Ready to see the market clearly?
Sign up now and make smarter trades today
Education
December 27, 2024
SHARE
Key Algorithmic Trading Strategies: From Trend Following to Mean Reversion and Beyond
Speed. Precision. Accuracy. These three terms perfectly sum up the traits every trader seeks to cultivate to make the most of their market escapades. The pursuit of these qualities and the constant march of technology gave birth to a revolutionary tool: trading bots. These bots trade using a method called algorithmic trading that relies on computer algorithms to automate trading decisions. This allows traders to execute strategies faster and more efficiently than ever before.
In this article, you will read about the diverse range of algorithmic trading strategies, such as trend following, mean reversion, arbitrage, breakout trading, and market making. Each strategy offers unique advantages and suits different trading styles and market conditions. You will also learn about the importance of risk management and how to pair your strategies with sound practices to protect your capital.
Furthermore, we will introduce you to the modern tools our platform Bookmap offers, Tradermap Pro and Tradermap Lite, which assist market makers in analyzing data and smartly managing orders. Lastly, you’ll discover how backtesting and simulation tools can help you refine your trading strategies before you apply them in real markets. Let’s get started.
What is Algorithmic Trading?
Algorithmic trading (often called algo trading) relies on computer programs to automate the trading of financial assets. These algorithms are programmed with predefined rules. They make trading decisions based on factors such as price, volume, and time. See the graphic below to check out some key features:
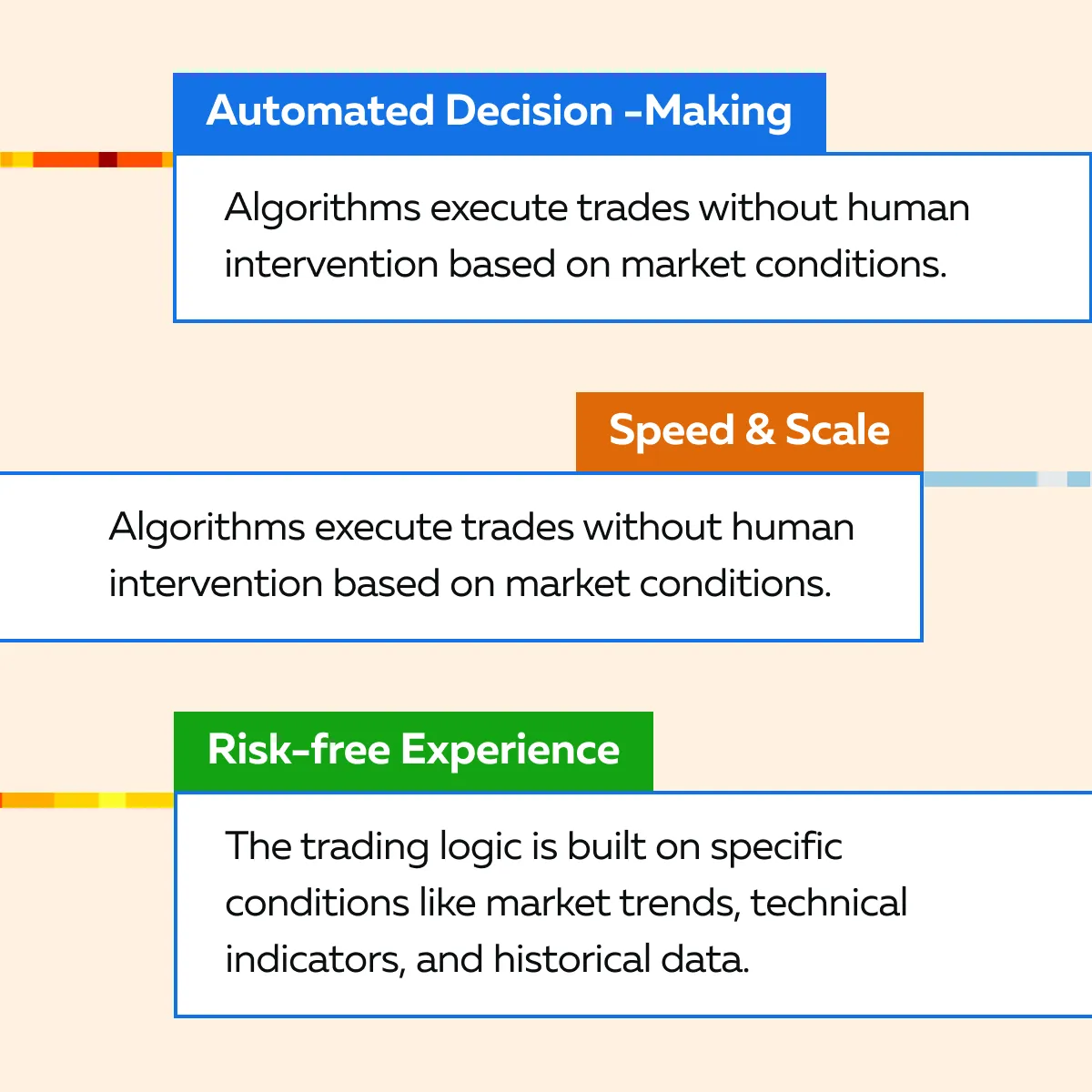
What is the Purpose of Algorithmic Trading?
