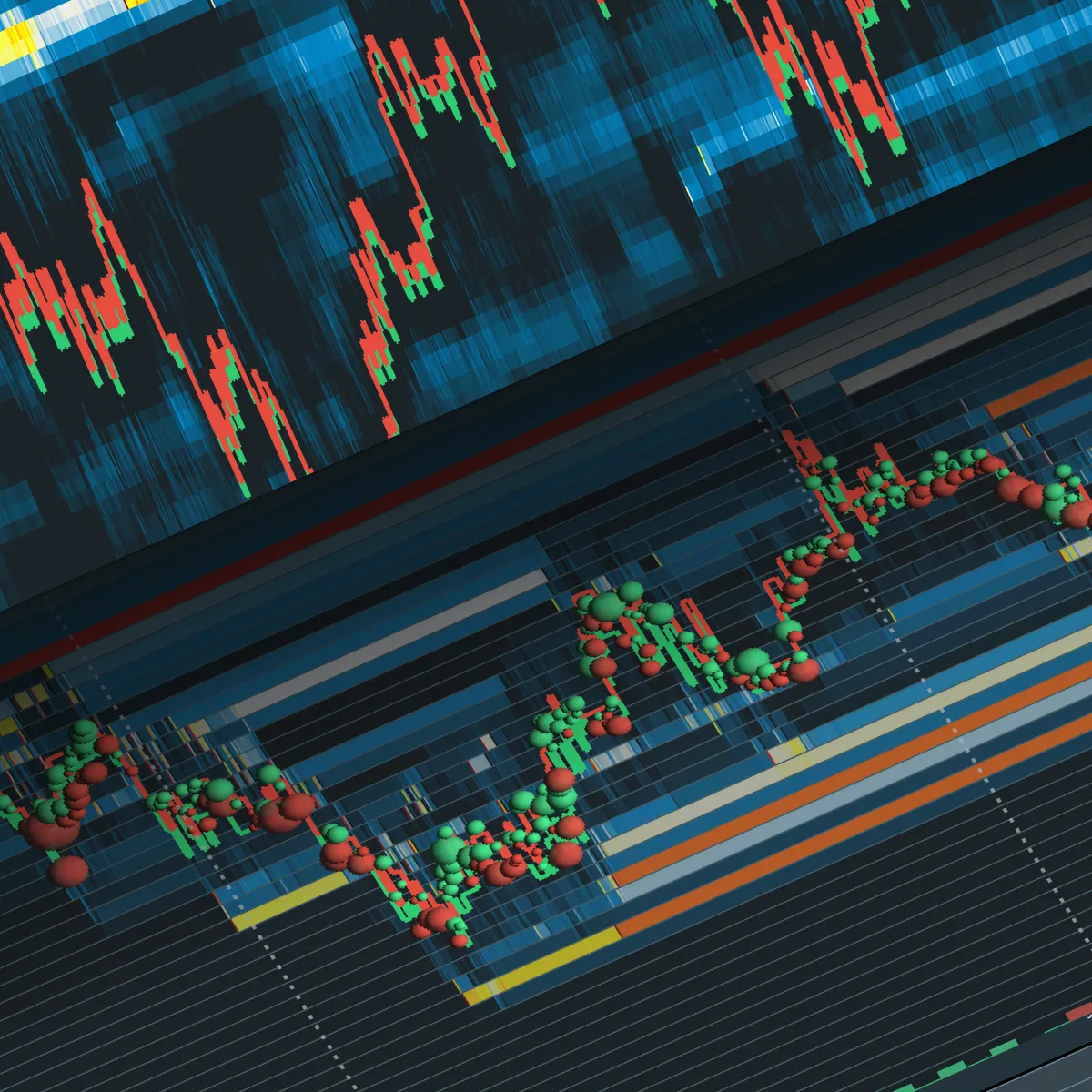
A thorough analysis of order flow helps to identify patterns and behaviors of traders who might be acting on insider information. For the unaware, “order flow analysis” refers to tracking the sequence and volume of trades. This tracking provides insights into the actions of buyers and sellers.
For example,
- There is a sudden rush of buying activity with consistently higher bid prices.
- However, there is no significant news.
- This situation indicates that some traders are privy to non-public information.
C) Footprint Charts for Volume Discrepancies

Market participants can also use “footprint charts” to reveal discrepancies in buying and selling volumes. These charts display detailed information about the volume of trades at different price levels, highlighting any unusual activity.