Algo trading removes emotions. Trading decisions are made objectively, without the influence of human emotions like fear or greed. Algorithms streamline trading operations and allow traders to take advantage of market opportunities quickly and at scale.
Furthermore, algo trading adjusts to different market conditions. It helps traders to optimize strategies in:
- Volatile,
- Stable, and
- Mixed environments.
Now, let’s talk about some popular markets for algorithmic trading:
| Stocks | Futures | Forex | Cryptocurrencies |
| Algorithms buy and sell shares of companies in the stock market. | Traders use algorithms to forecast future prices of commodities or financial instruments. | Algorithms track the price fluctuations in currency markets. They make trades based on exchange rates. | Due to its decentralized nature, crypto trading has a high adoption rate for algorithmic trading. Algos smartly takes advantage of crypto’s 24/7 market activity. |
Some Key Benefits
In markets where speed is essential, algo trading excels. That’s because it can execute orders in milliseconds. This maximizes opportunities in high-volume environments. Furthermore, algo trading reduces the need for manual intervention. In this way, algorithms reduce transaction costs and make trading more efficient.
Also, algorithms can incorporate risk parameters to minimize losses and execute stop-loss orders when required. For more detailed information, visit our comprehensive guide on algorithmic trading on our platform, Bookmap.
Exploring Key Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Algorithmic trading comprises a variety of strategies. Generally, these strategies operate under different parameters. Their implementation depends on factors like:
- Volatility,
- Liquidity, and
- Asset behavior.
They are aimed at achieving specific trading goals based on historical patterns and statistical models. Study the graphic below to check some common algorithmic trading strategies you can follow:
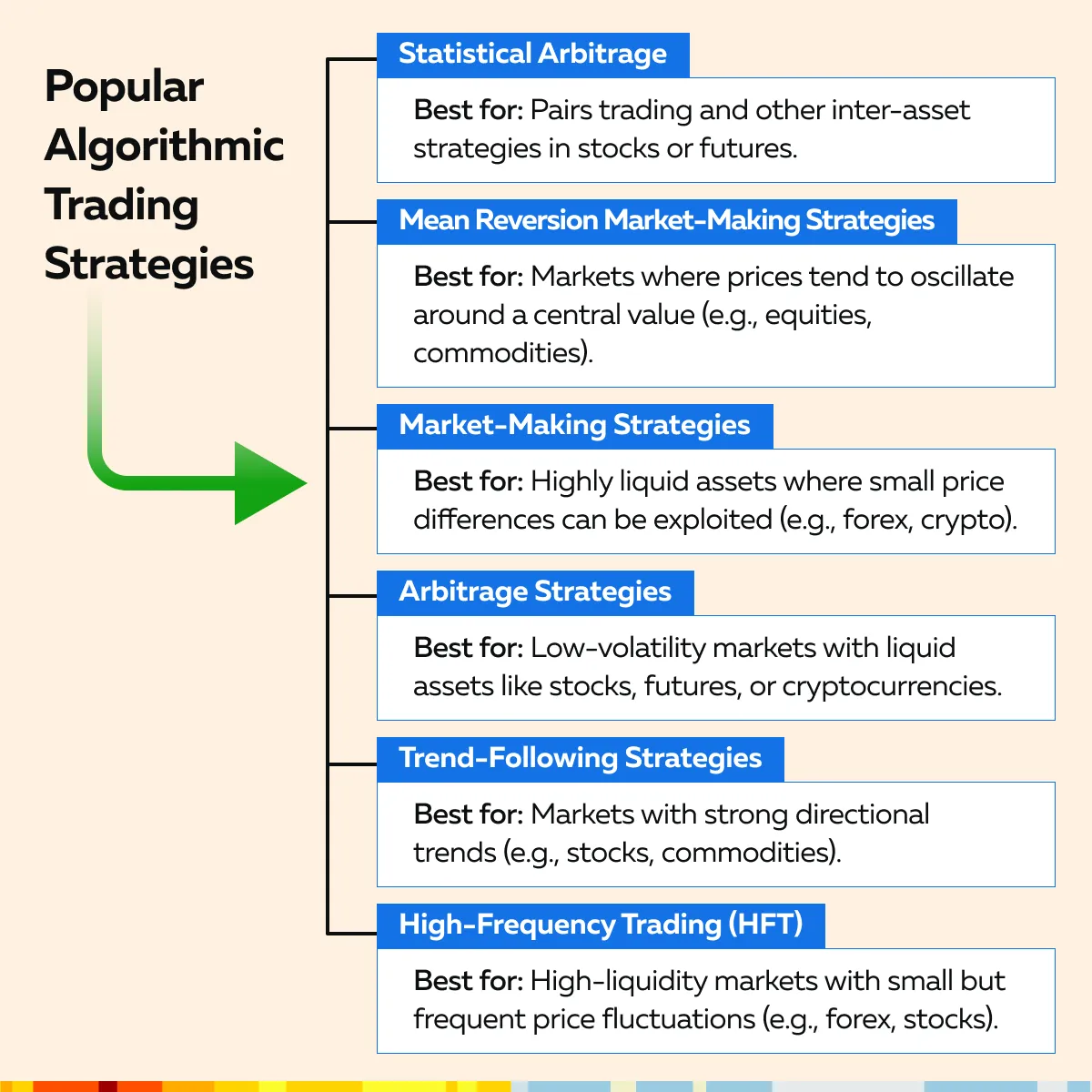
How to Choose a Strategy Based on Market Conditions?
Different market conditions require specific trading strategies. See the table below:
| Volatile markets | Stable markets | Liquidity considerations | Asset behavior |
|
|
|
|
How to Choose the Right Strategy?
Firstly, the choice depends on the trader’s objectives. Scalping or HFT suits traders aiming for fast and small gains. On the other hand, trend-following and mean reversion are better for those seeking longer-term profits. Next, when it comes to market conditions as a basis, traders should ideally adapt strategies based on the current
- market volatility,
- liquidity, and
- asset class behavior.
For example, arbitrage works well in stable conditions, while trend-following thrives in volatile markets.
Trend Following Strategies
Trend-following strategies capitalize on the momentum of financial markets. They trade along established trends and try to capture the “meat” of significant market moves. Study the graphic below to see what these strategies focus on.
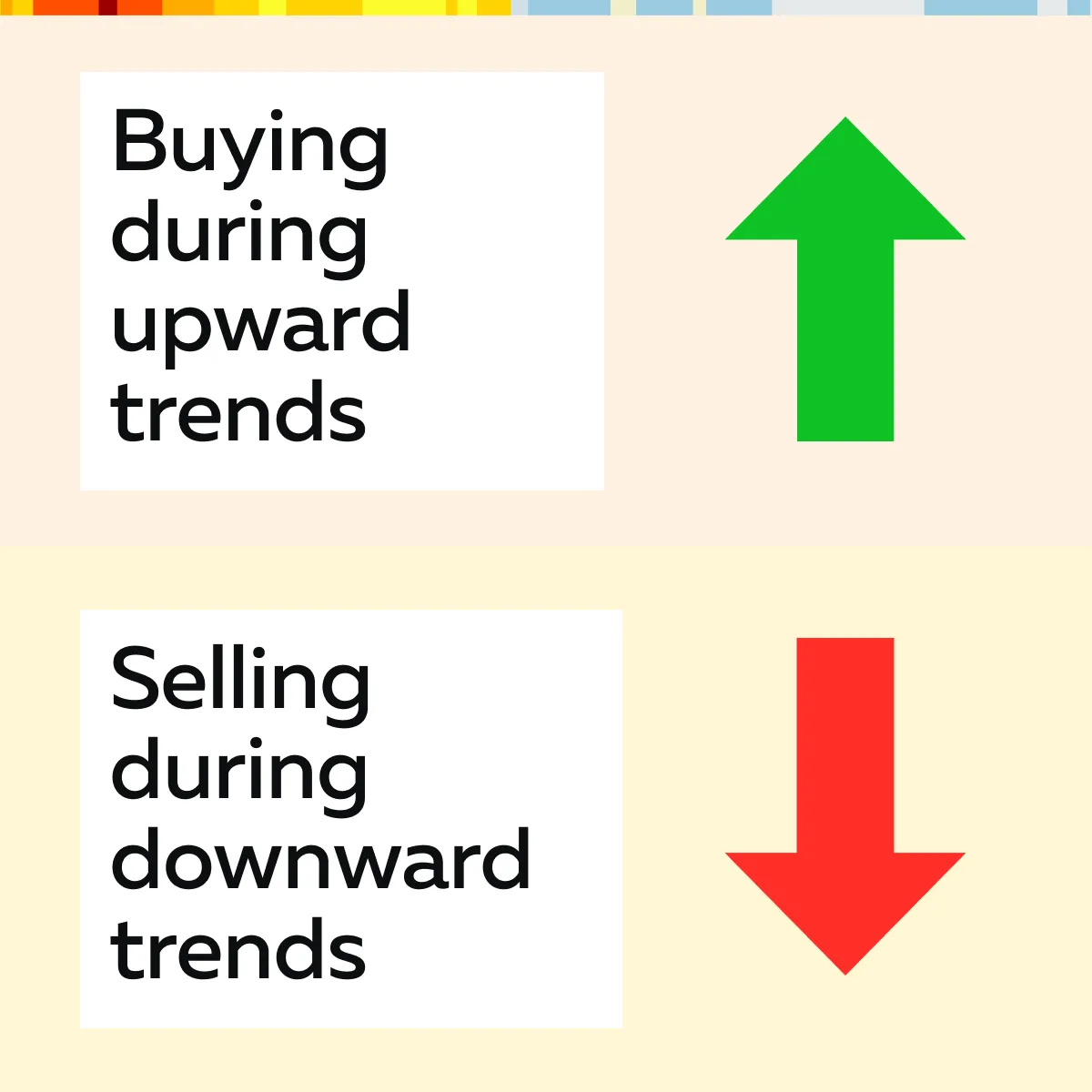
How Do Trend-Following Strategies Work?
These strategies profit from the continuation of existing trends rather than predicting reversals. If we talk about market conditions, they perform best in trending markets, where clear upward or downward movements can be identified, for example, during economic events or earnings reports.
For more clarity, let’s study a hypothetical example related to a bot trained on moving average crossovers.
- A trend-following bot buys when the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average. This is known as the “golden cross” as it indicates a potential uptrend.
- The bot sells when the 50-day moving average crosses back below the 200-day moving average. This is known as a “death cross” and signals a possible downtrend.