For example:
- Say there is an unusual spike in sell orders on a Footprint chart.
- This spike occurred just before a negative earnings report.
- Now, this suggests that insiders are offloading their shares ahead of bad news becoming public.
Use the Footprint Chart in Bookmap and stay ahead of the market! Detect potential insider trading activities easily. Join now!
Case Studies of Insider Trading Detection
To better understand the concept of insider trading, let’s study three most popular related historical case studies:
Case Study 1: Martha Stewart and ImClone Systems (2001)
The 2001 insider trading case involving Martha Stewart and ImClone Systems is one of the most well-known examples of insider trading practices. This case highlighted how unusual trading activities can draw attention to insider trading and lead to serious legal consequences.
Overview of the Case
| The Incident | The Information |
|
|
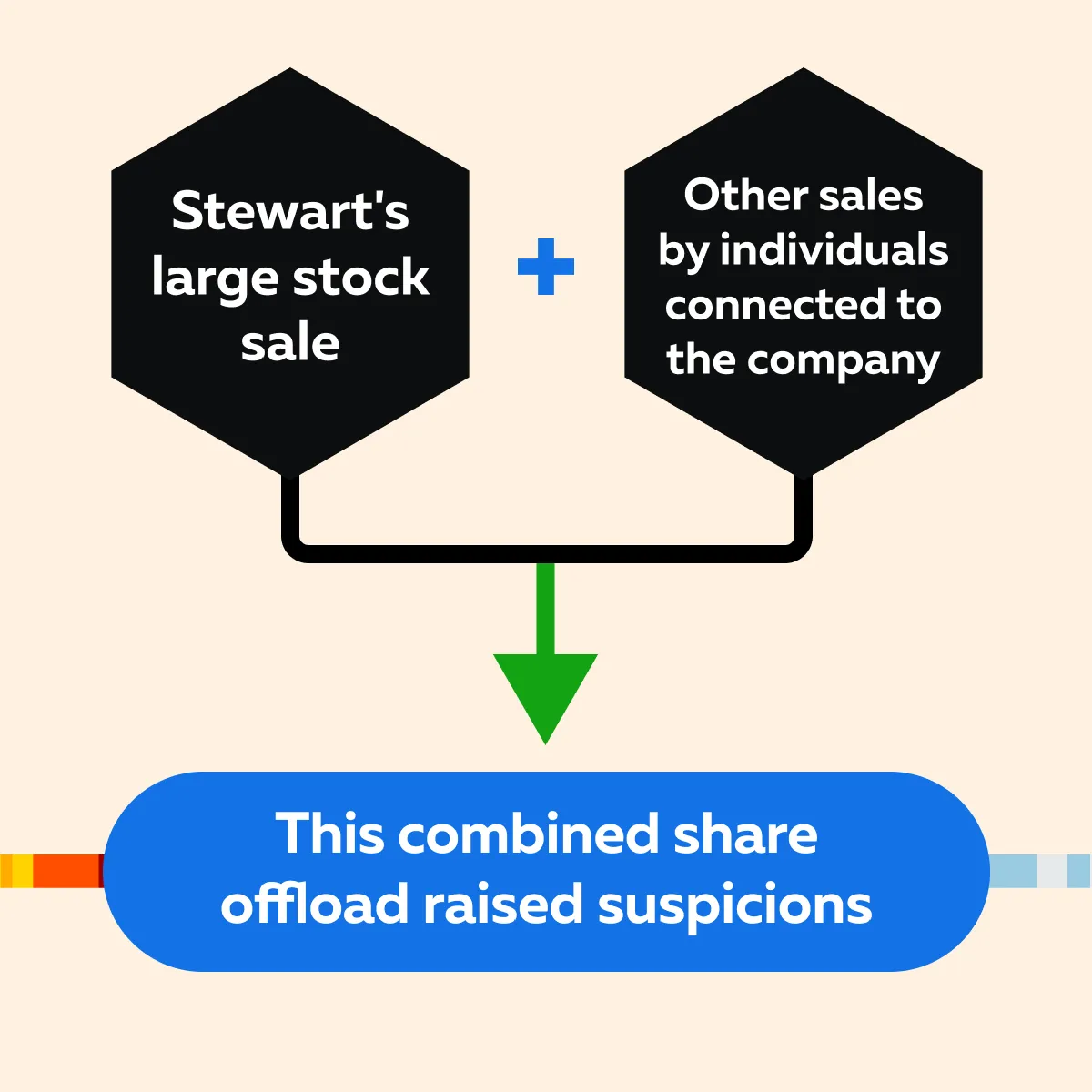
Detection
The SEC detected illegal insider trading due to unusual trading activity in ImClone shares. The sale of Stewart’s shares occurred just before the FDA’s decision was made public. This prompted the SEC to investigate. See the graphic below to see how it raised suspicion:
Outcome
Martha Stewart was found guilty of conspiracy, obstruction of justice, and making false statements during the investigation. Her conviction led to:
- Five months in prison, followed by five months of being confined to home.