Ready to implement automated trading strategies? Leverage our platform, Bookmap’s features to optimize your algorithmic trading approach. Join us now!
Is there an Optimal Market for the Trend Following Strategy?
Yes, trend-following strategies are particularly effective in liquid markets, such as futures or stocks. That too during periods of high volatility like earnings seasons. In these scenarios, the chances of strong directional moves increase. This enhances the effectiveness of trend-following approaches.
What are Some Popular Risk Management Techniques?
| Stop-loss orders | Trailing stops |
|
|
Mean Reversion Strategies
Mean reversion strategies subscribe to the principle that financial markets revert to their historical average prices after experiencing significant deviations. These strategies are specifically designed to identify when an asset is either overbought or oversold. This enables traders to capitalize on expected price corrections.
How do Mean Reversion Strategies Work?
The core idea of this strategy is that if an asset’s price stays too far from its average, it is likely to move back toward that average over time. Now, bots consistently monitor price movements. They identify overbought and oversold conditions and prepare to enter trades based on these signals.
For more clarity, let’s study an example of a mean reversion strategy related to Bollinger bands:
- Say a bot uses Bollinger Bands to execute trades:
- The bot automatically buys when the asset’s price touches the lower Bollinger Band.
- This indicates it may be oversold.
- The bot sells when the price reaches the mean or the upper Bollinger Band.
- This suggests it may be overbought.
What are Optimal Market Conditions for Mean Reversion?
Mean reversion strategies work best in ranging markets, where prices oscillate within a predictable range, such as equities with low volatility. In these conditions, assets usually revert to their mean prices. This reversion provides numerous trading opportunities.
What are some of the challenges of mean reversion strategies?
Mean reversion strategies can struggle in strongly trending markets. If an asset is in a persistent uptrend or downtrend, the price may not revert to the mean as expected. Sometimes, this leads to potential losses. Also, when markets fail to revert, positions incur significant losses. This particularly happens if the trader continues to bet against the trend and hopes for a reversal that does not occur.
Arbitrage Strategies
Arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies between different markets or assets. These strategies are based on the principle that identical or similar assets should have the same price, and any deviations present profitable trading opportunities. Please note that arbitrage bots are particularly sensitive to:
- Execution speed
and
- Market latency
That’s because profits depend on rapid transactions, and arbitrage opportunities only arise when there is a difference in the price of the same asset in different markets. Or we can say arbitrage exists when correlated assets deviate from their expected relationship.
Moreover, traders must note that the effectiveness of arbitrage strategies heavily relies on quick capitalization of fleeting opportunities before the market corrects them.
What are the Different Forms of Arbitrage?
| Aspects | Spatial Arbitrage | Statistical Arbitrage |
| How it works? | This process entails buying and selling the same financial asset on different exchanges to take advantage of price differences. | This form utilizes statistical models to identify relative mispricing between correlated assets. It analyzes historical price relationships to exploit short-term pricing inefficiencies. |
| Example | A crypto arbitrage bot purchases Bitcoin on an exchange that offers assets at lower prices and simultaneously sells it on another exchange where the price is higher. | Say two stocks move in correlation. One stock deviates significantly from the expected price. Now, a statistical arbitrage bot goes long on the undervalued stock and short on the overvalued one. Here, the bet or ideology is that they will revert to their historical correlation. |
What are some challenges and considerations related to arbitrage strategies?
Please note that execution speed is crucial in arbitrage trading. That’s because delays can erode potential profits. Additionally, transaction fees, withdrawal fees, and other costs associated with trading significantly impact the overall profitability of arbitrage strategies.
Moreover, the bot can perform better and identify arbitrage opportunities quickly only by using high-quality market data (such as Market By Order (MBO) data). MBO data provides detailed information about market orders and helps traders make better-informed decisions using real-time pricing information. Usually, this data is expensive which further adds to the cost.
Breakout Trading Strategies
Breakout trading strategies capitalize on price movements when an asset breaks through significant support or resistance levels. Following these strategies, you enter trades at the onset of a new trend and try to make a profit from the momentum of the breakout.
How Does Breakout Trading Strategies Work?
Breakout strategies are centered around identifying important price levels, such as
- Support: It is a price level where buying interest is dominant enough to prevent the price from falling any further.
and
- Resistance: It is a price level where selling interest is dominant enough to prevent the price from rising any further.
The goal of these strategies is to take up a position when the price breaks through these levels. The ideology is that the momentum will push the price further in the direction of the breakout. For more clarity, let’s study an example of a breakout trading strategy related to the Donchian Channel:
- A bot enters a long position when the price breaks above the upper Donchian Channel.
- For the unaware, it is a technical indicator and helps to identify breakout points.
- The upper channel line represents a resistance level.
- Breaking above it suggests strong upward momentum.
How to Manage Risk?
To minimize the risk of false breakouts (situations where the price briefly breaches a level but quickly reverses), traders should set stop-loss orders below the breakout point. This protects losses if the breakout fails and the price moves back into the previous range.
For Example:
- Say the price breaks above a resistance level.
- A trader places a stop-loss just below that level.
- This provides a safety net against sudden reversals.
What are Some Optimal Market Conditions for Breakout Strategies?
Breakout strategies perform well in volatile markets. These markets have a strong momentum and increase the likelihood of significant price movements. Some key events that generate volatility are:
- Earnings Reports: Company earnings announcements lead to strong price movements as traders react to the results.
- Macroeconomic Announcements: Economic data releases, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, or central bank interest rate decisions, create volatility in futures markets and other asset classes.
Market Making Strategies

Market-making strategies provide liquidity to financial markets. They place both buy and sell orders around the current market price. These strategies profit from the bid-ask spread by continuously adjusting quotes as market conditions change. For the unaware, bid-ask spread is the difference between the buying price (bid) and selling price (ask).
How do Market-Making Strategies Work?
Market-making bots ensure there are always buy and sell orders available in the market. These bots continuously place orders at various price levels. As the market moves, they dynamically adjust their quotes to:
- Stay competitive
and
- Maintain their presence in the market.