- She also paid fines and legal fees totaling over $30,000.
Notably, her conviction not only damaged her reputation but also impacted the market value of her own company, “Martha Stewart Living Omnimedia.”
Case Study 2: Raj Rajaratnam and the Galleon Group (2009)
Raj Rajaratnam founded the Galleon Group. He was involved in one of the largest insider trading schemes in U.S. history. This case highlighted the complexity and scale of insider trading, as well as the importance of surveillance and trading pattern analysis in detecting illegal activities.
Overview of the Case
| The Incident | The Information |
|
|
Detection
The case was initially triggered by unusual trading patterns in stocks connected to Rajaratnam’s trades. These patterns raised suspicion, particularly the consistent timing of trades around corporate earnings announcements made Rajaratnam a suspect.
As suspicions grew, the FBI began wiretapping Rajaratnam’s phone calls. They also used surveillance to gather evidence. This method of detection was unique in financial crime investigations and provided concrete proof of Rajaratnam’s involvement in insider trading.
Outcome:
Raj Rajaratnam was convicted on 14 counts of securities fraud and conspiracy. His sentencing included:
- 11 years in prison, which was one of the longest sentences for insider trading at the time.
- A $10 million fine and forfeiture of $53.8 million in profits made through illegal trades.
Identify unusual market movements with real-time data analysis using our tools on Bookmap. Sign up today!
Case Study 3: SAC Capital Advisors (2013)
SAC Capital Advisors was led by billionaire investor Steven A. Cohen. His company was one of the most prominent hedge funds involved in insider trading. This case revealed how widespread and profitable insider trading could be when conducted by a large financial institution.
Overview of the Case
| The Incident | The Information |
and
|
|
Detection
SAC’s insider trading was uncovered through a combination of:
- Whistleblower tips
-
-
- Here individuals within the firm or connected to it reported suspicious activities.
-
- Suspicious trading patterns
-
- These patterns were identified with SAC’s trades.
- They frequently outperformed the market just before key announcements.
- Investigators noticed that SAC’s stock positions often perfectly timed earnings announcements or other significant news raised red flags.
The SEC and FBI, using advanced data analysis tools, traced how SAC’s performance was repeatedly linked to illegal insider information. The firm’s suspicious outperformance, particularly around corporate earnings and M&A activity, led to deeper scrutiny.
Outcome
SAC Capital was ordered to pay a $1.8 billion fine, one of the largest fines in insider trading history. While several SAC employees were convicted of insider trading, Steven A. Cohen himself avoided criminal charges due to insufficient evidence directly linking him to the illegal trades. However, Cohen faced other consequences:
- He was banned from managing outside money (for institutional clients) for two years.
- SAC Capital effectively shut down.
- Cohen rebranded his firm as Point72 Asset Management and focused on managing his own wealth.
Insider Trading Conclusion
Insider trading, whether legal or illegal, can significantly impact market integrity. While legal insider trading involves executives trading their company’s stock with proper disclosure, illegal insider trading relies on non-public information. This creates an unfair advantage for certain individuals and undermines market fairness, often leading to financial losses for retail traders and damaging their confidence.
However, insider trading activities can be detected by identifying unusual market movements, such as sudden volume spikes, unexplained price changes, and abnormal patterns before major announcements. They act as important red flags and often indicate someone is acting on confidential information before it becomes public.
Furthermore, to detect insider trading, you will need the right tools, like Bookmap. Our tools are equipped with advanced technologies like real-time market data, order flow analysis, and footprint charts. By using these modern features, you can get insights into suspicious trading behaviors. With Bookmap, you can easily track these anomalies and monitor volume discrepancies. So, are you looking to protect your investments by spotting irregular activity? Join us today!