For more clarity, let’s study an example of a market-making strategy
- A market-making bot places a bid at $50.05 and an ask at $50.10.
- When trades are executed, the bot profits from the $0.05 spread between the bid and ask prices.
- If a trader buys at $50.10, the market maker sells at this price while having already bought at $50.05.
- In this way, they capture the spread as profit.
Enhance your trading strategies with Bookmap’s advanced real-time trading tools. Get started!
What are Some Requirements for Effective Market Making?
For market-making strategies to be successfully applied, deep liquidity is required. This means that there should be a sufficient volume of trades occurring so that the market maker can execute their buy and sell orders without significantly impacting the price.
Also, rapid execution is important. It helps to minimize losses during volatile market conditions, where prices can change quickly. If the market maker’s quotes lag behind the current price, they can incur losses.
What are Some Popular Tools for Market Makers?
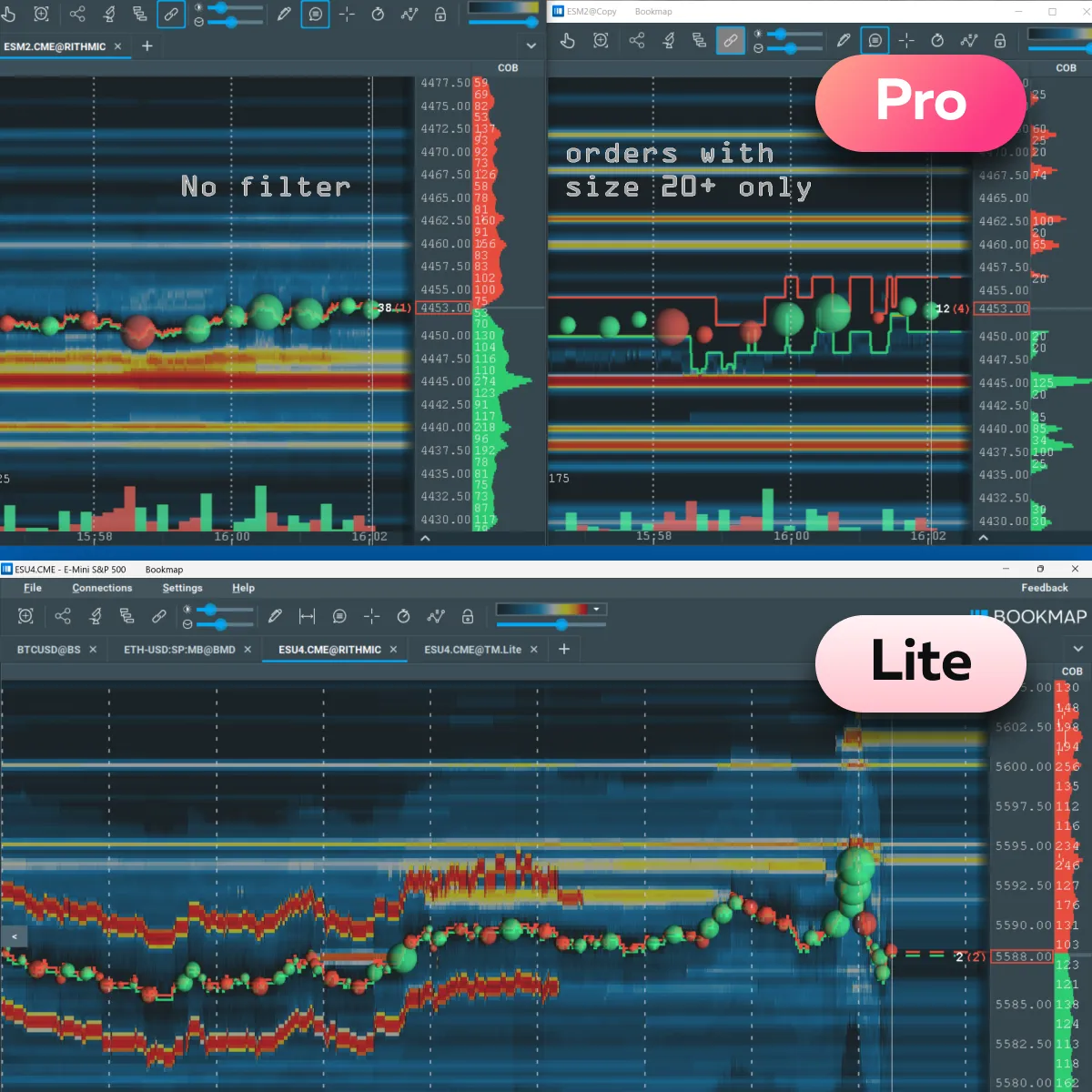
Our platform offers “Tradermap Pro” and “Tradermap Lite,” which are special tools designed to assist market makers. They help easily analyze market data and manage orders more smartly. Ultimately, by using them, market makers can optimize their profitability. Let’s see how these tools can help you:
- Perform real-time data visualization. Using it, market makers can instantly see:
- Price movements
- Order flow
- Liquidity across different exchanges
- Analyze the order book in depth. This helps identify key support and resistance levels.
- Place orders strategically at optimal price levels.
- Make dynamic order adjustments based on market movements. If the market shifts, market makers can quickly modify their orders.
- Identify liquidity zones where significant buy or sell orders are concentrated.
Please note that both Tradermap Pro and Lite are optimized for speed. They allow market makers to react quickly to market changes.
Other Key Strategies to Consider
While many traders are familiar with common algorithmic trading strategies like trend following and arbitrage, there are several other key strategies worth considering that can provide unique advantages in different market conditions. Let’s study some of them.
Pairs Trading
Pairs trading is a market-neutral strategy. It involves betting on the relative performance of two correlated assets. This strategy profits from the price divergence between the two, regardless of overall market direction.
How Does It Work?
A trading bot identifies two assets that historically move together (correlated). When the price of one asset deviates from its historical relationship with the other, the bot initiates trades in the following manner:
- Long Position: The bot goes long (buys) on the undervalued asset.
- Short Position: Simultaneously, it goes short (sells) on the overvalued asset.
For example,
Say Stock A and Stock B typically move in tandem. But Stock A drops significantly while Stock B remains stable. Now, the bot would buy Stock A and short Stock B. The ideology behind this move is that their prices will converge back to historical levels.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis strategies use algorithms to understand overall market sentiment. For this purpose, they evaluate
- news articles,
- social media, and
- financial reports.
These insights help traders make informed decisions based on public perception and emotional factors influencing the market.
How Does It Work?
The trading bot scans various sources for positive or negative sentiment related to specific assets or the market as a whole. It analyzes language, tone, and keywords to determine market sentiment. Based on this analysis, the bot executes trades:
- Positive Sentiment: If sentiment is bullish (positive), the bot may buy the asset.
- Negative Sentiment: If sentiment is bearish (negative), the bot may short the asset.
This strategy is particularly powerful in highly reactive markets like cryptocurrencies and stocks. Also, be aware that quick responses to sentiment changes create profitable opportunities.
Risk Management in Algorithmic Trading
Risk management protects capital and reduces the chances of incurring significant losses. To do so, algorithms should incorporate risk parameters. These parameters should automatically trigger during unpredictable market movements.
Also, a thorough backtesting of trading algorithms should be performed across various market conditions. This helps you to understand how the strategy would have performed in historical scenarios. By making this analysis, you can easily identify weaknesses and remove them before deploying bots in live markets.
How to Conduct Risk Management?
You can follow these techniques:
| Position Sizing | Adapt to Volatility | Monitor Regularly |
|
|
|
Make Real-Time Strategy Adjustments Using Bookmap
By using our advanced market analysis tool, Bookmap, traders get real-time insights and easily make necessary adjustments. Notably, Bookmap also offers order flow analysis. See the graphic below to check what you can visualize with Bookmap:
Conclusion
Algorithmic trading offers a variety of strategies. Each caters to different market conditions and trading methodologies. From trend-following strategies that capitalize on market momentum to arbitrage strategies that exploit price discrepancies between exchanges, there is a method for nearly every trader. Additionally, mean reversion, breakout trading, pairs trading, and sentiment analysis provide further options for those looking to enhance their trading approach.
Always make sure your selected strategy aligns with your individual trading goals, risk tolerance, and market understanding. Besides, traders need to experiment with different algorithms to find what suits them the best. To determine this, you can do backtesting and use advanced market analysis tools like Bookmap.
While the former allows you to test strategies against historical data and refine them before going live, the latter allows you to visualize market depth and order flow. Do you wish to trade confidently? Adjust your strategies based on real-time market insights offered by our platform, Bookmap. Get started now!
